In-Depth Analysis On Issues Of Zte Strategic Management
Question
Task: your assignment has to be a story in which the presentation of data and facts is followed by a clear analysis and explanation what is going on. Use models where they are appropriate and relevant before you answer any questions. Your analysis has to result in key findings and conclusions, both per discipline as well as overall. Show the reader of your assignment how and what you think in a story and (please) do not present bullet points! Answer the following questions in your paper (and make it clear which part of your paper is an answer to every question).
1. Describe chronologically how ZTE’s strategy has evolved since the start of thecompany until now. According to you, assess critically what ZTE is doing well and what should be improved? Critically argue which parts of their strategy made ZTE so successful and which parts are not successful (yet)? (maximum 25 marks)
2. Present a well-argued description of the strategy ZTE should pursue during the coming years to increase its strategic success. Assess ZTE’s organisation, market, current and potential future strategies through a structured approach, that entails all the relevant models and concepts: the objective/ target of ZTE, the company’s vision and mission, the internal organization’s strengths and weaknesses according to the value chain and theOsterwalder model, the external market’s opportunities and threats according to the PEST and 5-forces models, the company’s possible core problem, the confrontation matrix, an assessment of the company’s current and 3 potential future strategies as well as your selection of the possibly best strategy as well as a plan B, the contingency plan. (maximum 50 marks)
3. Following the selection of ZTE’s best strategic option, discuss the implementation issues regarding ZTE’s 4 key disciplines finance, marketing/sales, hrm and production as well as the links between these 4 key disciplines as well as the links between these disciplines and the overall strategy of ZTE. (maximum 25 marks)
Answer
1. Introduction
ZTE strategic management consists of some planning, monitoring, analysing and assessing all the necessity of the organisation so that the goals and objectives can be met (Rothaermel 2017). The companies will be assessing their strategies for bringing a few changes in the business environment. This will be further helpful for their success. Strategic management comprises of five major steps. They are setting a goal, analysing, and the formation of strategy, implementation and finally monitoring the strategy. In this report, the main aim is to understand the ZTE strategic management. Internal and external analysis will be done. The core issues of the company will be identified and finally, one strategy will be chosen for implementation.
2. Company Overview
ZTE stands for Zhogxin Telecommunication Equipment. This company is the largest handset manufacturer in China. In the world currently, it is the sixth-largest supplier of the handset. The sales revenue of the company in the nine months amounted to RMB 30,327 million. The growth is taking place each year. It is around 29.34%. There was net profitability growth in the parent company to 35.31% and the amount was RMB 816 million. ZTE was found in the year 1985 by Hou Weigui (Peng and Wu 2018). The company offers telecommunication hardware like phones, switching system, power supply, videoconferencing, monitoring and base stations.

Figure 1: ZTE Main Products Portfolio
(Source: ZTE.com 2020)
3. Strategies of ZTE
In the year 2008 ZTE was the sixth leading mobile phone player in the world. The main strategy of the company from the starting was to deliver custom-made and innovative products to the customers. This was being done in 135 countries. This ZTE strategic management approach was attracting customers and hence was helping to achieve growth in the revenue. The future of world communication was shaping through ZTE. The Chinese market was having limited competition. There was no such reputable telecom equipment. Hence, global manufacturers were taking advantage of the situation. Then ZTE owner realised that there was a need for telecom equipment for the domestic market. Hence, the company came into establishment. Slowly the company was expanding its base and currently, they were available in more than 50 countries. ZTE established two products for the Chinese market which was a remarkable landmark in the telecom history of China (Li and Cheong 2019).
The next ZTE strategic management approach that the company applied was to move into the global market. It almost took 10 years for emerging into the global market. In the year 2002, the company started to manufacture their own cell phones. ZTE was having an overseas market strategy of corporate development (Gao 2018). Some strategic changes were also done in the decision-making process. The aim of the company was to strengthen its research and development wing. This was giving them overseas market success. Innovation and custom made product strategy was successful for ZTE. Some of the advantages that the company from the strategy gained were customer-oriented products and services. There was proper product quality control and the service network became wide and powerful. The sales of the company were also jumping at higher levels. The CDMA equipment was getting doubled from the previous year. The business was emerging outside the home country. It was mainly because the company was focusing on mid-range and low-end handsets. However, some improvements can be done on the strategies of the company. It was also essential for ZTE to switch towards making advanced handsets. It is because the company was bringing innovative products and was also spending a large amount in the research and development department. The above ZTE strategic management approaches could not fulfil this point. The global market strategy was not that successful. It took a long time period and investments.
4. Internal Analysis
4.1 Aim/Objectives of ZTE
The main aim of ZTE was to become the top three suppliers of mobile phone in the coming five years. The company was also planning to move towards retail channels and operate under their brand.
4.2 Company mission and vision
The main mission of ZTE strategic management is to satisfy the needs of the customers. They want to connect the world with continuous innovation towards a better future.
The vision of the company is to have balanced and sustainable development in the environment, social and economic areas.
4.3 SWOT analysis

|
Strengths 2. The company was having a feature of custom-based orientation. 3. ZTE was gaining success by strengthening their research and development. 4. The company was having thousands of trained and in-expensive Engineers from China’s University. 5. The main ZTE strategic management approach of the company was corporate development. |
Weaknesses 2. In the technological front, the company is losing out to its competitors. The system is prone to virus attack. 3. The company is losing some of its customers because there is no advancement in the products. 4. The company took 10 years in global market expansion. 5. The company is far from their expectations and there is a need for continuous efforts. |
|
Opportunities 2. The company can strengthen its ties with domestic carriers. 3. The company is having a huge opportunity of capturing the global market just like the domestic one. 4. ZTE is having an opportunity of developing in the 3G handset market of China. 5. The company will have to look for the interest of the public towards high-end products. |
Threats 2. There is devaluation currency against the US dollar. 3. ZTE might be having threat due to training and investing in the workforce (Lasserre 2017). 4. The telecommunication market is highly competitive in nature which will be creating problems for ZTE. 5. Increase in taxes will be causing major issues for ZTE strategic management. |
4.4 Model Abell and Hammond
The matrix of Abell and Hammond is having a three-dimensional tool which is generally used in the business. The three main dimensions are customer groups, needs of the customers and technology. The main focus of this matrix is to focus on the requirement of the customer and not on the industry and products or services. The competitive scoop of the business can be defined by this tool. The description for each dimension is explained below for ZTE strategic management.
- Needs of the customers: The Company is looking after the customer needs because they have become volume suppliers of mid and low range handsets. However, they will have to understand that customers are looking for high-end and internet-capable devices. The domestic market was in need of telecom equipment and hence, ZTE was launched (Wu 2019).
- Technologies: Customers were in search of advanced handsets. The trend of smart-phones was increasing in the market. The company was searching for edge-cutting technology. IOT was trending for the past few years. This technology had unified communication standards globally. Customers were demanding for technologies that were sustainable in nature.
- Customer Groups: The main target of ZTE was customers who wanted to buy mid-range products. It mainly comprises of working-class people and students.
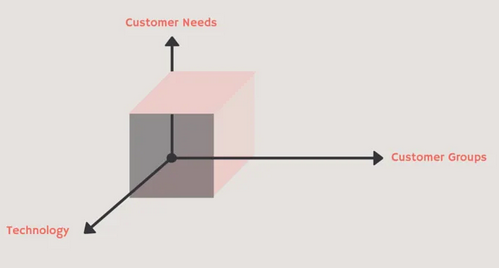
Figure 2: Abell’s Matrix
(Source: Wu 2019)
4.5 Model Value chain

|
Primary Activities |
|
|
Activities |
Description |
|
Inbound Logistics |
The company is streamlining its supply chain in most of the countries. The products are designed and manufactured in-house. The company is the largest exporter of telecommunication. |
|
Operations |
The company is working in three network carriers. They are making handsets of mid and low range. They are providing customer and consultant services. |
|
Marketing and Sales |
The company is following ZTE strategic management and is doing continuous marketing and improving their sales. The growth rate of the company is high. They are the leading GSM and CDMA leaders. They are supplying the operator with the trucking communication system. |
|
Service |
The company is providing custom based services to its customers. They are providing consulting services. It includes business consulting, innovation leadership, international exploration and operation consulting. There is proper support for the customers and some learning services are also available. |
|
Secondary Activities |
|
|
Firm Infrastructure |
The company is having some core values. They are faithful in serving their customers through their creativity. ZTE strategic management approach is having scientific management so that corporate performance can be increased (Fu, Sun and Ghauri 2018). They are driving into challenges and bringing something out of the box. The employees are working together and are practical in nature. |
|
Human Resource Management |
ZTE is one of the fastest-growing global communication solutions. According to HRM, the company is having talented employees from different races and nationalities (ZTE.com 2020). They are helping the company to obtain a strategic objective. There is space for personal development. The company is oriented for the people. This is a platform for dream and passion. |
|
Technology Development |
There is technological development in the approach of ZTE strategic management. They are ranked 2nd for CDMA equipment. The company is shining in the CDMA market. They are also producing GSM handsets for gaining international growth. |
|
Procurement |
ZTE is having a proper connection with the suppliers. The company has shipped 12 million handsets and sold 2 million handsets internationally in the year 2006. |
4.6 Model Oster Walder
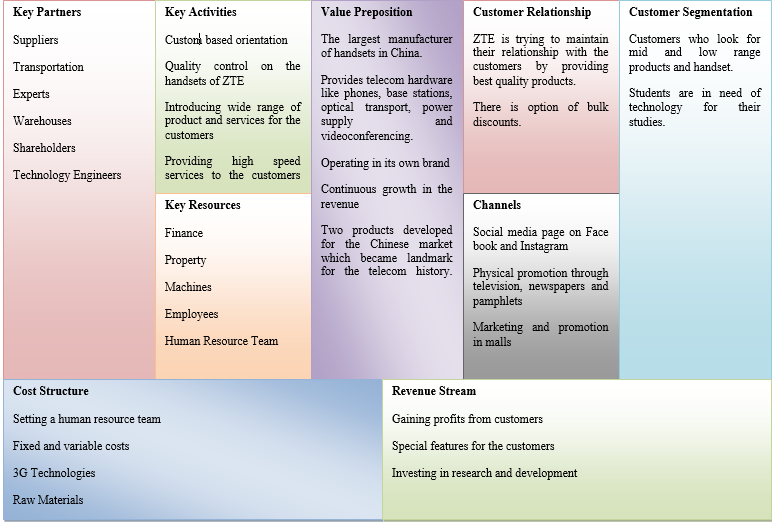
Figure 3: Business Canvas Model
(Self-Developed)
5. External Analysis for ZTE strategic management
5.1 MESO Environment
|
Porter’s Five Forces |
Description |
|
Threats of new entrants |
There is a low threat of new entrants in the existing ZTE strategic management approach. The challenges will be limited to the company. However, if there is new entrant then new players will be needing time and regulatory. There will be a discouragement for new entrants while dealing with ZTE. |
|
Threat of substitute |
There is a low threat of substitute for ZTE. The customers will not be getting the same quality product that ZTE is providing them (Poczter, Musacchio and Lazzarini 2018). The main emphasis of the company is about the products and services offered by them. ZTE is concentrating on quality which is not being done by other companies. |
|
Rivalry with the existing firms |
There is a high amount of rivalry among the existing firms in the telecommunication industry. The main competitors of the company are Nokia, Samsung and Motorola. The competitors are providing undifferentiated products at a lower cost. Each of the company is also using some aggressive strategies which are a concern for ZTE strategic management (Minin, Quan and Zhang 2017). |
|
Bargaining power of the suppliers |
The bargaining power of the suppliers is high for ZTE. The suppliers can handle some specific regions and more concentration is being provided to the buyers (Supplychaindigital.com 2020). The force is strong which helps in switching from one customer to the other. |
|
Bargaining power of the buyers |
There is a high power of bargaining which is exerting customer pressure on the company. The concentrated customer base is increasing and in some places, there are too many sellers. The products and services are prices sensitive to customers. |
5.2 Macro Environment
|
PESTLE Analysis |
Description |
|
Political |
In most of the countries, Chinese products and government are having goodwill. However, ZTE is banned in a country like the United States. But the government in the UK is having a proactive government along with political stability. There is also a split between the local and national administrations. ZTE strategic management might face some impact of Brexit (Amann, Jaussaud and Boqi 2018). |
|
Economic |
In most of the countries, there is fluctuation in the exchange rate, inflation and tax. ZTE is having a goal of expanding into third world countries (Feldstein 2019). But the economic situation of each country needs to be studied properly. ZTE will not be facing problems in the UK because of strong economic conditions. The economy is diversified in both private and public sectors. There is an increase in foreign direct investment. The profitability of small market can be seen in a diversified economy. |
|
Social |
ZTE is not interested to stay in limited cities or areas. The company is planning to expand into the rural cities of the UK. This will be increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. ZTE strategic management also wants to spread some awareness of data security among people. The living standard of people is high in the UK and hence ZTE can sell their handsets easily. |
|
Technological |
ZTE is planning for migration into the 5G network (Mo, Cheng and Contreras 2019). They are thinking of expanding their current communication system by the help of artificial intelligence and the internet of things. The UK is always supporting technological advancement and hence, the prevalence of fibre network is there. |
|
Legal |
Most of the countries are having data security protocols. ZTE is trying to follow the patent and licensing laws while entering a new market. In the United Kingdom, the company is following all the laws and regulations while is making their operations easier. |
|
Environmental |
ZTE is following all the environmental standards (Wu et al. 2016). It includes ISO 14001 along with their implications. They are also managing energy consumptions and carbon dioxide emissions. |
6. Core problems of the company
The core issue with ZTE strategic management is its product. The company was offering smartphones in America and had launched a flip phone C88 (Jain 2017). According to a magazine, this device is not a ground-breaking one. The users are having limited freedom and it’s just a simple alternative to the computer-like phones. The company is losing its sales in China because of the new rules. A supply ban will be there in the United States because the company violated an agreement. There was some illegal shipping of US goods to Iran. There are chances of share plunge which might create some more issues for the company.
7. Confrontation Matrix for ZTE strategic management
The confrontation matrix is helpful for finding the output of SWOT analysis. Here different combinations of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats are combined with each other. This is helpful in identifying the strategic issues faced by the company. In this matrix 4 is the highest and 1 is the lowest. 0 is for those columns that are not filled.
|
Opportunities |
Threats |
||||||||||
|
O1 |
O2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
T1 |
T2 |
T3 |
T4 |
T5 |
||
|
Strengths |
S1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
||||||
|
S2 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|||||||
|
S3 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|||||||
|
S4 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
3 |
|||||||
|
S5 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
|||||||
|
Weaknesses |
W1 |
1 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
||||||
|
W2 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|||||||
|
W3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
|||||||
|
W4 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
|||||||
|
W5 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
|||||||
8. Current and potential future strategies of ZTE
ZTE is having three current and future strategies for the customers. Currently, for a proper ZTE strategic management, the company is trying to provide innovative and custom made products. This is attracting customers from all over the world. Further, they are trying to strengthen their research and development department so that there is scope for advanced versions of handsets by ZTE (Kimura 2019). The company is trying to expand globally through the reputation of the Chinese market. The strategy of the company is to provide quality control products to the customers. This is mainly because of the manufacturers, supplier and purchase of the material.
However, for the future ZTE is having a new set of strategies that will be making them among the top three in the telecommunication industry. The company is planning and hoping to increase their international operations mainly in Ethiopia. The largest telecom of that country is Ethiopia Telecoms Corps (ETC) and the plan is to raise the telecom subscriber from 2.2 million to 15 million by the year 2010. ZTE will be financing US$1.5 billion. The company is going to set up its manufacturing plant along with Janora technology. The plant will be having a capacity of producing 3,000 cell phones each day. The next strategy is to enter the Indian branded mobile market by using own brand name. The company is trying to build its reputation. However, ZTE is search for partners for undertaking the activities of research and development. The company is going to pursue another aggressive ZTE strategic management. The company will be recruiting 2,000 experienced Engineers who are having an idea about 3G technologies, GSM and CDMA. This will be providing sophisticated solutions to the customers and ZTE will be following the trends of the industry. The best possible strategy for the company will be building its brand reputation and dealing in the Indian telecommunication market.
9. Contingency Plan
The contingency plan for ZTE will be to provide communication solutions in various events and shows. It simply means people will be getting awareness of the brand by participating in huge events like the Olympics. This plan will be used only when the selected future plan of the company will not be working. ZTE will need this plan so that they don’t waste time in thinking for new plan later. Events will be providing a lot of exposure to the company. The advantages of the products and services will be reflected in the customers.
10. Implementation issues of the selected strategic plan
There can be some implementation issues in the selected strategic plan for the future of ZTE. The company is planning to have a grand entry in the Indian market by implementing effective ZTE strategic management by using its own brand name. One of the biggest issues that might arise is the reaction of the customers and this had to be handled by the marketing team. It is usually seen that customers are dependent on big brands for handsets. It will be difficult for ZTE to sell its products to the customers in India (Rajagopalan and Biswas 2017). The company is also trying to improve their brand reputation. They also study the Indian market conditions in deep details. With the growing record, the company thought it will be easy to manage the Indian market. However, the company will need good of people in their research and development department. Human resource department had to look after the problems of hiring people. There will be limited resources that the company can use in India. This issue had to be managed by the production and financial team. However, proper planning can save the company from implementation issues.
11. The link between the strategy and various departments of ZTE
The selected strategy is quite important in various departments of ZTE. The clear focus of this strategy is to build a brand reputation in the Indian market. The four major departments that will be looking after this ZTE strategic management are finance, marketing, human resources and production. The finance department will be providing a proper budget for the overall strategy. The production department will be explaining their needs. They demanded a manufacturing facility at Maneswar in Himachal Pradesh. The capacity of the manufacturing place was around 3,000 cell phones each day. Further, the duty of the human resource department was to recruit experienced Engineers for the research and development department. It will be easier for this department to manage people and hire the right set of people. Further, the marketing team had to look after the promotional activities. Each of the department was playing an essential role in the company. Even if one department stops functioning properly then the consequences will be faced by the others. Without proper financial planning HRM and production departments can’t explain their demands. Recruitment process will also stop. Marketing team needs the financial and HRM departments for promotional activities and budget. The main duty was to make some ideas that would help ZTE to build brand reputation.
12. Conclusion
ZTE strategic management is not an easy task for any company. But following proper steps in this method will be saving companies from various issues and losses. The focus of this report was on the case study of ZTE. The company is trying to come under the top three mobile manufacturing brands in the world. There is an explanation of the current strategies. Both internal and external analysis on the ZTE strategic management was done to understand the condition of the company in the market. Further, the future strategies were discussed and one strategy was chosen. Lastly, it was linked with the various departments of ZTE.
Reference List
Amann, B., Jaussaud, J. and Boqi, Z., 2018. Chinese outward foreign direct investment: Strategies for international development. ZTE strategic management In China's Global Political Economy (pp. 97-126). Routledge.
Feldstein, S., 2019. The global expansion of AI surveillance. Carnegie Endowment. https://carnegieendowment. org/2019/09/17/global-expansion-of-ai-surveillance-pub-79847.
Fu, X., Sun, Z. and Ghauri, P.N., 2018. Reverse knowledge acquisition in emerging market MNEs: The experiences of Huawei and ZTE. Journal of Business Research, 93, pp.202-215.
Gao, X., 2018. Reflections on “Effective Strategies to Catch Up in the Era of Globalization”. Research-Technology Management, 61(3), pp.16-18.
Jain, D., 2017. Substantial determination of FRAND licence terms and competition issues by UK high court. ZTE strategic management Jindal Global Law Review, 8(2), pp.231-240.
Kimura, K., 2019. Overseas expansion and technological capabilities: The case of Chinese electronics firms. Global Journal of Emerging Market Economies, 11(1-2), pp.119-131.
Lasserre, P., 2017. Global strategic management. Macmillan International Higher Education.
Li, R. and Cheong, K.C., 2019. China’s “Commercial” State Enterprises—A Case Study of ZTE Corporation. In China’s State Enterprises (pp. 127-150). Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
Minin, A.D., Quan, X. and Zhang, J., 2017. A comparison of international R&D strategies of Chinese companies in Europe and the USA. International Journal of Technology Management, 74(1-4), pp.185-213.
Mo, L., Cheng, W. and Contreras, L.M., 2019, March. ZTE 5G transport solution and joint field trials with global operators. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference (pp. M1G-2). Optical Society of America.
Peng, J. and Wu, Q., 2018, June. International Performance Evaluation-Taking ZTE Corporation as an Example. ZTE strategic management In 2018 International Conference on Sports, Arts, Education and Management Engineering (SAEME 2018). Atlantis Press.
Poczter, S., Musacchio, A. and Lazzarini, S.G., 2018. How to Compete Against the New Breed of National Champions. ZTE strategic management MIT Sloan Management Review, 59(4), pp.65-70.
Rajagopalan, R.P. and Biswas, A., 2017. India–China Relations under Xi Jinping: An Indian Perspective. China: An International Journal, 15(1), pp.120-139.
Rothaermel, F.T., 2017. Strategic management. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
Supplychaindigital.com. 2020. Supply Chain of ZTE. Available at: https://www.supplychaindigital.com/company/how-zte-usa-streamlined-its-supply-chain-become-top-smartphone-supplier# [Accessed on 22nd January 2020]
Wu, D., Gu, X., Gu, J., Liao, W., Zhang, L. and Liu, Y., 2016, November. Cost optimization based network deployment strategies for future dense networks. In 2016 19th International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia Communications (WPMC) (pp. 19-24). IEEE.
Wu, Y., 2019. A comparative case study of crisis communication strategy between ZTE and Huawei within China’s telecommunications industry (Doctoral dissertation, University of Otago).
ZTE.com. 2020. Human Resources of the company. ZTE strategic management Available at: https://www.zte.com.cn/global/about/citizenship/Human-Resources [Accessed on 22nd January 2020]












