Economics Assignment: Impact of Covid-19 & World Response to Covid-19
Question
Task:
Prepare a report on economics assignment on the topic “Impact of COVID 19 and world response to COVID 19”.
Answer
Introduction
Coronavirus (COVID-19) is a contagious ailment, which is caused by respiratory syndrome. As per the research on economics assignment, the first case of Covid-19 was reported in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Ever since then, it has spread across the world, leading to an ongoing global pandemic. This virus's symptoms may differ from person to person but commonly includes fever, cough, breathlessness, fatigue, loss of taste and smell. The symptoms are visible after one to fourteen days of the revelation of the virus. Most people are infected with mild symptoms, while some develop respiratory failure due to swelling in the lungs. After recovery, the virus's effects include memory loss, muscle weaknesses, a problem in breathing, fatigue, and other cerebral issues. The ways to prevent this virus is maintaining physical distance from people, staying indoors, wearing a mask, using sanitizers, washing hands frequently, and quarantining. This report contains the impact and world response of Covid-19.
Impacts of Covid-19
The covid-19 pandemic has led to massive loss of lives across the world and introduces an unparalleled challenge to the food system, public health, and the professional world. The social and financial disturbance caused by this ongoing pandemic is disastrous.
Impact on the Economy
Nearly about ten million people are at the risk of falling into excessive poverty, while the numbers of undernourished people are rapidly increasing due to scarcity of food. The pandemic has affected the entire food systems as the buy and sell limitations, shutting down of borders, and incarceration assess the farmers' buying inputs for their agricultural activities. Thus, it disrupts the food system's supply and affects the international and domestic food chain in the market (Chudik et al., 2020). The economic growth of nearly all the countries was diminishing, but China was the only country to experience economic growth amidst the pandemic.
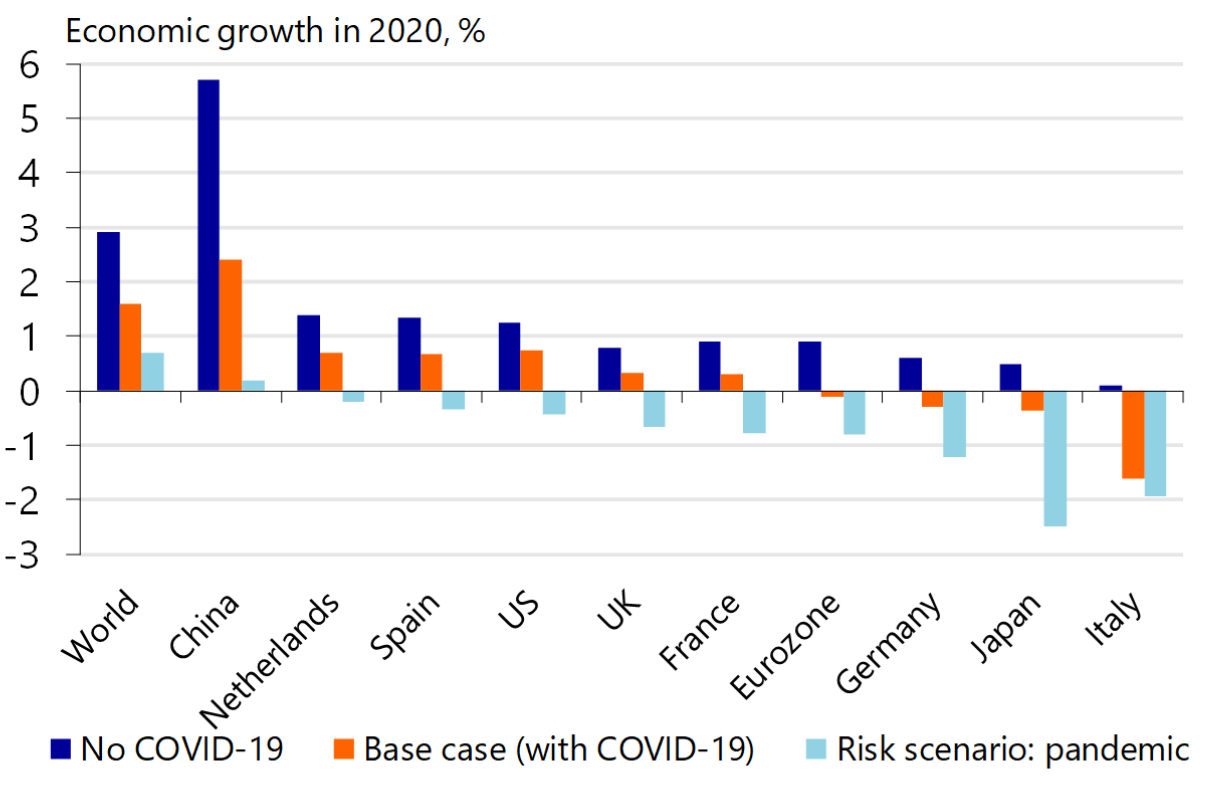
Figure 1: Bar graph showing economic growth
Source: (Chudik et al., 2020)
Impact on Employment
The pandemic has devastated jobs and placed millions of livelihoods in danger. The daily wage workers have been the worst affected as they lost their income source and failed to meet their daily life essentials. More than the virus itself, people started dying due to hunger and the unavailability of nutrition. The covid-19 pandemic has hit hard the small-scale farmers and native people. People below the poverty line were hardly having any access to health security, and ever since the pandemic has begun, it has worsened their health and daily lives (Ogata, 2020). With a lack of societal support and uneven earnings, people often continued working in precarious circumstances that possess' additional threat to their families' lives. In some cases, the income level reductions have forced some families to practice child labor, voracious mortgages, and possessions trade.
Impact on Mental Health
It is a well-known fact that pandemics have an impact on the mental health of people. Due to the outbreak, people are bound to stay indoors and not socialize with others, which have increased anxiety and depression among people. The people of young age and women with low sleep quality face a more significant threat of mental health issues. The feeling of hopelessness, panic behavior, and desperation often leads to committing suicide. An online survey conducted in May determined that the term "suicide" noticed a massive growth in the number of people searching it on Google (P. Joseph, 2020). The number of people committing suicide and self-harm have shown a rapid increase during the lockdown. It is an underrated issue as the government merely pays attention to it. The administrative gives the physical health, economy, and work-related problems of the people the utmost priority.
Impact on Public Health
The Covid-19 pandemic is far more than just a health disaster; it affects the economies and societies at its center. The impact of the disaster varies from country to country, but it increases inequalities and poverty worldwide. The global misery is continuously increasing without the urgent socio-economic reflexes (Brunier, 2020). Instant development responses in this pandemic must be carried out with a vision of the future. The United Nations is supporting 162 countries to develop the response of public health.
Australian legislations on Covid-19
The covid-19 has adversely affected all the nations across the world, imposing new challenges economically, mentally, and services availability. Therefore, different countries have introduced new ordinances to combat the virus and face its repercussions. For instance, the Australian government has summoned numerous new and subsisting laws, orders, and governmental regulations. The Australian government has passed particular laws as a financial response to the crisis of coronavirus. The government enacted Stimulus Package Acts, which trades with business, employment, and credit and documents flow. The act's critical services include supporting individuals and families through income support, an extension of the period of bankrupt notices, earmarking of funds to affected industries and regions, and provisional methods to support agitated firms.
In the context of the third financial response to the crisis, the Australian government introduced the Jobkeeper Payment Scheme that allows the employees who are affected by the scarcity to obtain allowance from the authority to continue payment of their personnel. Some specific modifications like Aged Care Legislation Amendment 2020 were promulgated to encourage the senior citizens and respond to their monetary problems. The Governor-General of Australia announced a biosecurity emergency under the Biosecurity Act 2015 that provides different methods and operations to stop the spread of diseases in their country (Rai, 2020).
One of Australia's contemporary eminent legal is COVID-19 Emergency Response Act, 2020 that compensates several other acts and laws to launch provisional commands to handle the ongoing pandemic. Some of the main modifications include an extension of temporary orders of household hostility for six months, allowing the employers to give fewer than sixty days of notice before taking extensive service leave, and permitting the director-general to adopt essential steps to stop the spread of the virus.
Finally, the government authorized COVID-19 Emergency Response Legislation Amendment Act, 2020. This act was passed to stimulate instant effect to operational responses and Commonwealth agreements to permit the government to accommodate supplementary methods to tackle the disaster.
Global legislations on Covid-19
Spain has authorized many orders to present different methods of dealing with the covid-19 crisis. The orders specify the methods to deal with the economy, health, and small and medium-sized corporations. In the pandemic's primary stage, the Spanish government has nationalized all the private hospitals and health care centers to make them accessible for all the country's citizens. The Canadian government has authorized three significant acts to reduce the effects of a pandemic on its residents. The three acts comprised the Income Tax Act, COVID-19 Emergency Response Act, and the Deposit Insurance Corporation Act. Canada Emergency Student Benefit Act was legislated to sanction payment to students whose income source was pandemic.
On the contrary, Singapore has authorized the COVID-19 Temporary Measures Act, 2020 that offers momentary assistance to the individuals and executives who are unable to implement liabilities of agreements and interrupt the court's trials (Hathaway & Phillips-Robins, 2020). The act minimizes the spread of coronavirus by limiting the citizens' movements with an exemption of emergency activities.
Coronavirus outbreak is an extraordinary time globally, so essential methods and actions must be implemented to stop the spread. The public can believe the legislation only if it is transparent and responsible. The introduction of necessary laws and regulations will play a vital role in reducing the impact of the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic in the world.
World Response to Covid 19
Countries are taking extraordinary measures to fight against the spread of the Corona Virus disease while revolutionizing its destructive effect on the world's labor and economy.
Stimulating the economy
Countries are changing the fiscal policy and adjusting the monetary policy by lending and supporting financially to the particular sectors like the agricultural and public health sectors. The government of the world backs up small enterprises to help the employees and the industry. The retention measures are implemented in employment to engage the employees during the covid crisis. The job retention proposal has put off a heave in the unemployment and lessened the economic hardship by sustaining the employees' income on lesser work time. The governments are providing tax obligations and other financial reliefs to the heavily affected companies by the pandemic. The reserve is presently accessible to all the state and the union level industries. The Covid 19 pandemic and its social and economic effects are cruel for the staff and labor in the unstable economy—the heavily impacted sectors' lockdown implications more than a billion informal employees and workers. Therefore, countries worldwide are proposing social protection for all the informal workers, including women in particular, by contributing social aid schemes. As lockdown has withdrawn in many countries, the industries have reopened but with safety and health measures (International Labour Organization, 2020). The health promotion of the workplace has integrated to improve the workers' working life and health. Implementing the work environment schemes has benefitted the workers by reducing heath pressures and contributing to enhanced industrial health practice. Many companies have arranged for employees to work from home for safety concerns. However, many companies are yet to adapt and implement work from home arrangements (International Labour Organization, 2020).

Figure 2: Measures of International Labour Organization
Source: (International Labour Organization, 2020)
Measures of World Health Organization
On January 3, 2020, the Chinese executives passed information to WHO on the "unidentified pneumonia virus" recognized in Wuhan. On the 9thof January 2020, WHO confirmed that a novel coronavirus causes the unidentified pneumonia virus. With the spread of the virus worldwide, WHO published an instruction manual to handle severe acute respiratory infection in many health care organizations (WHO, 2020). As the world's cases crossed 1 million in less than a month, the World Health Organization updated a suggestion to wear masks and sanitizers mandatorily to fight against the infection's spread. The new agreement was signed between WHO and UN refugee Agency on May 21 to support and protect 70 million deposed people from Covid 19. Countries worldwide undertook an initiative to provide tests, medicines, vaccines, and treatment freely accessible to all. More than 90 countries were incomplete lockdown to fight against the covid-19 diseases' spread. Social gatherings, religious practices, events, educational and recreational sectors were all stopped and avoided (WHO, 2020). The World Health Organization also recommended the states create and engage in clinical trials of the vaccines to stop the infection in a human body. It also published a regulation on home care and recovery of the patients with assumed covid-19. To reinforce Covid-19 and prepare the world for upcoming unpredicted pandemics and emergencies, the Global Preparedness Monitoring Board (GPMB) prepared a report to encourage dependable leadership to build strong health security, to invest sustainably, and to create global governance. WHO has listed 52 candidate vaccines in clinical evaluation and 162 in preclinical evaluation (WHO, 2020).

Figure 3: WHO Health Measures
Source: (WHO, 2020)
Safety Measures taken by Nations
Physical Distancing- One of the main approaches used universally to fight against the spread of Covid 19 disease is maintaining physical distancing of 1-2 meters from people. The worldwide lockdown has resulted in canceling any events and gatherings, closing down the business and companies to let everyone stay home to save lives.
Contact Tracing- This is a targeted strategy adopted by the nations to trace the cases of Covid 19 in communities by tracking down people who have had physical contact with a contaminated person. The tracking down method was used in the 1970s to eradicate smallpox and exterminate Ebola in 2014 by tracking down and immunizing the people. Some countries have developed smartphone apps to aware people who have been vulnerable to the disease.
Covid-19 Testing- Public testing of the Covid-19 disease has been adapted almost by every country to increase the correct picture of the extent of transmission of the virus in the regions. It is also done to discover and determine the people infected with Covid and take corrective measures to prevent and stop the increase of infection to others.
Personal Protective Equipment Supply- World health organization had cautioned the countries that lack PPE such as masks, gowns, sanitizers, and gloves might pose a risk to health workers' safety around the globe. The states have increased in the manufacture of the equipment and have also focused on advancing the numbers of beds and ventilators for the patients of Covid 19.
Clear Communication- Many nations have transmitted clear messages to the public about the Covid 19 virus's health hazards. Transmitting messages around simple methods like mask-wearing, hand washing, and physical distancing has also made the citizens aware of the virus and its risks (Gavi Organisation, 2020).
Restriction on International Travel- To stop the spread of Covid 19, more than 150 countries have banned international passenger flights. This measure has outlined the primary considerations for national health securities when executing the regular return to global travel operations. Many nations have uplifted the ban on international flights, but operations have been reduced to only once a month for emergency purposes (Gavi Organisation, 2020).
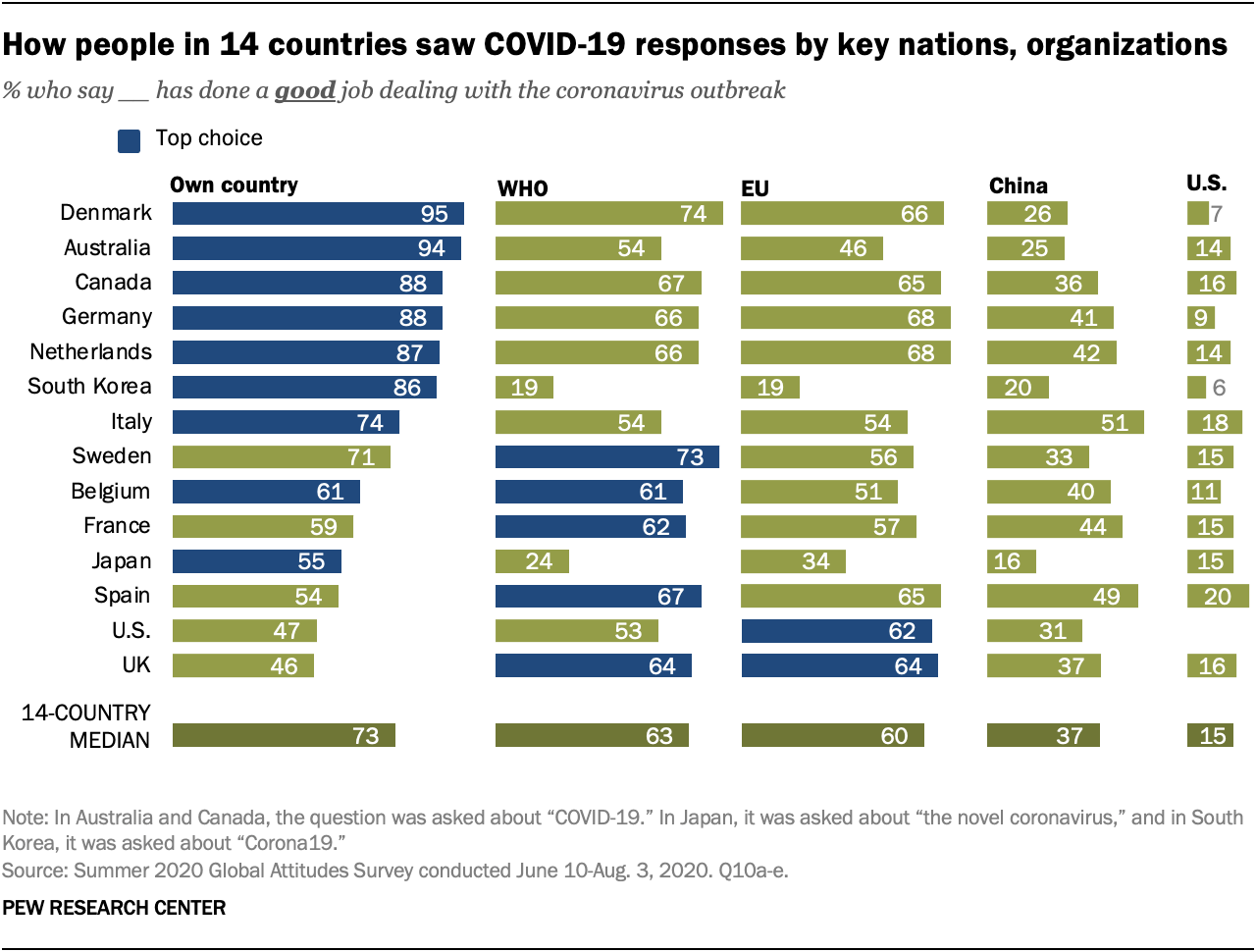
Figure 4: Country wise Response
Source: (Gavi Organisation, 2020)
Vaccines- World Health Organization has been working collaboratively with different scientists and health organizations to create vaccines to cure the virus. The World Health Organization has listed 52 candidate vaccines in clinical evaluation and 162 in preclinical evaluation. At present, there is no proper medicine to cure the virus; therefore, a vaccine is needed to fight the infection efficaciously.
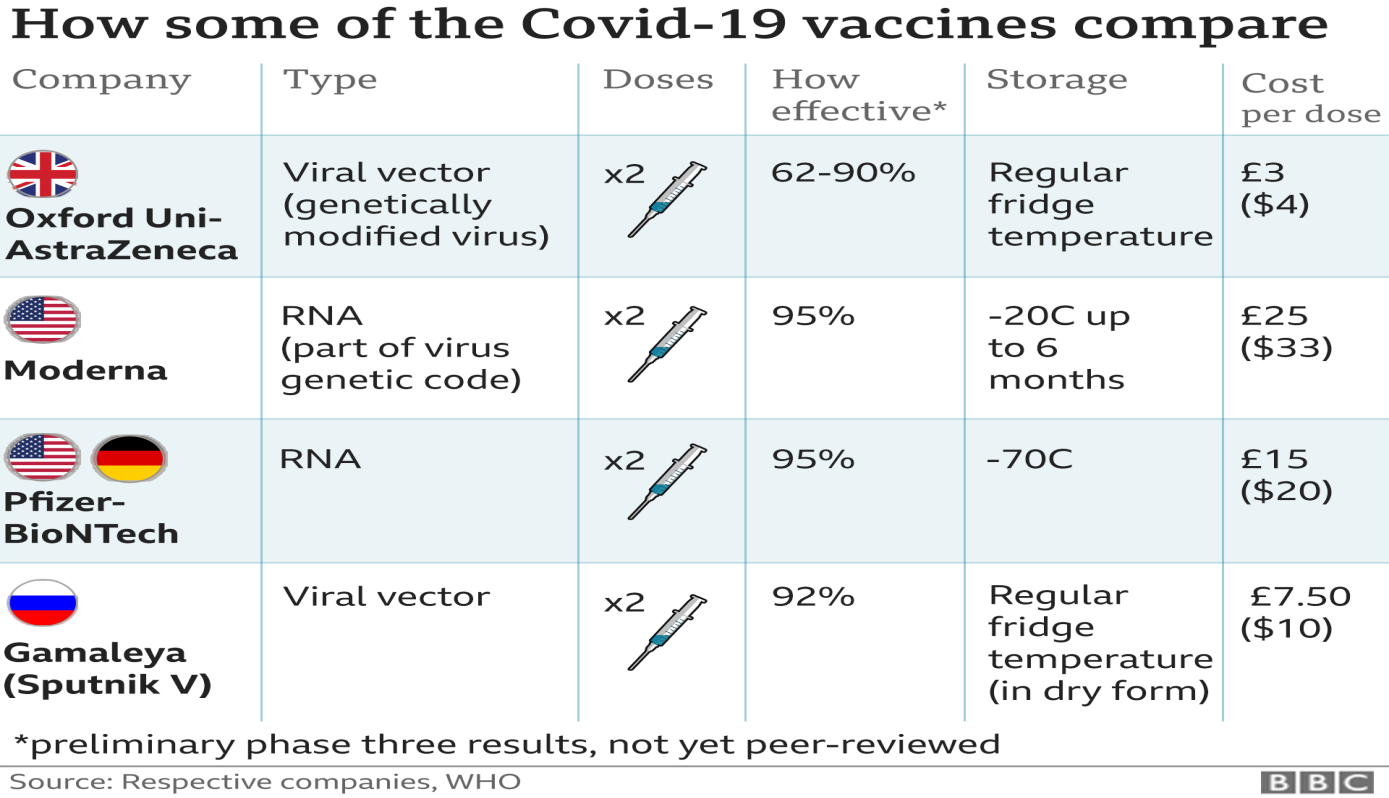
Figure 5: Vaccines of different countries
Source: (WHO, 2020)
Nevertheless, more than 170 countries have engaged in making a Covid 19 vaccine. Pfizer/ BioNtech vaccine has been trialed and has shown 95% effective results. The vaccines are given in two doses, three weeks apart. The vaccine is required to store at a temperature of -70 degrees Celsius. On December 2, the United Kingdom became the first nation to endorse the BioNTech vaccine. Moderna Vaccine uses the same method as the Pfizer vaccine. It has also shown promising results, and 30,000 have engaged in the trial. This vaccine is more comfortable to store as it can be stored at -20 degrees Celsius for up to half a year. The immunization is to be done two times, four weeks apart. COVAX aims to provide the world with effective vaccines across the globe (Gavi Organisation, 2020).
Conclusion
The assessment done in this economics assignment can be concluded with the affirmation that even though the pandemic has drastically impacted human lives with infections and death, the nations are working together to bring stability in the economic environment and the health environment. Many measures and strategies have taken to prevent the spread of the virus and tackle emergency concerns. The World Health Organization is dealing with the virus responsibly by developing vaccines to fight against the severe acute respiratory system. The virus may have hit the country's most exposed regions, but the governments are trying to assist by providing aid and support. The World Health Organization has played a significant role in tackling the Covid 19 pandemic ever since it was first identified in Wuhan. With its partners, the WHO sets up the Covid-19 solidarity response fund to give patients enough care and essential supplies to speed up the research and development of an effective vaccine. The WHO has also focused on working with economically backward countries to bring stability and harmony in the world.
References
?Brunier, A. (2020, June 1). COVID-19 significantly impacts health services for non-communicable diseases. Www.Who.Int. https://www.who.int/news/item/01-06-2020-covid-19-significantly-impacts-health-services-for-noncommunicable-diseases
Chudik, A., Mohaddes, K., Pesaran, M. H., Raissi, M., & Rebucci, A. (2020, October 19). Economic consequences of Covid-19: A counterfactual multi-country analysis. VoxEU.org. https://voxeu.org/article/economic-consequences-covid-19-multi-country-analysis
Gavi Organisation. (2020, June 22). Seven things countries have done right in the fight against COVID-19. Www.Gavi.org. https://www.gavi.org/vaccineswork/seven-things-countries-have-done-right-fight-against-covid-19
?Hathaway, O., & Phillips-Robins, A. (2020, December 8). COVID-19 and International Law Series: WHO’s Pandemic Response and the International Health Regulations. economics assignment Just Security. https://www.justsecurity.org/73753/covid-19-and-international-law-series-whos-pandemic-response-and-the-international-health-regulations/
International Labour Organization. (2020, June 20). Country policy responses (COVID-19 and the world of work). Www.Ilo.org. https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/coronavirus/regional-country/country-responses/lang--en/index.html
Ogata, E. (2020, May 27). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on employment. International Law Office.https://www.internationallawoffice.com/Newsletters/Employment-Immigration/Japan/Nagashima-Ohno-Tsunematsu/Impact-of-COVID-19-pandemic-on-employment
Rai, D. (2020, June 15). COVID-19 Legislations in Other Countries and India. leaders. https://blog.ipleaders.in/covid-19-legislations-in-other-countries-and-in-india-do-we-need-a-new-covid-19-specific-legislation/
P. Joseph, J. (2020, July 24). COVID-19 and Mental Health: Suicidal Tendencies and Self-Harm on the Rise. The Wire. https://thewire.in/health/covid-19-mental-health-suicidal-tendencies-self-harm-rise
WHO. (2020, September 9). Listings of WHO’s response to COVID-19. Www.Who.Int. https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline












