Safety Management Assignment: Emergency Planning & Crisis Management
Question
Task:
Background for safety management assignment
On the 22nd of December 2014 in Glasgow City centre the driver of a local authority refuse lorry lost control of his vehicle, with the subsequent loss of six lives and many serious injuries. Read paragraphs 9-33 and 513 – 559 of the determination of the Sheriff into this incident, which can be found here: http://www.scotcourts.gov.uk/search-judgments/judgment?id=e916fba6-8980-69d2-b500-ff0000d74aa7
You are the Safety Manager for a large UK local authority which includes a large city and which operates regular refuse collections throughout the city centre. Your Chief Executive has read about the accident and is concerned about the public reaction to the continued use of refuse vehicles in the city after such an incident. However, he is also concerned because he has been informed that there would be significant risks to public health if refuse collection had to be stopped for more than 48 hours in the city centre and that many shops and restaurants may be forced to close if their refuse remained uncollected for longer than this period of time.
Therefore, he has asked for a report from you that describes the emergency planning procedures that should be in place for dealing with the consequences of such an event should one take place in the city centre.
He has also asked for an assessment of the possible consequences the local authority (and individuals within in it) could face after such an incident.
Assignment Brief
You are required to write a two-part report that addresses the requirements of the Chief Executive. As a guide, Part 2 should be no longer than 1200 words as Part 1 should form the bulk of the assignment.
Part 1: Emergency Planning: Consider the information in Module 7 relating to emergency planning and crisis management and prepare a report for the Chief Executive that addresses the steps that could be taken to manage such an incident if it happened in your authority. You should consider the stages in the emergency planning cycle and how this could be applied to this situation (e.g. the immediate incident, cooperating and coordinating with the emergency services, the need to maintain refuse collection while dealing with the reputational risks and communication strategy etc)
Note: you do not have to demonstrate detailed knowledge of waste and refuse collection but should be able to explain how a system for adequate emergency planning could be applied to this scenario.
Part 2: Consequences: This should consider the possible outcomes of any investigation and the consequences could be for the local authority and individuals within it. Consider what enforcement action after a criminal investigation could be taken, what the main health and safety legislation would be and include an assessment of when a charge of corporate manslaughter/homicide might be considered likely.
Answer
Executive Summary
The deadly incidents at Glasgow examined in the safety management assignment wherein a refuse-loaded truck knocked down several pedestrians after losing control of the truck by the unconscious driver at the wheel injured multiple and killed 6 at Queen street. This concernedthe CEO of a large UK local authority that functions across the large areas of the city centre to collect the regular refuse collections.
The purpose of this report is to present an emergency planning procedure and crises management that should take place in the city centre for dealing with fatal consequences of a vehicular collision with the pedestrians to address the aforementioned concerns for the Board of director of the establishment. The primary and secondary data has been analysed and presented throughout the report. According to report findings, it has been ascertained that a systematic and structured emergency planning process along with crises management is extremely essential for an organisation to prepare, prevent, respond, recover, and mitigate the potentially detrimental consequences underpinned with strong leadership, collaboration, and communication.
In addition to this, the consequences speak about the impact of the investigations of the accident on the local authority and the community. The outcome of the study is to know who is liable for the cause of the accident. The investigation is likely to cause an economic loss of the local authority as they will be forbidden from continuing with their operations. After a proper investigation, the organisation should take certain enforcement actions, so that such accidents can be avoided in the future. Moreover, to help out the affected ones and restore normalcy as soon as possible with all kinds of resources, responses, prevention, and controlling of the emergencies reveals that integrated and holistic emergency planning have the potential to minimize the detrimental impacts of fatal situations. In addition to this, after a thorough investigation and analysing the consequences, it has been understood that public awareness regarding health and safety laws is crucial. Therefore, it could be concluded that the necessity of emergency planning and crises management is paramount and quintessential in dealing, responding, and coping up with emergencies. Furthermore, recommendations have been cited for the UK’s refuse collection firm to enhance emergency planning and crises management system like the incorporation of grades at the roads to separate the vehicular collisions with the pedestrians effectively and conducting regular health check-ups for the refuse collection drivers along with safety checks of the trucks. Along with these suggestions like training and developing the refuse collection drivers from driving efficiently to competently respond and manage themselves and their immediate members from disastrous situations as well as incorporating embedded technology into the operating system of the trucks to recognise incapacitation of the drivers and alert the individual and the concerned organisation promptly have been also put forth.
The limitation of this report was based on the statistics of thematic analysis, the primary and secondary data available on web portals which might not be factual. The interview with involved parties and perusal of incident location could be cohesive into the emergency plans devised.
1. Introduction
The report at hand addresses very crucial concerns of the ABC organisation that functions in the city centre as a regular refuse collections after the news of the dreadful collision between the pedestrians and refuse-loaded truck surfaced.
The aim of this report is to address the concerns of the ABC organisation by delegating the Safety Manager of this organisation to develop an emergency planning and crises management plan in place. This is because the risks associated with such unfortunate accidents is manifold from destruction of the physical assets to human casualties. Moreover, the emergency panning would be done to get aware about how to respond unforeseen accidents with planned emergency measures. This is done so that the organisation as a whole and the involved participants remains competent and aware if any dreadful accidents akin to the Glasgow occurs in the premises of the city centre.
Based on this aim objectives of the report are:
- To determine a probable emergency plan and crises management plan for the ABC organisation.
- To evaluate all the aspects of both emergency and crises management strategies
- To help the firm in coping up with similar situations by ascertaining the appropriate measures
- To evaluate the consequences on the different stakeholders
- Todiscussthe requirement of the enforcement actions and the health and safety legislation that could be put into place.
In addition to this, the primary data is collected from the original document of the inquiry headed by the Sheriff Court of Glasgow and Strathkelvin. While the secondary data has been collected from the various existing sources of the theoretical databases delineating the emergency plan and crises management strategies. All the data collected has been analysed through the thematic analysis as all the data garnered have been put under themes and analysed subsequently to link one theme to another and thereby forged a comprehensive and analytical understanding of the required emergency and crises management plan in times of the unforeseen situational crises.
2. Part 1: Emergency Planning
2.1 Overview of the scenario
The inquiry into the sudden and fatal accidents at the Glasgow City Centre that unfortunately took the lives of 6 pedestrians, revealed that they succumbed to death by sustaining multiple injuries in the road traffic collisions. The inquiry further disclosed how the misbalance and loss the control of the heavily loaded refuse truck caused by the sudden health deterioration of the driver of the truck. This led to the detrimental collisions with the pedestrians and the subsequent deaths (scotcourts.gov, 2015). This is the scenario based on which the emergency planning and crises management plan have been built up gradually for the ABC organisation.
2.2 Contextualizing the stages of Emergency Planning into the given scenario
As per the statements of Smith (2014), emergency planning is an ongoing process of identifying risks, planning, implementing, testing, and improving the emergency plans reiteratively to help the organizations and people efficiently respond and manage emergencies. The importance of emergency planning lies in the fact it enables the concerned authorities to prepare an emergency plan beforehand so that they could facilitate the required measures to minimize the life-threatening risks. As per the observations of Fagel (2013), since the actions are taken from the very moments of the initiation of the emergency are extremely crucial and important it holds the potentiality of managing and navigating across the rough course of the emergencies that lasts from few seconds to few minutes. Moreover, the prompt and reliable response activities to the ongoing emergency could evade the chances of highly mortal and dreadful consequences.
Therefore, it is highly pertinent that concerned authorities responsible for the welfare of the communities, or the national government during national crises or the individual should be prepared and aware of how to respond to an unforeseen emergency. This calls for emergency planning on the part of the concerned authorities of the UK's local refuse collection at the Centre to effectively deal with the emergency planning. A basic emergency plan would involve the core elements, or the stages as enumerated below:
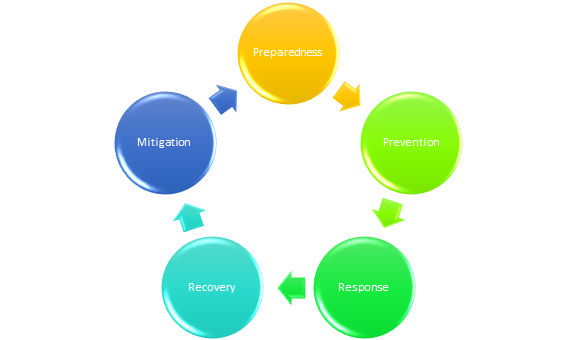
Figure 1: Core phases of the emergency planning
(Source: self-created)
Preparedness: One of the crucial stages in emergency planning involves the preparedness of the involved human and organisational entities to enhance their abilities to respond to disasters and emergencies. Furthermore, the organisation must have the equipment, people, and systems ready to cope up with the emergencies so that the preparedness could be levied highly on the degree and intensity of the fatal impacts (Alexander, 2015).
Keeping in context, the Glasgow Road traffic collisions, it could be ascertained that the preparedness was necessary for the concerned authorities and truck driver, Clarke. Though one of the essential duties to check on the operational efficacies and safety of the functionalities of the vehicles themselves before driving was responsibly carried out by Clarke what he failed to do is his routine check-up (scotcourts.gov, 2015). Had the association responsible for hiring Clarke taken the health check-up routinely, then perhaps any inconsistencies or abnormality could have been identified and thereby, the accident could have been mitigated. Therefore, the refuse collection operators at the city centre, UK, must be trained to inform his immediate authorities of their uneasiness before-hand they seated themselves at the wheel. Even the organisation itself must facilitate the health of the truck drivers. Besides this, the truck drivers shouldn't present deceitful medical history before driving and should have the presence of mind and knowledge to implement the right actions which would enhance the emergency preparedness plan.
In addition to this, the city centre authorities in collaboration with ABC organisation must facilitate careful route risks assessment across the different refuse collections points. This would helpto devise ways to minimize the number of the individuals or pedestrians being present at those routes around the approximate time of the refuse collection thereby, limiting the risks of unforeseeable vehicular collisions. This collaboration is highly essential in strengthening the perpetuation of a potential emergency plan.
Prevention: This would include identification of the threatening scenarios through the risks assessment process and devising the actions to avoid those incidents from occurring. This is possible through issuing constant surveillance (Levacet al., 2012). In the case of road accidents or collision preventive measures could have been taken by the drivers and the Glasgow city council as part of their risk assessment process. This would have helped the refuse collection operators to be more reliable, contingent, and efficient in emergency planning.
The truck drivers could have been mandatorily provided with important and essential written guidance in large fonts in language best understandable by them and placed at an eye-level view for the drivers in the truck itself. This would enable the drivers to read through the important instructions or guidance at a very quick glance during emergencies such as brake failures, lost control, personal discomfort. Eventually then they would know how to respond to the emergencies
In addition to this, an assistance must accompany each driver who would be equally competent and trained in responding to the emergencies so that they could prevent fatal collisions or at least minimize the human casualties to an extent. This is because in the Glasgow Road collisions though the Glasgow First’s truck driver, Clarke was accompanied by Telford and Toal, the refuse lorry uncontrolled for 19 seconds and consistently crashed and smashed every other thing it collided with. Even the misbalanced truckknocked down multiple pedestrians and injured them fatally and seriously. This shows that there is a need for acompetent driver's assistance who must know to respond emergencies adequately as fatalities could be lessened if managed effectively at the right moment.
Furthermore,Gopalakrishnan (2012), states that calling the traffic police or the road surgeons present must be another priority for the people present at the accident spot. Even calling up emergency medical services and getting the right and prompt aid from the concerned personnel could minimize the depth and intensity of the destructive impacts. In addition to this, activation of the hazard lights or loud emergency horns by Telford or Toal before the final collision and during the emergency time could have alerted the pedestrians or the stationed traffic police or anyone present at the Queen Street. This could have reduced the intensity of the damages because if external efforts were put to slow down the truck into gliding onto the footpath further, it could have lessened the mortalities and damages (scotcourts, 2015).
Therefore, using emergency lights and horns are also very crucial in preventing greater damages during an emergency in-vehicle driving which must be kept in mind by the refuse collector organisation at the city centre. Moreover, it is evident that by examining and identifying all the possible vulnerabilities that could be caused by the specific situations, reliable and contingent measures must be put into place. This would enable the present participants involved during the moments of high emergencies to try one or the other responsive measures or at least alert the authorities quickly.
Response: The actions carried out from the moment and at the aftermath of the hazardous impacts, emergency response comes into play. Contingentresponses must be facilitated as quickly and viably as possible to save human lives, physical assets, and ameliorate the sufferings and losses of all kinds (Fagel, 2013). Therefore, the emergency responses that could be taken by the CEO of the local refuse operator in the UK's city centre are delineated below:
- Activating the local medical emergency services immediately because the crash victims hold the chances of surviving if timely first aid and hospitalized medication are provided. Therefore, the response team must be aware of the preliminary hospitalisationtechniques and othermedical aids that must be given to the victims. The team should be quick to inform the nearby hospitals so that the victims receives all kinds of treatment at the soonest possible.
- The team must cooperating and coordinate amongst themselvesfor formulating emergency actions and emergency handling. For instance, the members of the rescue team must extensively communicate with the members engaged in hospitalisation of the injured ones to make preparation for the treatments rapidly. Moreover, the people responsible for contacting with the family members of the victims must ensure that they are cooperating with the police and proper legal wayscarried out to inform the acquaintances.
- Informing the residents about the potential damages caused and risks involved so that the people get aware and don't visit the vicinity of the place for the time-being. This must be done unfailing by the response team because it would be help in restricting the further risks to the human life. Moreover, it would be help in conducting the necessity duties at the accident spots by the emergency response team as well as the police.
- Evacuating and taking the injured people to the hospitals by implementing prompt rescue and medical care. The response team must be proficient in handling the crowds and make sure that the accident place is not crowded as it would delay the swift and rapidly execution of the emergency response of clearing the area and offering first aid to the injured ones.
- Furthermore, the response team must take initiatives to restrict the further escalation of the tragic impacts through effective leadership that would help in guiding and leading the team to facilitate the required measures.
- Moreover, the response team should extensivelycommunicate to the media about the happenings and actions perpetuated by the emergency coordinator so as to lessen the panickingamongst the common people and affected families. By being communicative the emergency responseteam could make the execution of the emergency duties efficient and faster. In this context,Verhoevenet al. (2014), opined that the communication during the crises serves a crucial purpose of easing the mounting tensions, apprehension, and anxieties of the immediate families of the victims. It also helps in reaching the authentic details from the accident premises to the concerned ones through creditable internal reporting to the media and other important stakeholders.
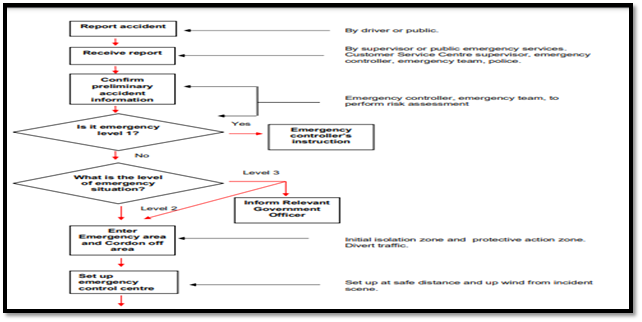


Figure 2: A flow diagram of the emergency response
(Source: asiaiga, 2021)
Recovery: This phase of emergency planning involves the actions that must be facilitated to help the affected ones and the whole immediate community to resume their daily livelihoods. Furthermore, they must be ensured with all kinds of resources and aids required to cope with the physical damages, bodily injuries, and traumas caused and try to restore normalcy as soon as possible through sustained mass care (stlouis-mo.gov, 2021). The organisation involved in the refuse collection must be competent in delivering and assisting skilful and effective measures during the recovery phases. This could include checking up on the hospitalised victims and catering to their medical needs or obligatory legal responsibilities that they have to go through for proper investigation of the accidents. The team members responsible for the recovery phase of the emergency planning must make sure that all the affected members along with their families are helped with all kinds of required resources possible. So that the recovery process is accelerated and executed with utmost proficiencies. Furthermore, the crashed vehicle and the area must be cleared out as soon as possible so as to restrict any kind of further accidents and people would be alerted about the same. This would empower the recovery team to make the common people aware what they must do to avoid such unfortunate vehicular clashes. Even the recovery team must inform and communicate with the responsible city council members to implement measures to secure the safety of the pedestrians further as well as promote greater awareness regarding the driving of the large trucks.
Mitigation: This stage refers to the measures that must be taken to prevent emergencies along with reducing the chances of the emergency happening or alleviating the damaging effects of the unavoidable emergencies. Therefore, the refuse collector operator at the city centre must ensure significant paperwork before driving to ensure an all-encompassing safety.
2.3Contextualizing the stages of Crises management into the given scenario
As per the observations of Hayes (2021), Crises Management could be defined as the recognition of the probable threats that are looming large over the organisations and could entail pernicious consequences and fatal repercussions if befallen on the involved participants.Therefore, crises management empowers organisations to identify the threats, ascertain the contingent steps, design and then implement the steps to alleviate the scope of destructive threats. It also possess the potential to cope up and recover from the situational crises. As per the types of sources of the crises that are generally divided into three categories namely the Accidental Disaster, Natural Disaster, and the Technological Disaster, the dreadful incidents at the Glasgow City Council could be explained under the crises type ofAccidental Disaster. This calls for an effective crises management system to be undertaken by the concerned authorities to recover from similar kinds of unfortunate incidents to combat the unforeseeable and potential risks (Bundy et al., 2017).
In the words of Williams (2021), a flexible crises management strategy could induce an influential sway to come out of the situational crises like that of the road traffic collision at Glasgow. However, one of the best practices of crises management is to follow its three-phased process that is preparedness for any kind of crises, responding during the crises, and reviewing the steps and needs post-crisis. Therefore, this tactic of crises management could be implemented at the city centre of the UK to enhance the crises management strategy as illustrated below:
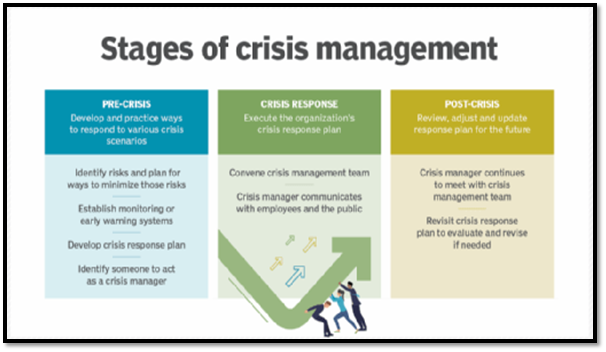
Figure 3: The stages of crises management
(Source: Posey, 2021)
During the pre-crises, risks assessment measures could be followed that would include identification of the possible risks by considering all the possible threatening avenues. This would be followed bythe identification of the stakeholders affected by crises in the given context. The next step would be followed by the crises response that would encompass controlling of the crises management plan underpinned with effective leadership accordingly. This would help inhandlingand implementing the best possible measures to get rid of the maximum negative implications. The response and recovery measures must be mandatorily assisted by extensive communication with the media and the required stakeholders. Furthermore, the next steps would entail the activities surrounding the post-crisis stage that would include efforts to restore the affected people to normal life along with accelerating the progression of the recovery process.
3. Part 2: Consequences
3.1. Examining the possible outcomes and consequences of the investigation on the local authorities and the individuals involved
After a proper investigation and scrutiny, it was found out that the accident caused a lot of damage to the peace and harmony of the society. There can be various possible outcomes and consequences of the investigation of the accident. The immediate result of the investigation is to look for the reason behind the cause of the accident. Another outcome was to find out if anyone liable for the cause of this accident. The main target of the investigation was to find out if the driver was in the right state of health and mind (Arthur and Roper, 2018). The outcomes on the local authorities will be that the local authorities will be restricted from using some of the routes on which the accidents took place. The individuals involved in the accident will be scrutinised to find out if they were responsible for the cause of the accident. The main target was to ensure that such events do not take place in future. The outcomes will help in the identification of the causes of such harmful incidents.
The probable consequences for this investigation will be that local authorities will be restricted to using the streets, and they will also be asked to keep a hold on their refuse collection lorry services this will cause a lot of economic loss to the local authorities and the. The legal consequence of the incident will be criminal charges for such an irresponsible act of the Corporation. They might also have to bear the additional costs for causing damage to society. People will be reluctant about using the refuse truck services for a certain amount of time even after the investigations are done, as they will fear such mishaps shortly. This will cause a significant quantity of losses and a disruption in the services of the local authority. Apart from the local authority, the individuals who were present at the lorry will be facing a lot of harassment as they will the prime suspect for the cause of the accident. The other individuals who were involved were the ones who got injured; the investigation can provide them with a hope of justice and assurance that such incident and accident will not occur shortly. The ultimate goal is to ensure peace and harmony in society and provide the public with the assistance of safety and security in the future. This investigation will also create awareness among the people regarding the health and safety assessments (Day and Nielsen, 2017).
3.2. Consideration of the enforcement actions that could be taken after the criminal investigations.
After a proper criminal investigation, the enforcement actions that should be taken are that the local authority must ensure that the refuse collection lorry does make use of busy streets. Secondly, it should also be made necessary for the refuse collection lorry to honk at the main points of the street so that the people on the roads become aware from before and can give way to the refuse collection lorry and make it easier for it to pass. A detailed enforcement action plan must be laid out and enforced for the safety of the society, also some important legislations must be followed that can help to prevent such harmful accidents in the society. An important legislation is the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 and other laws of risk assessment must be followed. After the criminal investigation, the Local authorities should also ensure to keep a regular health and safety check of their drivers so that such kind of mishaps can be avoided shortly. Before the driver sets out for the day, it is necessary to provide him with all the necessary instructions regarding the alternative routes he should take to reach the refuse collection points. In the case of the public some enforcement actions that will be taken care of, make them aware of the health and safety regulations and make sure that the pedestrians are mostly making footpaths for walking on the road (Pal et al., 2019).
3.3. Evaluation of the health and safety legislation that can be put into place
The health and the safety legislations that can be put into place are:
- To make sure that the occupational health doctors perform a D4 medical examination and provide guidance to the employers regarding the applicant drivers and the employers of the drivers who help their drivers to renew the licenses for group 2 without involving GPs. They should reconsider whether the applicant should be given a consent form for the release of GP which is relevant to any medical records to occupational health doctor.
- DVLA, Crown office, Crown Prosecution Service should take an effort to review if the policies are in place that can prevent prosecution and breach of section 94 and 174 of the Road Traffic Act of 1988 (Bondjeet al., 2020).
- The department for transport and DVLA should think of measures for creating public awareness of the effect of medical conditions on fitness.
3.4 Assessing when a charge of homicide/corporate manslaughter likely to be considered:
If the accident is considered corporate manslaughter, then that turns out to be a criminal offence that is a punishable act under the eyes of the law. It is considered to be an act of homicide that an organization commits. The driver, Mr Clarke will be convicted if he is found guilty of homicide. During the investigation, it was found out that this was not an intentional act, and the driver was suffering from Neurocardiogenic Syncope. A bill was introduced to the House of Commons by the Home Secretary on the Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide act 2007 in the U.K. The bill had sought to eliminate the offence of the common law for manslaughter due to gross negligence that applies to the corporations (Mudenhaet al., 2018).
In the event of failure to comply with the Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide act 2007 requirements, then it might lead to serious consequences for the individuals as well as for the organizations. As per the Corporate Manslaughter and the Corporate Homicide Act, 2007, it can be said that an offense is generally said to be committed when the senior officials fail to keep an eye on the substantial element or the duty of care that results in death (A Guide to Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide Act, 2008).
The local authority is likely to face the charge of homicide or corporate manslaughter, then it might face massive turmoil regarding resolving the case (Perez et al., 2017). There are high chances of this investigation causing hindrance to the operations of the local authority. The driver is likely to get harassed for killing innocent lives on the street. The manager who was in charge of looking after the health and safety of the driver will be equally charged for the malfunction of the organization, and the entire organization will be defamed.
In addition, other associated health and safety legislation which may considered are as follows:
- Health And Safety at Work Act 1974
- Management Of Health and Safety At Work Regulations 1999
- Reporting Of Injuries, Diseases and Dangerous Occurrences Regulations1995
4. Conclusions
From the aforementioned discussions, therefore, it could be evidentially concluded that the necessity of emergency planning and crises management is paramount and quintessential in dealing, responding, and coping up with emergencies. Furthermore, the necessity of inducing adequate measures and resources of all sorts along with effective collaboration and communication with all the members working in emergencies is being fostered. Furthermore, from the investigation, it has also been understood that there was some negligence of the Local Authority as they did not take care of the Health and Safety of the workers and no proper health examination was done. So, the entire organizations stand responsible for the mishap and are subjected to homicide or corporate manslaughter. For assuring that such an incident does not take place in future the organization must work collaboratively on these problems and try to find out a solution to them. Awareness should be spread among the communities and the local authorities.
The entire organization must be more alert about the health and safety of workers, and ways must be found through which peace and harmony can prevail in society. The local organizations must try to avoid such accidents in future. In addition to this, it is expected that by adhering and implementing the recommended measures, the ABC organization could make themselves competent and efficient in fighting with any similar unfortunate situation as that of Glasgow, rather conveniently avoid the occurrence of any such accidents and even it occurs, the firm could be able to tackle the emergencies underpinned with individual efforts of the truck drivers themselves and the collective endeavours of the firm. In these ways, it could be inferred that the concerns and anxieties of the ABC organization have been reliably and creditably addressed.
5. Recommendations
Few measures have been cited for the enhancement of the emergency planning of the ABC organisation.
- The city council or the concerned authorities of the city center must ensure measures that would alleviate the scope of crashes between the pedestrians and the vehicles. One of the preventive and effective ways of vehicular collisions with the pedestrians is that they could be placed on the different levels or incorporate grades at the roads to separate them. This could help to reduce the chances of sustaining serious injuries and fatal consequences that involve the bicyclists and pedestrians along with improving the traffics flow movements.
- The ABC organisation must ensure that proper and regular medical screenings and health surveillance are being conducted for the drivers appointed for the refuse collection before the commencement of duty along with mandatory checking about the safety and efficiencies of the operative mechanisms of the large vehicles itself. Moreover, the authorities must cross-check and receive updated and transparent health information about the drivers in consultation with an eminent general physician and vehicle mechanic recruited at the organization to facilitate effective and timely health and safety checkups of the driver and the driving vehicle.
- The organization could further train and develop the refuse collection drivers from driving efficiently to competently respond and manage themselves and their immediate members from disastrous situations. They should be aware, conscious, informed, and trained by successfully implementing emergency measures that ought to be implemented to stimulate amelioration of the negative impacts and save the community from further losses of life and damage.
- The ABC organisation must make use of the technological advances embedded into the operating system of the large vehicles which could help in detecting or recognizing the incapacitation of the drivers and alert the individual and the concerned organization about the need of refraining from driving on that particular day or time. Furthermore, the technology of detecting pedestrian’s beforehand could be fitted into the trucks for reliable protection of the pedestrians during the time of the emergencies along with the installation of Advanced Emergency Braking System mandatorily.
References
Alexander, D.E., 2015. Disaster and emergency planning for preparedness, response, and recovery. Oxford University Press.
Arthur, R. and Roper, V., 2018. Criminal liability for child deaths in custody and the Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide Act 2007. Child and Family Law Quarterly, 30(2), pp.121-144.
asiaiga.org 2021. Asiaiga.org. [Online] Available at:
Bondje, S., Barnes, C. and Nagendran, V., 2020. 146 Documentation of official driving guidance after a stroke or transient ischaemic attack; a quality improvement project.
Bundy, J., Pfarrer, M.D., Short, C.E. and Coombs, W.T., 2017. Crises and crisis management: Integration, interpretation, and research development. Journal of management, 43(6), pp.1661-1692.
Day, A. and Nielsen, K., 2017. What Does Our Organization Do 16 to Help Our Well-Being? Creating Healthy Workplaces and Workers. An introduction to work and organizational psychology: An international perspective, p.295.
Fagel, M.J., 2013. Crisis management and emergency planning: preparing for today's challenges. CRC Press.
Gopalakrishnan, S., 2012. A public health perspective of road traffic accidents. Journal of family medicine and primary care, 1(2), p.144.
Hayes, A., 2021. What Is Crisis Management? [Online] Available at:
Levac, J., Toal-Sullivan, D. and OSullivan, T.L., 2012. Household emergency preparedness: a literature review. Journal of community health, 37(3), pp.725-733.
Mudenha, W.F., Naicker, N. and Chadyiwa, M., 2018. Awareness of health and safety responsibilities among contract cleaning workers. Occupational Health Southern Africa, 24(6), pp.172-176.
Pal, R., Ghosh, A., Kumar, R., Galwankar, S., Paul, S.K., Pal, S., Sinha, D., Jaiswal, A.K., Moscote-Salazar, L.R. and Agrawal, A., 2019. Public health crisis of road traffic accidents in India: Risk factor assessment and recommendations on prevention on the behalf of the Academy of Family Physicians of India. Safety management assignment Journal of family medicine and primary care, 8(3), p.775.
Perez, P.A., Ndekugri, I.E. and Ankrah, N.A., 2017, June. A Critical Review of Convictions of Construction Industry Organisations Under the Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide Act. In Joint CIB W099 & TG59 International Safety, Health, and People in Construction Conference (p. 88).
Posey, B., 2021. What is Crisis Management? [Online] Available at:
Roper, V., 2018. The Corporate Manslaughter and Corporate Homicide Act 2007—A 10-Year Review. The Journal of Criminal Law, 82(1), pp.48-75.
scotcourts.gov.uk 2015. INQUIRY INTO THE FATAL ACCIDENTS AND SUDDEN DEATHS INQUIRY (SCOTLAND) ACT 1976 INTO THE DEATHS OF JOHN KERR SWEENEY, LORRAINE SWEENEY, ERIN PAULA MCQUADE, STEPHENIE CATHERINE TAIT, GILLIAN MARGARET EWING AND JACQUELINE MORTON [Online] Available at:
Smith, E.N., 2014. Workplace Security Essentials: A Guide for Helping Organizations Create Safe Work Environments. Elsevier.
stlouis-mo.gov 2021. Steps of Emergency Management [Online] Available at:
Verhoeven, P., Tench, R., Zerfass, A., Moreno, A. and Ver?i?, D., 2014. Crisis? What crisis?: How European professionals handle crises and crisis communication. Public Relations Review, 40(1), pp.107-109.
Williams, P., 2021. Crisis management (pp. 152-171). Routledge.












