Biology Assignment: Process Of Bread Making
Question
Task:
Write a detailed report on biology assignment discussing the step by step process of bread making.
Answer
Executive summary
The paper has offered distinct findings regarding the use of salt with varying proportions in bread baking. As per varied salt proportion, bread making would be different but the structure of the dough can be developed as per the amount of salt and can affect the rising time and can be slower one. The factories can have a deal with high energy wastage if the rise of the initiation process needs too much time. Further, the process would lead to expensive bread from the customers' point of view. In addition, customers can have a complaint regarding the quality of the bread if there would not be enough salt. Otherwise, consideration can have issues of health concern if the bread consumes lots of salt for preserving purpose (Cashman et al, 2019). Salt adds flavor as well as tightens the gluten structure to offers strength to the dough. Through the help of it, the loaf can carry enough amount of carbon dioxide during fermentation through a better volume. Using the apt amount of salt helps the dough to be efficient for reserving carbon dioxide which gets released from the dough as a by-product through its fermentation. From the results section, it has become clear that salt of 7 grams and sugar of 4 grams however provides the best rising of the dough as it rises to 9 cm which is the highest among all other variations of no sugar, high sugar, no salt, and high salt. Through the result section, it is also clear that the properties of dough can be affected by salt. Through the rising level of the dough, it is evident that the dough gets the highest rise through a higher amount of salt however to make the process cost-friendly and time friendly it is important not to use a higher amount of salt.
Introduction
The paper will offer a proper introduction of the process of bread making with emphasizing the problem of varying salt proportion needs and appropriate measures to be used for perfect bread. The paper will also offer its consideration for different approaches that can be taken to understand the exact amount for making bread. The significance of the problem for the entire making process even will be discussed. The result of the three different types of concentration in using the amount of salt even will be explored and explained with much significance. Finally revealed outcome will be developed as an influencing ingredient.
Problem: As per varied salt proportion bread making would be different but the structure of the dough can be developed as per the amount of salt and can affect the rising time and can be slower one. Bread made improperly can have issues of crumb. On the other hand, putting a higher amount of salt for bread recipe can slower process of the initiation of the dough. The presence of no salt can lead to quicken the process with the collapse of the dough (Saavedra-Garcia et al, 2016). The procedure can extract better flavor and aroma of the flour with stronger gluten network and better crumb and crust though the procedure is a time-consuming factor for commercial purposes. A higher amount of salt can even flatten the bread before it is ready for expansion.
Significance: the factories can have a deal with high energy wastage if the rise of the initiation process needs too much time. Further, the process would lead to expensive bread from the customers' point of view. In addition, customers can have a complaint regarding the quality of the bread if there would not be enough salt. Otherwise, consideration can have issues of health concern if the bread consumes lots of salt for preserving purpose. The problem can be significant to have a hold over the entire process of bread making as the absence of salt can make the dough rise too quickly and collapse during baking. Salt plays a complementary role for yeast, the most important ingredient for bread making as salt helps the yeast to be stabilized.
Technical information: the stabilization of yeast further presents water in the bread to crack the dough for making the yeast active through the initiation of carbon dioxide. Salt competes with the yeast for extracting water. Further salt adds flavor as well as tightens the gluten structure to offers strength to the dough (Ogyzit et al, 2020). Through the help of it, the loaf can carry enough amount of carbon dioxide during fermentation through a better volume. With the help of these ingredients, enzyme and fermentation activity of dough can properly be sustained in the procedure. Using the apt amount of salt helps the dough to be efficient for reserving carbon dioxide which gets released from the dough as a by-product through its fermentation. Salt even retorted both high concentrations and a high amount of salt can kill it. However, the exact amount of salt can control the east growth followed by nice crumb. The lower amount of salt can be influential for yeast activity which can be followed by bread-making in crust color, flavor, and structure whereas an excessive amount of salt even stops yeast activity.
Aim of the work: considering all the concerns regarding salt in the making of bread, it is clear that salt proportion is important for the entire process to make the process successful. Thereby, the paper will try to offer findings regarding which exact proportion of salt can be decided. Interface illustration of such concern the experiment will be incorporated through which a varying result can be seen. Thereby the aim of the work compares different variations of the salt proportion and to decide which amount of salt needs to be added with what consideration. Further, the aim of the work will even justify if salt variation can be understood with the process of baking and what outcomes can be there for different salt variations. The work further will try to objectify through its discussion part that how the varying proportion of salt is leading to a different outcome.
Results
Through the result section for different variations of the bread-making process, it can be seen as no sugar, high sugar, no salt, and high salt. In the no sugar though it has seen that before proofing the dough was 4.3 cm to 4.7 CM; where after proofing at 45 minutes of the process it rises to 6.4 cm to 6.2 cm; and after baking at the end at 30 minutes it rises to 7.6 cm to 9.5 CM. For high sugar dough at the initiation, the rising of the do was 5.8 to 5.9 CM; where after 40 minutes it rises to 7.5 to 7.9 CM; and in the end, it rises to 8.9 to 10.3 cm. In the no salt dough the dough rising starts from 6.5 CM at the initial stage and rises to 7.4 CM at 45 minutes and finally its rising consumes 8.1 CM after 30 minutes baking. For the high salt dough initially, it was of 4.9 to 5.7 cm; and at the middle, it becomes 7.5 to 7.9 cm; and finally, it consumes 9 to 9.1 CM with different variations in its ingredients
Discussion
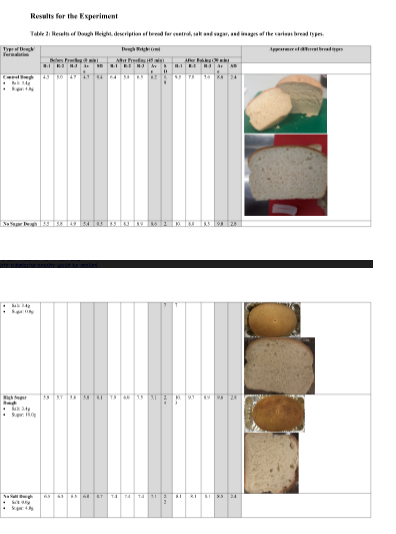
From the results section, it has become clear that salt of 7 grams and sugar of 4 grams however provides the best rising of the dough as it rises to 9 cm which is the highest among all other variations of no sugar, high sugar, no salt, and high salt. Through the result section, it is also clear that the properties of dough can be affected by salt. It is evident from the result section that the properties of dough get influenced by the salt proportion in different ways as salt generally stabilizes the fermentation rate of the yeast of the door. The rheological study can offer proper findings regarding this for the bread-making process (Farhadi, Peighambardoust, and Alirezalu, 2019). Through the experiment result, it even has observed that control or fermentation rate if even done through salt by decreasing gas production rate followed by longer processing time. The concern takes place due to initiated osmotic pressure along with chloride ion and sodium of the yeast cells membrane. Finally, yeast cell growth gets retarded (Tuhumury et al, 2018). Dough without salt performance the yeast however has come as a slower and gassy dough. The poor texture of the bread has been seen through a low amount of salt dough; as lower gas production then sodium chloride confines such a result. Different salt concentration traditions get measured simultaneously through the experiment and the result facilitated maximum height of dough which can be marked as increased baking quality through decreasing salt level. In order to have quality bread, control over gas production to the minimum level is important as salt level can offer poor quality. The reduced salt level gets consistent through higher gas production but reduced retention of gas in it which ultimately affects the rising level of the dough. It is already stated that strengthening the dough can be done through salt and salt interaction gets followed by gluten protein with positive net charges for the flour-water system (Verbauwhede et al, 2019). The reduced salt level tends lower resistance in the extension through poor gluten network. However, it is an important concern to be taken care of that no major structural changes for the dough can take place through reduced salt instead of quality flour gets used. The properties of the dough even get affected through salt during mixing requirements as it has been seen through the experiment that mixing time for the dough gets increased by a portion of salt. Dough without salt hydrates the gluten proteins faster and make the procedure shorter and less time consuming (Man et al, 2019).
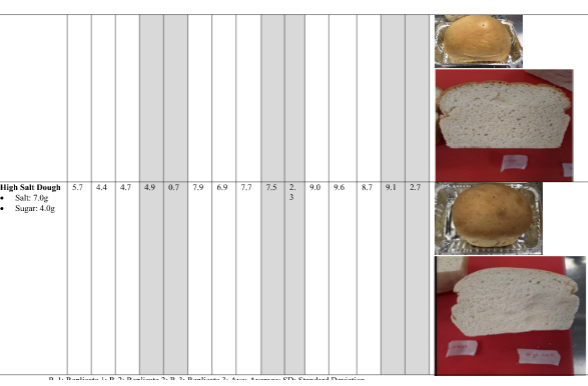
However, with a greater amount of salt, the same process becomes slower with longer mixing time. Longer mixing time can be a serious problem for the bakers with increased energy consumption during mixing make the entire process expensive followed by increased price for the bread which cannot attain the market due to its expensive nature. It is recommended that a higher amount of salt cannot be used during the baking of bread the comparative load amount of salt can be beneficial (Gally et al, 2016). Through the rising level of the dough, it is evident that the dough gets the highest rise through a higher amount of salt however to make the process cost-friendly and time friendly it is important not to use higher amount of salt.
Conclusion
From the entire process, it becomes evident that baking bread is an easy thought process of perfection through all the steps. In the wake of the yeast, canola oil should be included with the yeast blend. In bowl half flour, the proper amount of sugar, and salt and the holdup blend should be blended for the batter. In the wake of blending everything, extra half cup flour should be added to make it a delicate bread mixture. Effective blending is significant to build up the gluten to make appropriate chewy bread structure. Proofing of the dough even should be finished by observing air rises in a warm domain. Through the entire discussion, the conclusion extracts the fact that longer mixing time can be a serious problem for the bakers with increased energy consumption during mixing which cannot attain the market due to its expensive nature. It is recommended that a higher amount of salt cannot be used during the baking of bread the comparative load amount of salt can be beneficial. Through the rising level of the dough, it is evident that the dough gets the highest rise through a higher amount of salt however to make the process cost-friendly and time friendly it is important not to use higher amount of salt.
References
Cashman, K.D., Kenny, S., Kerry, J.P., Leenhardt, F. and Arendt, E.K., 2019. ‘Low-Salt’bread as an important component of a pragmatic reduced-salt diet for lowering blood pressure in adults with elevated blood pressure. Nutrients, 11(8), p.1725.
Farhadi, A., Peighambardoust, S.H. and Alirezalu, K., 2019. Effect of adding different levels of water on rheological, technological and sensory characteristics of corn starch gluten-free bread enriched with buckwheat flour. Food Science and Technology, 16(90), pp.127-139.
Gally, T., Rouaud, O., Jury, V. and Le-Bail, A., 2016. Bread baking using ohmic heating technology; a comprehensive study based on experiments and modelling. Journal of Food engineering, 190, pp.176-184.
Man, S.M., Paucean, A., Chis, M.S., Muste, S., Pop, A., Muresan, A.E. And Martis, G., 2019. Effect Of Nettle Leaves Powder (Urtica Dioica L.)Addition On The Quality Of Bread.Hop and Medicinal Plants, 27(1-2), pp.104-112.
Ozyigit, E., Eren, ?., Kumcuoglu, S. and Tavman, S., 2020. Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (LAOS) analysis of gluten-free cake batters: The effect of dietary fiber enrichment. Journal of Food Engineering, 275, p.109867.
Saavedra-Garcia, L., Sosa-Zevallos, V., Diez-Canseco, F., Miranda, J.J. and Bernabe-Ortiz, A., 2016. Reducing salt in bread: a quasi-experimental feasibility study in a bakery in Lima, Peru. Public health nutrition, 19(6), pp.976-982.
Tuhumury, Helen & Studi, Program & Hasil, Teknologi & Fakultas, Pertanian & Pattimura, Pertanian-Universitas. (2018). THE EFFECTS OF SALT ON BREAD: TECHNOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR REDUCED SALT LEVELS. AGRICA. 4. 10.37478/agr.v4i2.458.
Verbauwhede, A.E., Lambrecht, M.A., Fierens, E., Shegay, O., Brijs, K. and Delcour, J.A., 2019. Impact of aqualysin 1 peptidase from Thermus aquaticus on molecular scale changes in the wheat gluten network during bread baking. Food chemistry, 295, pp.599-606.












