Business Economics Assignment Analysing Demand & Supply and Economic Theories
Question
Task 1 –
Demand and Supply analysis are fundamental to any business thus every business must understand its impact and dynamics. Demand and Supply analysis therefore underlines to some extent the growth and success of most businesses in our society today.
Critically analysed the following microeconomics concepts with reference to any business of your choice.
1.1 Explain the law of Demand, movement along the same demand curve (with the aid of diagram) and changes in demand curve (with the aid of diagram).
1.2 Explain the law of Supply, movement along the same supply curve (with the aid of diagram) and changes in supply curve (with the aid of diagram).
Task 2 –
1.1 Compare and contrast emerging theories and models in 21st century contemporary economics with those of the 20th century, and relate both of these to modern business practices.
Answer
Introduction to Business Economics Assignment
Introduction to notion
Business Economics is a very crucial part of economics which includes various aspects of business-like marketing, finance, infrastructure, business methodology, etc.
Research Aim
In the first task, the concept of demand and supply will be explained with reference to the business of Apple Inc. In the second task, the economic models and theories of the 21st century will be compared and contrasted with the theories and models from the 20th century.
Company Overview
The business organisation whose demand and supply will be considered in Task 1 is Apple Inc. Apple Inc. is a multinational company from America operating in the technology industry. Apple Inc. is popular for its smartphones, iPhone. The demand for these smartphones and its supply will be discussed in the below section.
Task 1
The Law of Demand
As per the law of demand, the quantity of a good/ service demanded increases (decreases) when price for the commodity or service reduces (rises) (Cerreia-Vioglio et al, 2021). In case of the law of demand, the other factors impacting the demand of the commodity or service are considered to be constant. Therefore, in this case, when the price of iPhones rise the quantity demanded of iPhones fall. On the contrary, as the price of iPhones fall the quantity demanded of iPhones rise. This is shown through the movement along the demand curve. However, there is no shift of the demand curve while abiding by the law of demand. As per Fatimah (2021), the inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of the commodity or service and the price of the commodity or service is reflected in the downward slope of the demand curve.
Movement along the same Demand Curve
The movement along the same demand curve indicates the change in quantity demanded of iPhones due to changes in price of iPhones. Movements along the demand curve can be of two types. The first kind of movement is known as extension of demand. In case of extension of demand, the quantity demanded of iPhones increase due to the decrease in the price of iPhones. The other kind of movement along the demand curve is referred to as contraction of demand. In case of contraction of demand, the quantity demanded of iPhones decrease due to the increase in price of iPhones (Bakar and Rosbi, 2020).
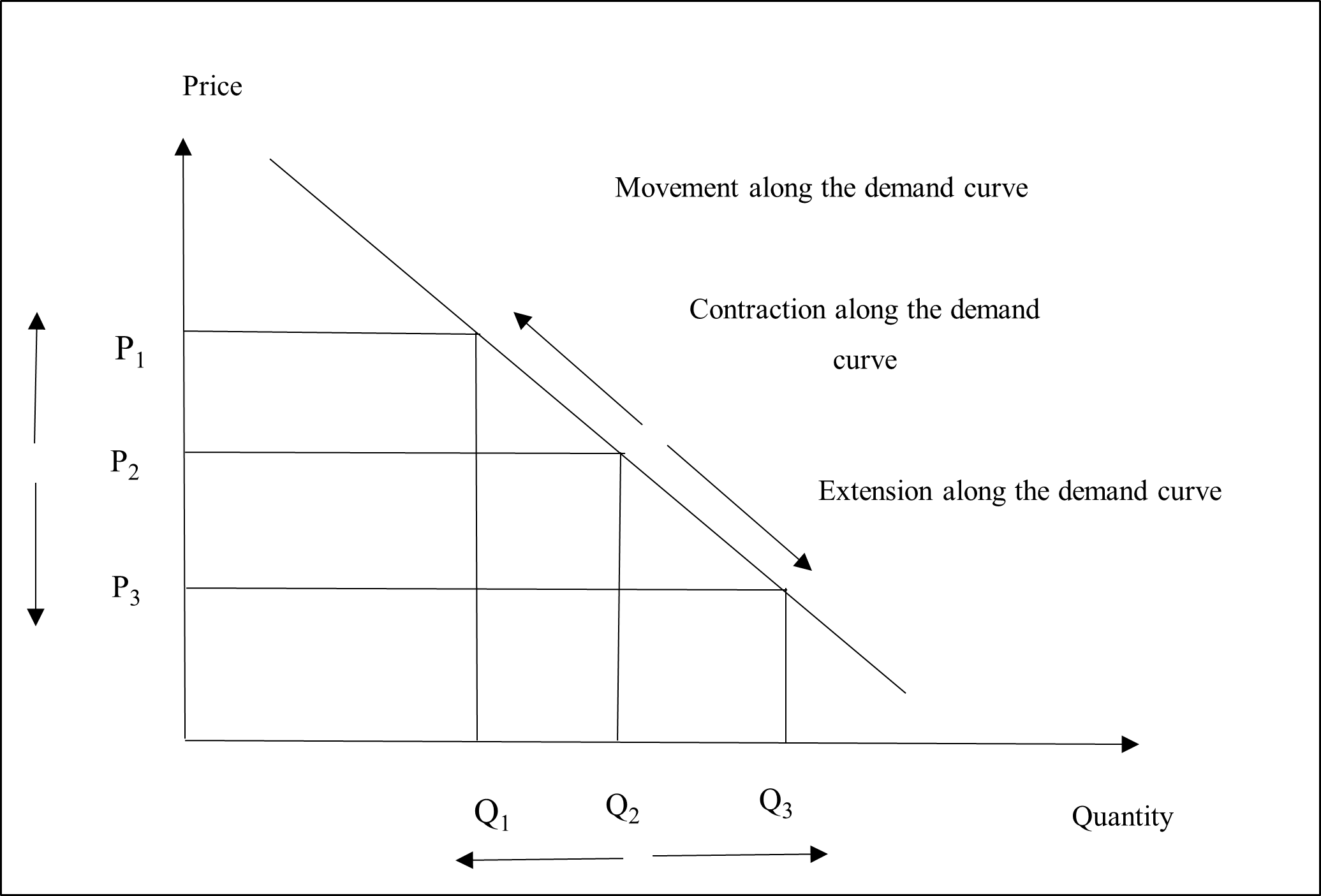
There is only one factor determining the movement along the demand curve. The factor is price of iPhones. There is no impact or influence of any other factor on the movement along the demand curve. In the diagram above, it has been shown that the downward movement along the demand curve shows the extension in demand, while the upward movement along the demand curve denotes contraction of demand. As the price of iPhones rise from P2 to P1, the quantity demanded of iPhones decrease from Q2 to Q1. This is contraction in demand. Similarly, when the price of iPhones fall from P2 to P3, the quantity demanded of iPhones increase from Q2 to Q3. This is extension in demand. As per Lokeshgupta and Sivasubramani (2018), in case of movement along the demand curve, factors that have the potential of affecting the demand for iPhones, are considered to remain unchanged. The price of related commodities/ services, the income of the people, tastes or preferences, etc. do not change in case of movement along the demand curve.
Changes in the Demand Curve
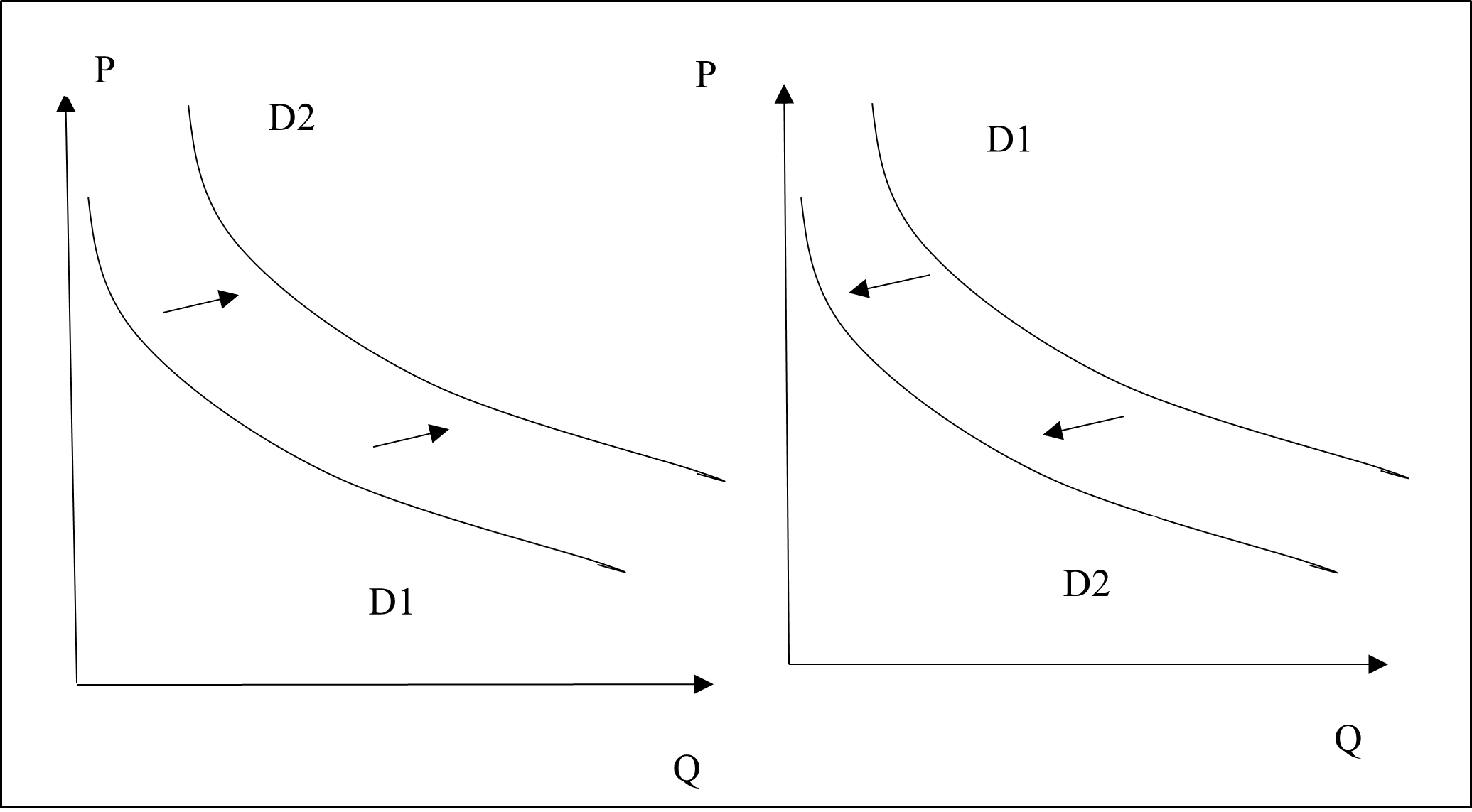
Change in demand curve is a situation where the entire demand curve shifts, either to the right or to the left (Alquist, Bhattarai and Coibion, 2020). In this case, the price of iPhones remain unchanged. The factors which impact and cause the shift in the demand curve of iPhones include the income of consumers, the preferences and taste of the consumers, the population size, the composition of the consumer population, the expectations of consumers, the change in the price of the complementary and substitute goods, etc (Gao et al, 2019). When the factors are in favour of iPhones, demand for smartphones increase. For instance, as the income of the consumers increases, the demand for the iPhones also increases causing a rightward shift of the demand curve, which is known as increase in demand. However, if the price of the substitutes of iPhone like Samsung or LG smartphones decreases, the demand for iPhones will decrease, because consumers will replace the demand for iPhones by its substitute. This will cause a leftward shift of the demand curve, which is referred to as decrease in demand. In the below given diagram (diagram on the left), the rightward shift of the demand curve for iPhones from D1 to D2, known as increase in demand is caused by some favourable factors supporting the demand for iPhones. The leftward shift (diagram on the right) of the demand curve for iPhones from D1 to D2, known as decrease in demand is caused by some factors which go against the demand for iPhones.
Law of Supply
As per law of supply, price of commodity or service is directly related to the quantity supplied of the commodity or service (Meyer, 2020). The relation between price of iPhones and the quantity supplied is determined by the law of supply showing that when the price of iPhones increases, quantity being supplied by a seller increases. This is because the seller gets more (less) price for iPhones, he is willing to offer more (less) quantity of iPhones for sale. The only determinant of quantity supplied is the price of the commodity or service (Mutangili, 2019).
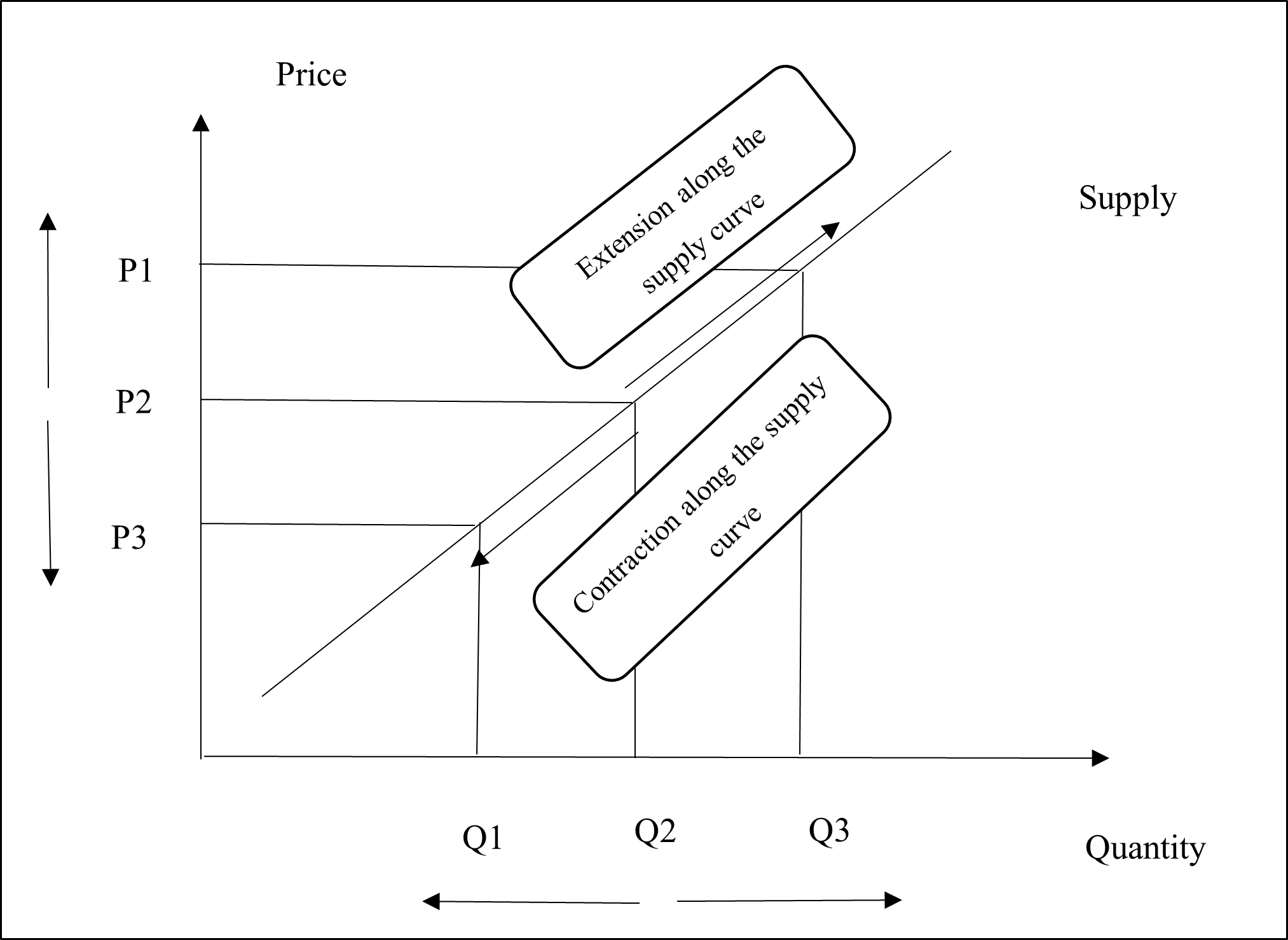
Movement along the same Supply Curve
The movement along the same supply curve takes place because of the change in the price of iPhones. The upward movement along the supply curve denotes extension of supply while the downward movement along the supply curve illustrates the contraction of supply (Brinca, Duarte and Faria-e-Castro, 2021). The below given diagram shows the extension and contraction of supply. As the price of iPhones increases from P2 to P1, the quantity supplied of iPhones increases from Q2 to Q3. This shows extension in supply. When the price of iPhones falls from P2 to P3, the quantity of iPhones supplied falls from Q2 to Q1. This shows contraction of supply. The former occurs when the price is high while the latter takes place when the price of iPhones is low.
Changes in Supply Curve
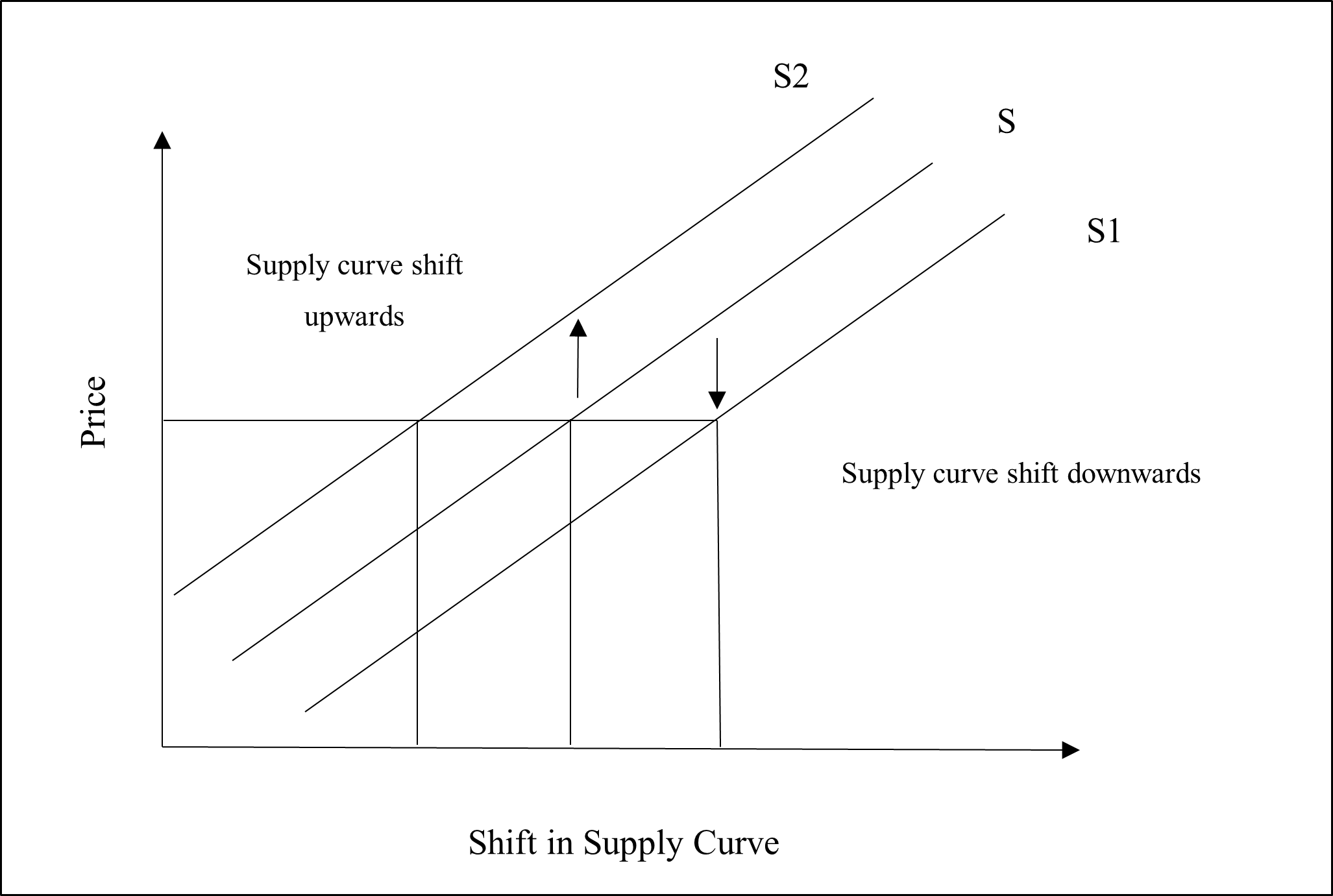
According to Lalon (2020), unlike the movement along supply curve, the change in supply curve is the shift of supply curve, either upwards or downwards. Shift of the supply curve occurs due to the changes in the other factors which remained constant during the movement along same supply curve. The shift or change of supply curve for iPhones occurs when the price of iPhones remains unchanged, but the supply is affected by the other factors like technology, price of inputs, number of firms in the market, etc. The downward shift of the supply curve for iPhones occurs when the factors are in favour of the supply. For instance, if the technology improves, the price remaining constant, the supply curve for iPhones will shift downwards showing an increase in the supply. On the contrary, if the price of the inputs or complementary goods like cellular network increases, the supply of iPhones will be decreasing showing an upward shift of supply curve (Gereffi, 2020). Therefore, the upward shift of the supply curve illustrates a decrease or reduction in the supply of iPhones while the downward shift of the supply curve shows the increase of the supply (Maital and Barzani, 2020). The below given diagram shows the upward and downward shift of supply curve. The change of the supply curve for iPhones from S to S2 shows upward shift of supply which denotes decrease in supply of iPhones while price remains constant. The change of the supply curve for iPhones from S to S1 shows downward shift of supply which denotes increase in supply of iPhones while price remains constant.
Task 2
Emerging theories & models of the 21st century in contemporary economics
Today the contemporary global economy is engaging in international trade, which is raising several economic issues. The global interaction across national economies fosters economic development. This facilitates satisfaction of human wants, better production and increase in economic growth. However, the contemporary global economic issues include economic inequality, credit availability, hyperinflation, depression, poverty, recession, public debt, etc (Sepashvili, 2020). To develop a better idea about these issues will help resolving many modern business issues. Thus, in this paper the emerging models and theories from the 21st century will be compared with the theories and models of the 20th century to develop a framework for understanding the decisions and actions of the businesses, individuals and governments. This facilitates better comprehension of the market driven economy. Furthermore, knowing contemporary economic theories and models will enable better analysis of the government policies which impact the families, lives of the people and jobs.
According to Comert (2019), the ideas of the contemporary Keynesians is based on the General Theory of Keynes which was based on the assumption that wages and prices are sticky. The Walrasian general equilibrium theory and the Keynesian economics can be studied differently without considering prices to be sticky. These are among the emerging theories of economics in the 21st century. The microeconomic theory and the Keynesian economics are the two main ideas of the 21st century contemporary economics. The Keynesian economics is a very crucial theory in contemporary economics. There are several implications of this theory in modern world. The theory suggests that the free market economies might be supporting any rate of unemployment as in equilibrium. The equilibrium in contemporary world is selected through confidence, which is referred to as animal spirits by Keynes. On the contrary, the idea adopted from the microeconomic theory states that the individuals are goal-oriented and rational in their thinking (Mohammadi and Rezvani, 2019). The theory further suggests that the individuals do not make any systematic errors in forecast.
The Keynesian economics and microeconomic theory are applicable in the contemporary world in case of modern business practices. The market system could be leading to various outcomes which are insufficient with the high rate of unemployment. As per Oravský, Tóth and Bánociová (2020), in the current situation created by Covid-19, i.e., the global economic crisis is affecting all the economic activities across the world. However, going by the ideas of Keynes with Walras, fiscal policy is not the appropriate response to the economic crisis.
Comparing with theories & models from 20th century
The economic theories and models from 21st century have evolved out of the models and theories of the 20th century. Over the past hundred years, the new economics of the millennium has been carved out of the neoclassical economics. The changes in the theories and approach have changed drastically during the first half of the present century (Kanev and Terziev, 2017). The economic theories and models of the 21st century have grown out of the theories from 20th century under the influence of the technological improvements. During the 20th century, especially during the first half, economics was considered to be a social science. The economists like John Maynord Keynes and Irving Fisher and their theories stressed more on the psychological attributes for defining the economic behaviour. However, economic theories and models started changing their approach with the mathematical revolution during 1940s. The economists like Paul Sammuelson and John Hicks started optimizing the economic agents during 1950s. The micro foundations were being formulated and developed by Keynes. This led to the development of rational models which have their implication in the 21st century (Keohane, 2019). These models eventually evolved to include the economic agents which were termed as hyperrational by the detractors.
Application in Modern Business Practices
The Keynesian theory can be applied to various paths of modern business today. The theory of Keynes and microeconomic theory can be applied to resolve the economic crisis of the contemporary times. Out of the theories of the 21st century, the Keynesian theory is the most promising one. The economists associate the Keynesian theory with the expenditure of the government throughout the recessions. This theory is effective during the real time crisis like Covid-19, across the globe. Though the theories of 20th century are effective and applicable in the contemporary times, it is high time to drop the hypothesis of natural rate. It would be beneficial for the economies to return to the General Theory by Keynes. This suggestion for modern businesses is not a baseless rhetoric. The adoption of the General Theory by Keynes would find its way in the policy formulation, that is required for stabilising the 21st century’s real economy (Stanford, 2017).
At present the world is facing huge crisis. The sudden outbreak of Covid-19 pandemic has led to recessionary effect on the global economy. To handle the situation, the economic models and theories need to be applied to real life. The Keynesian theory has found its application in the present situation. The governments of various countries need to formulate policies for managing the aggregate demand. They need to address the economic recession and prevent such recessions from occurring further. The primary tools recommended by Keynes or economists who are followers of the Keynesian theory include the monetary as well as the fiscal policies. In order to manage the economy during a crisis, it is important to formulate effective policies. No business can uplift the economy from such a crisis like Covid-19. Therefore, the government spending is the best possible solution to improve the economic condition of the nations. The main problem which the global economy is facing today is that of unemployment. To fight out unemployment, the Keynesian theory can be applied to the current situation (Pollitt et al, 2021).
Conclusion
From the above research based on the law of demand and supply (Task 1), it can be clearly understood that these are the two determining factors of a market place. The analysis of demand and supply are fundamental to the discipline of business economics. It can be concluded from task 2 that economics is a very significant and inseparable part of today’s contemporary world. In the everyday life, the global population needs economics. The study of economics facilitates a better understanding of the past, present and future theories and models. This understanding will be beneficial while applying these theories and models to the modern business practices. The governments, societies, individuals and businesses are using economics in the contemporary world. The comparative study of the theories and models of the 20th and 21st century has provided a better insight into effective modern day business practices.
References
Alquist, R., Bhattarai, S. and Coibion, O., 2020. Commodity-price comovement and global economic activity. Journal of Monetary Economics, 112, pp.41-56.
Bakar, N.A. and Rosbi, S., 2020. Effect of Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) to tourism industry. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Science, 7(4), pp.189-193.
Brinca, P., Duarte, J.B. and Faria-e-Castro, M., 2021. Measuring labor supply and demand shocks during COVID-19. European Economic Review, 139, p.103901.
Cerreia-Vioglio, S., Maccheroni, F., Marinacci, M. and Rustichini, A., 2021. Law of demand and stochastic choice. Theory and Decision, pp.1-17.
Cömert, M., 2019. Revival of Keynesian Economics or Greening Capitalism:“Green Keynesianism”. Sosyoekonomi, 27(42), pp.129-144.
Fatimah, A.T., 2021. Mathematical Reasoning of Vocational High School Students on Mathematical Tasks in the Law of Demand Context. Business economics assignment AlphaMath: Journal of Mathematics Education, 7(2), pp.101-113.
Gao, W., Darvishan, A., Toghani, M., Mohammadi, M., Abedinia, O. and Ghadimi, N., 2019. Different states of multi-block based forecast engine for price and load prediction. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 104, pp.423-435.
Gereffi, G., 2020. What does the COVID-19 pandemic teach us about global value chains? The case of medical supplies. Journal of International Business Policy, 3(3), pp.287-301.
Kanev, D. and Terziev, V., 2017. Behavioral economics: development, condition and perspectives. IJASOS-International E-Journal of Advances in Social Sciences, 3(8).
Keohane, R.O., 2019. The theory of hegemonic stability and changes in international economic regimes, 1967–1977 (pp. 131-162). Routledge.
Lalon, R.M., 2020. COVID-19 vs Bangladesh: Is it Possible to Recover the Impending Economic Distress Amid this Pandemic?. Journal of Economics and Business, 3(2).
Lokeshgupta, B. and Sivasubramani, S., 2018. Multi-objective dynamic economic and emission dispatch with demand side management. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 97, pp.334-343.
Maital, S. and Barzani, E., 2020. The global economic impact of COVID-19: A summary of research. Samuel Neaman Institute for National Policy Research, 2020, pp.1-12.
Meyer, T., 2020. Trade Law and Supply Chain Regulation in a Post-COVID-19 World. American Journal of International Law, 114(4), pp.637-646.
Mohammadi, A. and Rezvani, M.H., 2019. A novel optimized approach for resource reservation in cloud computing using producer–consumer theory of microeconomics. The Journal of Supercomputing, 75(11), pp.7391-7425.
Mutangili, S.K., 2019. Influence of Transportation and Logistics Law on Supply Chain Performance of Energy Development Agencies in Kenya. Case of Kenya Power and Lighting Company Limited. Journal of Procurement & Supply Chain, 3(3), pp.21-38.
Oravský, R., Tóth, P. and Bánociová, A., 2020. The ability of selected European countries to face the impending economic crisis caused by COVID-19 in the context of the global economic crisis of 2008. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 13(8), p.179.
Pollitt, H., Lewney, R., Kiss-Dobronyi, B. and Lin, X., 2021. Modelling the economic effects of COVID-19 and possible green recovery plans: a post-Keynesian approach. Climate Policy, pp.1-15.
Sepashvili, E., 2020. Digital Chain of Contemporary Global Economy: E-Commerce through E-Banking and E-Signature. Economia Aziendale Online-, 11(3), pp.239-249.
Stanford, J., 2017. The resurgence of gig work: Historical and theoretical perspectives. The Economic and Labour Relations Review, 28(3), pp.382-401.












