Change Management Assignment: Leading Strategic Change in Greenwich Leisure Limited
Question
Task: Choose a company (or context) with which you are familiar. Ideally, it should be based on a real company which can include a small company that is not well known or a large national, multinational or global organisation.
Change Management Assignment tasks
Task 1
a) Develop a new mission statement for your chosen organisation and suggest the role and actions the CEO will need to undertake to communicate this to staff and other key stakeholders. Use relevant theories and models in your answer.
b) Critically discuss the leadership styles needed to create and embed the organisation’s mission throughout its operations. Use relevant theories and models in your answer.
Task 2
The newly developed mission statement represents a significant change for your organisation. Critically evaluate a range of suitable models that will enable the CEO to lead this change programme successfully.
Task 3
a) Using the Mendelow matrix, identify the range of stakeholders and explain ways the CEO can gather feedback on the proposed new mission statement.
b) Select THREE different types of stakeholders. Propose a different method for each to ensure these stakeholders’ expectations are met and they are kept engaged throughout the change process.
Task 4
a) Critically evaluate the skills and behaviours needed by the CEO to lead this strategic change successfully within your chosen organisation.
b) Develop SMART objectives and development initiatives to enable the CEO to acquire any skills needed to implement the change successfully.
Answer
Introduction
Greenwich Leisure Limited is a charitable organisation that provides local services to the local authorities (Findlay-King et al., 2020). In this change management assignment, we have developed a new mission statement and stated the roles, responsibilities and actions to be undertaken by the CEO of GLL to communicate this mission to the employees and key stakeholders of GLL. Moreover, suitable models that enable the CEO to lead the change programme have also been critically evaluated. GLL is one of the UK’s largest service providers in sport, cultural, public leisure, community, and health. Better is responsible for promoting physical activities and healthy lifestyles. Educational courses, athlete programmes, health intervention services, and work programmes which are recognised nationally are operated by GLL.
Organizational background
Greenwich Leisure Limited is a non-profit organisation. Recently it operates under the brand Better. Better is a charitable organisation in the social enterprise sector. To run the local services in London Borough situated in Greenwich, GLL was founded in 1993 (GLL, 2021). After a few years, it expanded its services for other local authorities. GLL is the largest operator in providing leisure facilities. This organisation runs over 250 sport, culture, and leisure facilities. Its local authorities are far spread across London and all across the UK. The headquarters of GLL is in Middlegate House, Royal Arsenal which is situated in South East London. The type of organisation is industrial and provident. As of 2017, the revenue generated by GLL is EUR 274 million and the number of employees working is 13,500. GLL organises various sport and cultural events in Olympics that provide leisure to the people. The main customer segment of GLL would be the people who are talented in sport, culture, and leisure activities and the people who are interested to watch such activities. This may include the 11-45 age group where people are fit and enthusiastic about leisure activities. The key competitors of GLL would be the Olympic Events that are organised internationally.
Task 1 :Provide a mission statement of Greenwich Leisure Limited. Identification of the role and actions the CEO to communicate this to staff and stakeholders
Mission
The mission of GLL is to provide better access to facilities, better value, better service, better inclusion and sport, better environment, better staff, better health, and better information and feedback.
Roles and Responsibilities of a CEO at GLL:
1. Communicate the Vision: For a CEO of GLL, to communicate his mission, he first needs to communicate the vision of GLL to his staff and other stakeholders. To imply this he needs to own the vision himself. The vision of GLL is to make community spaces and services better for everyone. Therefore, the CEO of GLL must know and own this vision in order to communicate the mission statement to its staff and stakeholders. Owning a vision is to encompass the values, vision, overall strategy of GLL, and the mission (Kaehr Serra and Thiel, 2019). The CEO of GLL must communicate the complete mission to its staff and key stakeholders in a compelling manner. This will allow them to understand and analyse their contribution to the growth of GLL in leisure service, sport, health, and other programmes operated by GLL. The CEO of GLL must know how to engage their stakeholders, customers, and employees and how to communicate the direction and mission of the company clearly.
2. Tie the mission to Stakeholder goals: Stakeholders of GLL are interested in investing in the company due to the clear values, mission, and vision that GLL has. A CEO must know how to exactly attract the stakeholders. For stakeholders of GLL, the shares they get in return are partly financial but it keeps them motivated to invest for completing and supporting the mission of GLL. 3. Keeping the Mission fresh: Another role of a CEO at GLL in communicating the mission to everyone is to prevent it from becoming stale. With timely updates of activities and their success in health, sport, and public leisure can help the CEO of GLL to communicate the mission clearly (Freiwirthet al., 2017). To provide access to fitness facilities and community leisure of GLL, the CEO must be deeply ingrained in the culture of the company.
4. Strike the balance: To balance the necessary optimism for GLL along with the maintenance of credibility is an obvious challenge for the CEO in communicating the mission to its employees and other key stakeholders. Being the primary caretaker of the mission must be the key strategic responsibility of GLL’s CEO.
Actions to be undertaken by the CEO of GLL:
• List the key points of both the new vision and the new mission of GLL.
• Prepare and give slide shows, PowerPoint presentations, and other communication strategies that will help in conveying the key points to the employees and stakeholders of GLL.
• Schedule a meeting for employees, management, and key stakeholders to unveil the new mission statement at corporate headquarters.
• Present the idea and new mission of GLL in a very optimistic and actionable way.
Relevant Theories and Models
Theories related to the employee motivation and leadership styles and strategies adopted by the CEO of GLL can be the most relevant theories and models for a CEO to communicate the new mission statement to the employees and stakeholders of GLL. Following are the leadership styles that the CEO of GLL must implement to communicate the mission statement to its employees and stakeholders:
• Transformational Leadership: This style of leadership focuses on the empowerment and motivation of the employees to drive change in building the mission of GLL. A transformational CEO is a charismatic and innovative leader (Zuraik and Kelly, 2019). He has a clear vision of values, goals, and ethics that are required to decide the mission of GLL for its betterment(Duignan and Pappalepore, 2019). This will allow the CEO to communicate with the employees and stakeholders clearly. The CEO of GLL enthusiastically leads by fostering mentorship and open communication strategies.
• Strategic Leadership: Implementing this style of leadership will allow the CEO to adapt to the change, to sustain the core values of GLL, and to communicate with the other employees and stakeholders effectively. This type of leadership will help the CEO of GLL to be flexible, steadfast, think big, and be able to see minute details that will help in the growth and expansion of GLL (Kowo and Akinbola, 2019). It will help the CEO in constant learning, analysing, synthesizing, and gathering information for stating the new mission of GLL and communicating it to the employees and stakeholders of GLL.
Critically discuss the leadership styles of GLL company
A leadership style refers to the characteristic behaviour of the CEO of GLL while motivating, managing, guiding, and directing the employees and the stakeholders of GLL towards the mission of this non-profit social enterprise (Al Khajeh, 2018). The leadership styles required to embed and create GLL’s mission through its operations are as follows:
1. Authoritarian Leadership (Autocratic): The CEO of GLL must adopt this style of leadership as it will give him the direction to provide clear expectations to GLL from employees and stakeholders. These expectations include things to be done, when they should be done, and how they should be done. The CEO can give the command to its employees to look up to the mission if he implements this type of leadership style (Dyczkowska and Dyczkowski, 2018). Following the mission and the desire to accomplish it will keep the employees and stakeholders motivated to their part of contribution. The CEO can make decisions independently with no input from other employees and stakeholders of GLL. However, this may affect the creativity in decision-making as there is no variety in the opinions and ideas for the betterment of GLL. Therefore, clearly, this type of leadership will not be able to create and embed GLL's mission throughout its operations.
2. Democratic Leadership: According to the study done by Kurt Lewin on leadership styles, this leadership style is typically the most effective for the CEO of GLL to communicate the mission to its employees and stakeholders. The CEO of GLL must be a democratic leader which will allow him to offer guidance to the team and allow input from employees and key stakeholders (Rifaldiet al., 2019). The CEO of GLL can encourage its team to participate and share their ideas. Using this leadership style will make employees be more productive and deliver high quality of work to GLL. Therefore, this type of leadership will be the most effective one in creating and embedding GLL’s mission throughout its operations as it will make employees feel like they are an important part of GLL.
3. Delegative Leadership (Laissez-Faire): According to Lewin the leaders of this style are the least productive (Drescher, 2017). If the CEO of GLL adapts this leadership style then GLL will not be able to expand its firm as the delegative CEOs leave the decision-making completely on the employees and key stakeholders. This leadership style often leads to poor roles and lack of motivation by the leader which will distract employees of GLL away from achieving the mission of GLL. Therefore, this type of leadership should not be implemented by the CEO of GLL.
Task 2: The newly developed mission statement
Mission
The mission of Greenwich Leisure Limited is to organize the structure of the non-profit charitable organization. These proceeds will assist the administration across various departments of the management into efficient commencement of the company
Critical evaluation of a modelthat will enable the CEO to lead this change program successfully
Greenwich Leisure Limited is one of the non-profit charitable organizations that run over 250 sport and leisure facilities across London and the United Kingdom. The organization uses a traditional local government model of management which includes management that is divided according to the departments. It is essential to understand the suitable models that can be used by the CEO to change the program successfully in the long run (Odor, 2018). As the external business environment is changing continuously, Greenwich Leisure Limited is required to change the model to increase operational efficiency and profitability. The different models that can be used by Greenwich Leisure Limited are the McKinsey 7-S Model, and John P. Kotter’s Eight Steps of Change Management.
McKinsey’s 7S model was developed by McKinsey and Company in 1981 which is used to analyze the effectiveness of the organisation at large. The key seven elements that govern the model are Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills. As Greenwich Leisure Limited has a departmental organizational structure, it is essential for the organization to communicate its strategies, change its structure and enhance its systems. It is essential to draft strategic goals which are required to formulate its actions accordingly (Razmi, 2020). Moreover, the CEO will be benefited if this model is undertaken because it provides a clear outline of the goals and objectives that the CEO has proposed in the mission statement. Due to the structure of Greenwich Leisure Limited, there have been difficulties with respect to operational efficiency as the work in hand gets delayed as it has to pass through several departments. It is also important to change the structure accordingly.
Understanding the structure to the extent of decentralization that can be used for effective delegation of authority and fast-paced work momentum. Similarly, the systems will be required to be enhanced to increase productivity. On the other hand, the style, staff, and skills are required to be developed by the CEO. Skills and Staff are essential to carry out the process faster and with equal efficiency through good communication. The style of the work needs to be changed by the CEO and communicated to several parties. Not only will it facilitate the change but also bring in innovation in the organisation. This integration of the 6-S leads to the shared view finally which helps to keep Greenwich Leisure Limited at a similar momentum and give the first-mover advantage. It is an effective process that can be undertaken by the CEO for the change (Gökdeniz, et. al, 2017). Although the model seems to be easily implemented in the framework, it is quite time-consuming.
Another major drawback of the model is that it ignores the external environment. As Greenwich Leisure Limited is based in London and the United Kingdom, the effects of Brexit and other trade and commerce deals will not be looked into account after taking up the model. It solely focuses on the internal structure and functioning of the organization(Shaqrah, 2018). It becomes difficult to assess its viability in both the short-run and long-run. As these perspectives are not taken into account, there can be loopholes in the strategy that has been made with respect to the organization. Due to such limitations, often the model is considered to be a static model.
John P. Kotter’s Eight Steps of Change Management is a model that helps the organization to adapt and prepare for the various changes that it will face in the daily course of action. The eight processes are establishing a sense of urgency, forming a powerful guiding coalition, creating a vision, communicating the same vision, empowering others to work on those visions which have been set up, planning and achieving the short-term wins, consolidating improvements, and institutionalizing the new approaches(Rajan, et. al, 2017). Greenwich Leisure Limited having an organizational structure that causes a delay in its operation should take up this model because it gives a holistic view to the change the CEO is looking for. It is essential for an organization like Greenwich Leisure Limited to communicate the change to its staff and other members as soon as possible. The CEO should look into the dynamics that can cause a threat or create an opportunity for the organization and communicate the same to the members. While interacting, the management should also take up a due course of action which would help the members to carry out the actions that are required. As Greenwich Leisure Limited is a non-profit charitable organization, it should assign short-term goals like providing leisure in particular parts of the city.
These goals should be the metrics by which the CEO can understand the effectiveness of the model that has been undertaken. Not only the CEO needs to keep the track of improvements made but also focus on the changes that need to be addressed (Paraschiv, et. al, 2019). The changes in the external environment like Brexit, the COVID-19 pandemic, and other trade deals are taken into consideration in this model, and institutionalizing the same is extremely important. Although the model gives a proper model of change for Greenwich Leisure Limited it only focuses on the part of urgency and not the details. The entire process is extremely top-heavy and it is left onto the key managerial personnel to take up the initiatives. Due to the lack of emphasis on the members and employees, it can lead to repercussions from the employees so as to which the change may not be viable for the long run. The model takes into account the external factors which are essential in the current scenario but it looks towards the short-term wins instead of the long-term goals. Greenwich Leisure Limited requires a long-term goal that it can adapt to increase its operational efficiency and surplus in the long run.
Thus, either of the two models can be used by the CEO of Greenwich Leisure Limited for the change that needs to be made in the mission statement. These two models can help the CEO to carry out the changes effectively and efficiently.
Task 3: a) Identification of stakeholders using Mendelow matrix
The Mendelow matrix classifies the stakeholders on a grid whose axes are the power to influence and the interest in the organizational activities. This model helps to understand the relationship between the stakeholders and the organization. (Laurisz, 2019)
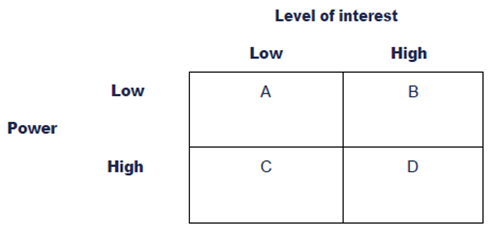
Figure 1: Mendelow matrix
(Source:Krivtsov, 2019)
In this case, the box that is denoted by A refers to a region where there is a lack of interest and power. This region is known as Minimal Effort. For Greenwich Leisure Limited, this region will have stakeholders like other social organizations in the UK and London. The other social organizations like the British Red Cross will not have any power to influence or the interest in the organization. Therefore, it is treated in Box A. Green Leisure Limited can ensure feedback by trying to take up policies that may impact the other businesses in a positive way. For instance, the organization can take help from delivery companies to get feedback from such stakeholders.
The region that is denoted by Box B indicates that the stakeholders have low power to influence but have a high level of interest. In this situation, Greenwich Leisure Limited needs to be convinced to adhere to the strategies and believe in the same. This region is known as Keep informed. The stakeholders who are present in this region are the customers and the employees. The customers and employees do not have the power to influence the organization because in the UK and London there are several customers and the labour market also has abundant labor. As the switching cost is low, the power to influence also reduces accordingly. To gain feedback, the CEO can try to reduce the switching cost further.
The region that is denoted by Box C is the region in which stakeholders have substantial power to influence but do not have the level of interest. In this case, the stakeholders try to move towards box D. This region is known as Keep Satisfied. This region shows the stakeholders like the government and other local communities that are present in the UK for Greenwich Leisure Limited. The local communities in the UK are not interested in the operations of the organization. The government also has a low level of interest in the working of the organization. But they have substantial power because any change in the government policies in the country can affect the sales and services of the organisation. Similarly, the local communities in the UK are interlinked and they have an immense amount of power to influence the types of goods and services that are being provided by the company. For feedback, Greenwich Leisure Limited can take up some activities which adhere to the cultural aspect of the local communities.
Finally, the region that is denoted by Box D is the region where the stakeholders are key drivers of the change and can stop the management if they are not satisfied with the policies that are being undertaken. This region will comprise a majority of the stakeholders for Greenwich Leisure Limited. This region is known as Key players. It includes primary actors, creditors, suppliers, and labor unions. The creditors and suppliers are actively interested in the day-to-day working of the organisation. They have the power to influence the credit policies of the organization which can lead to low cash during the need for procurement of goods. They are also interested in the organization because they try to know about the working as their money needs to be repaid as soon as possible.
They take in active participation with respect to interest towards the organization to reduce the financial risks associated with it(Elsaid, et al. 2017). Similarly, labour unions have substantial interest in the company’s policies as they provide labour to the organisation. If they stop providing cheap labor to Greenwich Leisure Limited, it would lead the organisation to incur heavy costs if they try to go into the open market. The switching cost will become comparatively higher than the present. The feedback can be taken through changing any minor organisational policy which affects the parties.
b) Identification of stakeholders and propose the methods to meet their expectations
Stakeholders are the individuals who tend to show interest in some investments made in a project or an organization. Different stakeholders have different taste and interests in trade-offs where companies try to please them to invest in their projects (Luo et al. 2020).

Figure-01 Different Types Of Stakeholders.
(Source- Internet)
The different types of stakeholders are employees, customers, government, lenders, owners, society, suppliers and community are a few common types of stakeholders and see through the unique needs each one has. GLL finds difficulty to prioritize the stakeholders and their interests (Symeou and Georgiou, 2017). Identifying the interest and learning attributes of the stakeholders is the aim of any organization.
Customer: It's a debate in the market that business serves its customers. Customers are the main stakeholders of any business. They impact the quality of product, service and values. Greenwich leisure limited has its customers as the major stakeholders at the company where the customers are the stakeholders who donate funds for the leisure centers and the customers who take up the services and products of the GLL company (Attanasio et al. 2020). The customers always tend to take their businesses to the competitors in the market, to hold the potential customers the company should focus on innovating products and offer good value to their money where they will stay for a long time.
Employees: Employees have a direct link in the company where the employees earn an income in the firm to support themselves with other benefits provided by the company. They are the ones who develop and deliver services or products to the customers (Yuan and Ip, 2018). GLL benefits its employees with health and safety insurances at the company.
Government: The government is considered as an important stakeholder at GLL. The government fetches taxes from the company and the employers working at GLL. The government benefits from the overall profit of the company and the GDP that the company contributes.
Task 4: a) Critically evaluate the skills and behaviours needed by the CEO to lead this strategic change successfully within your chosen organisation
The critical aspects of effective leaders in a company is the potential to create change. This digital era causes changes at a higher speed, where the entire industry can change overnight.
The role of a CEO in GLL is influenced by the nature of the transformation, magnitude, Urgency, capabilities and the personal styles of the leader. The organisation which is not willing or unable to change is faced with a stern future (Nghia, 2017). They are responsible for every positive and negative action and decisions are taken by the members of an organization. They should always be proactive for the changes required with means of adding changes to the service lines, merger, implementing new softwares, approaches to their customers.They are also responsible for the decisions they are not aware of. Replacing CEOs is an extravagant proposition for any organization. The company should bring changes in their strategic plans with uncertainty and little observation. To create the change they should possess a constructive change management infrastructure. The skills required by a CEO at GLL are:
• The Potential to be innovative: Innovation is the key to any organization in the business. The main motive is to constantly innovate and deliver innovative features in the products and services provided by a company in the market. To build and show such innovative services and products in the market a CEO of GLL should be able to ideally anticipate the design and future of the strategies which will effectively bring change and profits to this organization in the long run (Bell, 2020).
• Risk Taker: The CEO should possess the ability to analyse the risk after doing an in-depth analysis of the profits and loss associated with the decisions. A CEO should have the potential to deal with any kinds of risk occurring in a GLL organization with regards to the clients, products, internal decisions, and services provided by the company (Sundström et al. 2021).
• Optimistic by nature: A CEO should be able to recognize opportunities in difficult situations and be optimistic in nature. They must have the potential to think out of the box for solutions and create strategies which can combat the threats occurring in the GLL organization. They should carry a positive attitude and inspire other members with the same attitude and encourage them to work hard in bad times.
• Ability to take measures: The CEO should take timely decisions and actions based on the changes in the working environment. They should be impulsive in taking any action and decision which should be done on a detailed analysis and evaluation (Harrison et al. 2018). They should take responsibility to execute their action in such a manner that they bring profit to the GLL organization.
• Communication and coordination: The CEO should be open-minded to the strategies or ideas suggested by the staff rather than concentrating on the strategies made by them alone. The CEO should have the skills to communicate with the staff and examine ideas and recommendations made by the team. The communication skills are based on their lexicon and the extraordinary way to communicate with the subordinates and team members of the GLL company.
Controllers Emotions: The CEO should have control over their emotions which doesn't mean they should be rigid in nature. They should never fail to praise success or identify the failures. The emotions should be controlled in such a way that the members of the firm should understand the meaning of the underlying emotion (Conte et al. 2017). The CEO of GLL company should be well behaved and should not show excess hyper activeness at petty things or overjoyed at tiny achievements.
Incorporation in Decision Making: The CEO must have the skills to engage all the other members in the decision making processes and encourage a culture where all employees work together as a team to achieve common shared objectives and goals. In GLLCompany the CEO should be an independent decision-maker and should make decisions in pressure periods and time constraints (Choudhury et al. 2019).
b) Smart Objective
The objective provides a foundation for the measures. They are time-based, actions that help a CEO to acquire any skills to implement the changes in the GLL organization. Keeping things sharp helps the CEO to focus on the important issues and requirements in a company. The CEO should have the skills to create a vision for the team members and identify the priorities of the GLL organization (Confetto et al. 2018). The priorities include employees, service, finance, products, customers, operations, quality and developments in the organization.
|
Specific |
Build efficiency and capacities to improve potential customer growth. |
|
Measurable |
Focus on past and future goals. Evaluate the work and performance of the organization. |
|
Achievable |
Ensure to maintain social responsibilities to do great businesses |
|
Realistic |
Maintaining awareness of competitive markets, opportunities, and expansions. |
|
Time scale |
4-5 months |
A great organization should have leaders who are efficient and are effective in leading changes in the organization. The skills are enhanced and the objectives are acquired by the smart CEO to successfully lead the firm.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Greenwich Leisure Limited has also known under the brand Better is a public servant that provides leisure services to the people and works as a non-profit social enterprise. In this assignment, we have clearly mentioned the mission of GLL and how a CEO must communicate it to employees and key stakeholders of the company. Evidence and outcomes of the research state that the CEO of GLL must implement the Democratic leadership style to create and embed the organisation's mission throughout its operations. According to the findings, the leading strategic change of GLL has been effective in its operational management. With the help of the Mendelow matrix, we have also identified the range of stakeholders for GLL and how can the CEO of GLL gather the feedback on the proposed new mission statement.
References
Al Khajeh, E.H., 2018. Impact of leadership styles on organizational performance.Journal of Human Resources Management Research, 2018, pp.1-10.
Attanasio, O., Blundell, R., Conti, G. and Mason, G., 2020. Inequality in socio-emotional skills: A cross-cohort comparison. Journal of Public Economics, 191, p.104171.
Bell, R., 2020. Developing entrepreneurial behaviours in the Chinese classroom through value creation pedagogy. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, pp.1-12.
Choudhury, P., Wang, D., Carlson, N.A. and Khanna, T., 2019. Machine learning approaches to facial and text analysis: Discovering CEO oral communication styles. Strategic Management Journal, 40(11), pp.1705-1732.
Confetto, M.G., Conte, F. and Covucci, C., 2018. Empirical evidence on CEO reputation: Perspectives, actions and influence. International Journal of Business and Management, 13(12), pp.215-226. Conte, F., Siano, A. and Vollero, A., 2017. CEO communication: engagement, longevity and founder centrality: an exploratory study in Italy. Corporate Communications: An International Journal.
Drescher, G., 2017. Delegation outcomes: perceptions of leaders and follower’s satisfaction. Journal of Managerial Psychology.
Duignan, M.B. and Pappalepore, I., 2019. The visitor (im) mobility, leisure consumption and mega-event impact: the territorialisation of Greenwich and small business exclusion at the London 2012 Olympics. Leisure Studies, 38(2), pp.160-174.
Dyczkowska, J. and Dyczkowski, T., 2018.Democratic or autocratic leadership style?Participative management and its links to rewarding strategies and job satisfaction in SMEs.Athens Journal of Business & Economics, 4(2), pp.193-218.
Elsaid, A., Salem, R. and Abdul-Kader, H., 2017. Research Article A Dynamic Stakeholder Classification and Prioritization Based on Hybrid Rough-fuzzy Method.
Freiwirth, J., Burns, M., Gifford, G., Hiland, M. and Beck, D., 2017. Voices of Board Chairs: A National Study on the Perspectives of Nonprofit Board Chairs-How They Prepare for and Perceive Their Role in Relation to the Board, Community, and CEO. The Journal of Nonprofit Education and Leadership, 7(4). GLL.(2021). About Us.Available at: https://www.gll.org/b2b [Accessed on: 3rd February 2021]
Gökdeniz, I., Kartal, C. and Kömürcü, K., 2017. Strategic assessment based on 7S McKinsey model for a business by using analytic network process (ANP).
Harrison, C., Burnard, K. and Paul, S., 2018. Entrepreneurial leadership in a developing economy: a skill-based analysis. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development.
Kaehr Serra, C. and Thiel, J., 2019. Professionalizing entrepreneurial firms: Managing the challenges and outcomes of founder?CEO succession. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 13(3), pp.379-409.
Kowo, S.A. and Akinbola, O.A., 2019.Strategic leadership and sustainability performance of small and medium enterprises.Ekonomicko-manazerskespektrum, 13(1), pp.38-50.
Krivtsov, A.I., 2019. Sustainable Development of Economic Entities: Key Objectives, Stages, and Stakeholder Interests
Laurisz, N., 2019. The Role of Stakeholders in Development of Social Economy Organizations in Poland: An Integrative Approach. Luo, Y., Yao, L., Zhou, L., Yuan, F. and Zhong, X., 2020. Factors influencing health behaviours during the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China: an extended information-motivation-behaviour skills model. Public Health, 185, pp.298-305. Nghia, T.L.H., 2017. What hinders teachers from translating their beliefs into teaching behaviors: The case of teaching generic skills in Vietnamese universities. Teaching and Teacher Education, 64, pp.105-114.
Nichols, G., Findlay-King, L. and Forbes, D., 2020. The Community Asset Transfer of Leisure Facilities in the UK: A Review and Research Agenda. VOLUNTAS: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations, 31(6), pp.1159-1172.
Odor, H.O., 2018.Organisational change and development. Paraschiv, D., Ni?u, M. and Savin, M., 2019, May. Change management within companies. Rajan, R. and Ganesan, R., 2017.A critical analysis of John P. Kotter's change management framework.
Razmi, J., Mehrvar, M. and Hassani, A., 2020.An Assessment Model of McKinsey 7S Model-Based Framework for Knowledge Management Maturity in Agility Promotion.
Rifaldi, R.B., Ramadhini, N. and Usman, O., 2019. Effect of Democratic Leadership Style, Work Environment, Cultural Organization, Motivation and Compensation to the Employees Performance. Work Environment, Cultural Organization, Motivation and Compensation to the Employees Performance (January 6, 2019). Shaqrah, A.A., 2018. Analyzing business intelligence systems based on 7S model of McKinsey.
Sundström, M., Lundberg, C. and Ziakas, V., 2021. Episodic Retail Settings: A Sustainable and Adaptive Strategy for City Centre Stores. Sustainability, 13(5), p.2482.
Symeou, M. and Georgiou, S., 2017. Externalizing and internalizing behaviours in adolescence, and the importance of parental behavioural and psychological control practices. Journal of adolescence, 60, pp.104-113. Yuan, S.N.V. and Ip, H.H.S., 2018. Using virtual reality to train emotional and social skills in children with autism spectrum disorder. London journal of primary care, 10(4), pp.110-112.
Zuraik, A. and Kelly, L., 2019. The role of CEO transformational leadership and innovation climate in exploration and exploitation.European Journal of Innovation Management.












