Economics Assignment: Managing Recovery from COVID-19
Question
Task:
Evidence on Problem
Literature and Data could be substituted one for another. A chart created by yourselves could be substituted for literature and vice-versa. One literature could be approximated to ½ page review text or 1 chart. A figure could also be substituted by a diagram.
In the evidence section, please consider the following:
• Depth/Understanding
• Quality/Clarity of Analysis
• Quality of Sources/ Frameworks (Some sources can be reports, trade journals.Does not always have to quality academic journals).
• Citation/Referencing (any style)
Task 4: Evidence on Problem – Literature
Remember you are a team. The evidence will be in both literature as well as data.
You will need to augment the literature search for this, even if you are working on the same thing. Divide and conquer. At least 4 journal articles are expected for literature review pertaining problem FROM EACH MEMBER. About ½ page per article reviewed is sufficient. The key literature or discussion points should be non-overlapping between members (if same shared article, need to emphasize different aspects).
The individual students may choose between emphasising on problem space literature or tools space literature. However, as a whole team, at least half your team are expected to choose the problem space (there is a preference for problem space literature review). The rest have the freedom to choose either the problem or tool based literature search.
(a) Problem Related Literature
The problem related literature search has been included to provide an opportunity for each of you to immerse yourself in the literature relating to the problem, so that you can identify and choose the right problem.
Some Questions to consider:
• Find at least four high-quality publications (e.g. Journal articles, NGO reports, articles of investigative journalism) that investigate aspects of the problem. For each publication, briefly describe:
• How does this publication add to your understanding of the problem? Does it help explain the causes? Does it give evidence of the effects? Explain.
• What methods does it use? What data was gathered, how was it gathered, and how was it analysed?
• How reliable is it? Is there any limitations or concerns, or something about the methods that raises any doubt about their findings?
• Provide full details (i.e., UTS Harvard references) for each publication.
Your research must explain the causes and provide evidence of the effects. Do not focus exclusively on one or the other. [Optional: you may replace one of the publications above with your own research by collecting your own data through observation, surveys or interviews, but you need to consult with teaching staff before collecting primary data] In the absence of literature, literature can be substituted by data (1 literature = 1 data item such as charts with descriptions= 1 representation diagram). (b) Tools Application Related Literature (Optional and to substitute shortage of literature in problem space)
The purpose of including Tools Application into this problem is to give students some time to research the tools. Find out in literature how well (or badly) the key tools have been applied to solve problems.
The problem area that you have chosen and the tools discussion do not have to exactly match (while it would flow better for your own write up, if they do). You can choose any 2 of the tools or techniques used in the course.
• Design Thinking
• Systems Thinking
• Agile Project Delivery (e.g. Scrum/ Kanban)
• Participatory Modelling
• Online Tools for Collaboration. E.g. MURAL, Miro etc
Task 5: Evidence on Problem – Data
Search for information quantitative information about the problem.
The data can be in visualization, or tabular information, but you need to provide sources and supportive argument, especially when it is borrowed. It is OK to borrow charts or graphs with acknowledgement. Interpretation of the visualization is expected especially when borrowed.
At least ONE item to be contributed by EACH MEMBER. The item can be data, statistics etc. If it required processing data, a visualization can be shared among group, but you need to show that there was extra work required.If you are working with raw data, as a group, please create 2+ visualizations.
In the absence of data, data can be substituted by literature (1 literature = 1 data item such as charts with descriptions) or with a representation diagram.
If using information from elsewhere (including data), please provide in-text references (citation) in this section clearly to show where you found the information.
Task 7: Co-design criteria and template for evaluation of solutions as well as projects as a whole
Please note that this is criteria for evaluating and picking solutions. This is not exactly improvement criteria that show up earlier, but there can be common elements between them in some cases. You will only design solutions in the next assignment, but you can create the criteria now. You could also collaboratively extract the weights for each criteria. (You can give weights to criteria collaboratively). Then, you can use a scoring approach when evaluating solutions. However, it is important you justify this.
Grading:
There is no restriction as to how many criteria are necessary. In general, the group should be able to come up with at least 2-3 improvement criteria, assumptions, constraints. The about 4-6 evaluation criteria could be useful. Again, these differ from problem to problem.
Where in shortage, you can also substitute with evidence of how you collaborated to produce this, and how collaboration enhanced the quality of criteria etc.
Answer
Part II
Economics Assignment Task 4: Evidence on Problem – Literature
(a) Problem Related Literature
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., Agha, M. and Agha, R. 2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. International journal of surgery (London, England), 78, 185.DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018
Article by Nicola et al (2020) depictslessons that are learned from Covid-19 which can assist in preparation for economic transformation for climatic change.Covid-19 has become a global phenomenon spreading global suffering which in turn has been spreading economic suffering as well. This virus has been seen in spreading contagious economic suffering similar to medical suffering. OECD's growth forecast along with SAARC countries have been tremendously impacted. Hence it needs to be evaluated the far-stretching and far-reaching damages associated with the virus. The article assists in understanding the recovery phase which will overlap with global efforts for dealing with crises in tourism post-COVID-19 scenarios. This article suggests economic models that might assist in dealing with challenges facing the tourism industry. The article assists in explaining the factors which have impacted the impending economic crisis post the period of Covid-19. The various factors associated with Covid-19 such as self-isolation, social distancing restrictions, and travel restrictions have led to a reduction in the workforce which has brought about recession and economic crisis. This article primarily outlines the socio-economic effects of Covid-19 on the entire world economy. The article provides varied evidence associated with such socio-economic impacts across varied sectors in the world economy. The article makes use of qualitative data assessment of the varied factors and then analyses the same by qualitative reviews. The data in this article have mostly been gathered from sources secondary in nature. The study is highly reliable with a high impact factor and a high citation score of the same. The study has been published in Elsevier publication and also available in NCBI literature. There have been no limitations that were discussed in this paper or concerns. Neither there was any doubt raised regarding the methods which were used in the study.
Prideaux, B., Thompson, M., &Pabel, A., 2020. Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies, pp.1-12.https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2020.1762117
Article by Prideaux et al, (2020) analyses and points out the economics prevalent during the time of Covid-19. The article clearly points out the numerous economic challenges faced during the Covid-19 times as regards the time as being extraordinary. The article points out the impact of Covid-19 on international travel at the starting of 2020. The article examines the effect of the pandemic and states that immense time will be needed for recovering the economy to its pre-pandemic stage. The article mainly examines the impact of the pandemic on the tourism industry. The article hence provides an understanding of the problem through an exploration of the various underlying factors associated with the pandemic situation. The article builds upon existing knowledge and also adds relevant discussion to understand the impact of the pandemic on the economy in general and tourism industry specifically. This article also examines relevant strategies that can allow overcoming the current situation in the current global economic crisis. The article also deeply examines the relevant causes that have led to the occurrence of the economic problem. It does provide evidence to the problem by highlighting some data and information from sources secondary in nature. Hence rightly point out some of the evidence of the effects that are being caused by the virus. Through qualitative evaluation of the research, it provides evidence of the several impacts that are being caused by the virus. It undertakes an appropriate evaluation of the existing state of knowledge it provides details of evidence related to the study. The research article makes use of qualitative knowledge and literature review for arriving at the understanding related to the topic. The data was collected mainly by analyzing the latest peer-reviewed literature on the topic from well-known journal articles. It was analyzed using a literature analysis methodology. With the qualitative evaluation of literature sources, the strategies as well as outcomes related to the study. The literature analysis has undertaken methods of qualitative research to arrive at the findings of the study. The study is highly reliable in nature as it has a high impact factor as well as citation score and has been published by world-renowned journal Taylor & Francis. This journal publishes works of scientific relevance and application. There are no limitations or concerns that have been encompassed into the study, though there might be raised questions regarding the only qualitative data collection and analysis of the study. Accommodation of quantitative research techniques might have been important to undertake the study.
(b) Tools Application Related Literature
Tools can provide relevant insights into the examination of a problem and applying them to resolve problems. In the current tools related literature design thinking tool and systems thinking tool has been analyzed.
Design Thinking
Elsbach, K.D., &Stigliani, I., 2018. Design thinking and organizational culture: A review and framework for future research. Journal of Management, 44(6), pp.2274-2306.https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206317744252
The scope of this article evaluates the scope of design thinking for solving complex problems. It explores the use of tools that are traditionally used in design thinking for designing commercial products, environments, and processes. It also analyses the impact of design thinking within organizational-level constructs. The article assists in the understanding of design thinking and also provides evidence of the effects through relevant examples. It makes use of theoretical analysis and literature evaluation. Data in the article have been gathered by making use of prominent and relevant sources from peer-reviewed articles. The article has a high citation score along with an impact factor and has been published by Sage journals, which reflects its reliability. There have been no concerns or limitations regarding the article or methods used or findings of the study.
Systems thinking
Williams, A., Kennedy, S., Philipp, F., & Whiteman, G., 2017. Systems thinking: A review of sustainability management research. Journal of Cleaner Production, 148, pp.866-881.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.002
The scope of this article makes use of scholars from a wide range of disciplines as well as perspectives to understand the perspective of systems thinking. By undertaking case-based approach systems thinking on a management sustainability topic has been evaluated. The article adds to the understanding of systems thinking in revealing their capability to solve management related problems. The article is highly reliable and of scientific relevance. It has a high citation score and impact factor and is published by Science Direct which reveals the reliability factor of the article. It makes use of qualitative data and it has been gathered by way of literary analysis. It has been analyzed by way of the qualitative review process. It has undertaken literature evidence in recent times to reveal the application of the study.
Task 5: Evidence on Problem – Data
In order to search in-depth regarding the problem, it is crucial that relevant quantitative information is searched regarding the topic. Interpreting the visualization of the data is relevant and with four visualizations undertaken for understanding the topic in depth.
The first figure visualization reveals the impact of Covid-19 on the Australian economy in April with demand being hit badly. This figure undertakes the PMI data which reveals business activity across the private sector in Australia with lockdown measures being implemented, affecting the demand for their services. Further such lockdown measures badly impacted the workforce employees across these businesses, which were reduced in a sharp manner. The cost of factory input was seen to increase in a sharp manner, leading to shortages arising in the supply and weakening of the currency. This led to the entire business activity slumping. Thus the lockdown restrictions brought about tremendous dampening of economic as well as business activities.
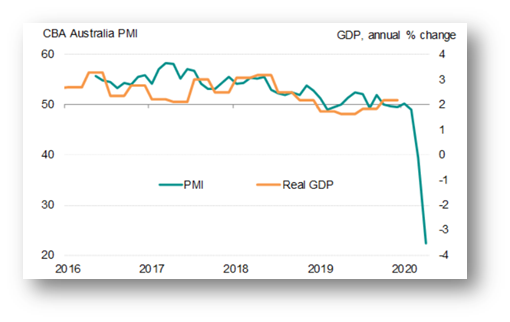
Figure 1: Lockdown impacting businesses in Australia
Source: (Aw, 2020a)
The data as shown above reveals The Commonwealth Bank Australia Flash PMI where the manufacturing, as well as service economy, dropping from 39.4 to 22.4. Such a steep slide reveals the deepening of economic downturns in the second quarter with rising risks anticipating the economy of Australia will contract by 6.6% annually in the second quarter itself. The figure given below analyses the varied measures undertaken by the government to prevent the steep downturn of the Australian economy.The figure below depicts the downturn in Real GDP compared against the PMI. With the dropping of PMI, there has been a considerable impact on increasing the likelihood of an increase in recession for containing the spread of Covid-19.
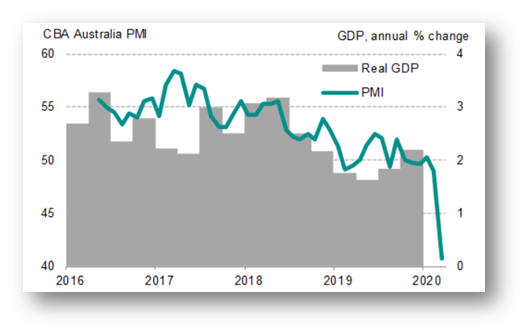
Figure 2: Measures to halt the spread of COVID-19 dampens private sector business activity
Source: (Aw, 2020b)
As the Real GDP is seen to contract in the second quarter of 2020, not only jobs were hit, the virus outbreak had hit demand. Sales were affected in a worse manner with weakening capacity in the private sector in spite of job shielding.
The data depicted below is a report by McKinsey & Company depicting the curse of Covid-19 on the economy. The report along with the data explores ways Australian consumers as well as their businesses are faced with the triple condition. These conditions include the threat from increasing public health, rapid and deep financial pressures being experienced, and regulated restrictions on movement as well as everyday freedom. Thus the figure reflects the deep emotional situation arising from Covid-19 with its consumers being unsure regarding the recovery of the economy.
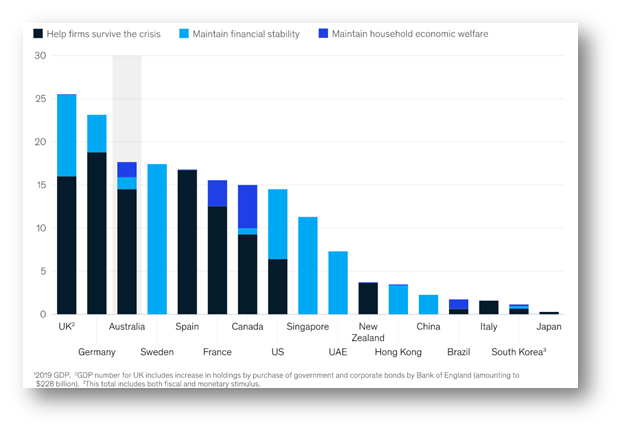
Figure 3: Economic support response to COVID-19 by country
Source: (Child et al, 2020)
Though Australia (in the above data visualization) is seen to outpace other countries in the world except for Germany and the UK with the GDP of the country showing support towards the economy.The figure is a reflection of Australia's combined action of the government with consumer sentiments in battling with the Covid-19 condition prevalent in the economy. The figure depicted below shows Covid-19 transforming from being a health issue to becoming an economic issue. The figure found in a report published by PWC, Australia reveals the impact of Covid-19 and recovery that the economy will look at the post-COVID-19 world.
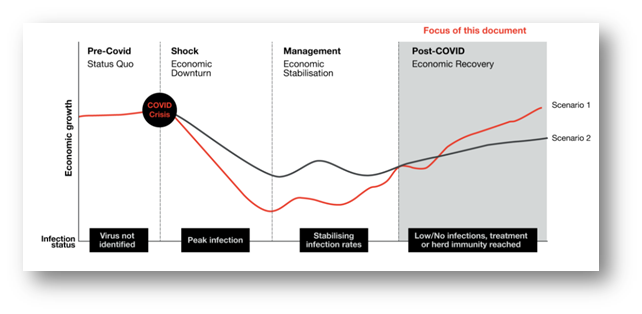
Figure 4: The four phases of the Covid-19 pandemic
Source: (Pwc, 2020)
The figure clearly identifies and groups recovery into a four-staged model. As depicted by quantitative data collected by the author, it can be ascertained that Australia is expected to recover faster. There have been identified nine major forces that will assist in changing the Australian economy in the near future. Such forces include greater involvement of the government, debt and capital inflows, consumption pattern in the country, acceleration in digitalization and reliance on data, productivity, flexibility and distributed working, resilience on securing supply chains, consolidation of industries, tax reforms and increased migration in the country.
Part III
Task 7: Co-design criteria and template for evaluation of solutions as well as projects as a whole
Some of the criteria for evaluation and picking solutions as found from the literature as well as data visualization presented include adopting factors for recovery appropriately. The criteria for resolving and arriving at the solution will be ascertained factors for recovery, then assign factors of success by ascertaining scores to them. Scores will be assigned from 1 to 10. Factors will include government, debt and capital inflows, consumption patterns in the country, acceleration in digitalization and reliance on data, productivity, flexibility and distributed working, resilience on securing supply chains, consolidation of industries, tax reforms, and increased migration in the country factors in the solution. In case the scores add up to greater than 5 then it will be considered as a probable solution. The template shown below will assist in ascertaining of scores.
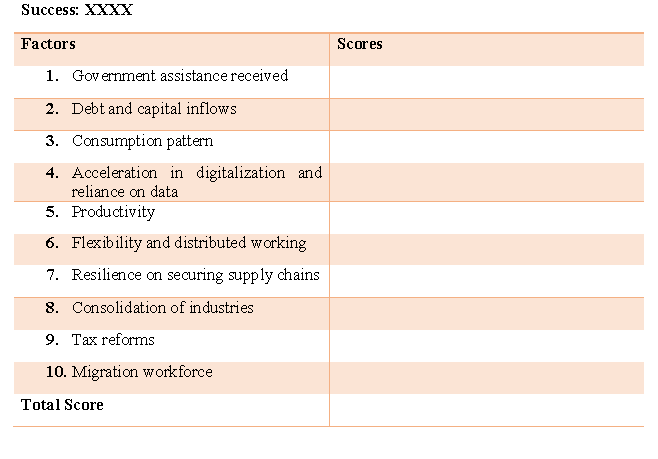
Reference
Aw, B., 2020a. Australian economy slumps in April as COVID-19 lockdown hits demand. IHS Markit. Retrieved from [https://ihsmarkit.com/research-analysis/australian-economy-slumps-in-april-as-covid19-lockdown-hits-demand-Apr2020.html]
Aw, B., 2020b. Flash PMI points to a steep downturn in Australian economy as COVID-19 hits. IHS Markit.Retrieved from [https://ihsmarkit.com/research-analysis/flash-pmi-points-to-steep-downturn-in-australian-economy-as-covid19-hits-Mar20.html]
Baldwin, R. & Mauro, B.W.D., 2020.Economics in the Time of COVID-19. Retrieved from [http://dln.jaipuria.ac.in:8080/jspui/bitstream/123456789/2757/1/Economics%20in%20the%20Time%20of%20COVID-19.pdf] Child, J., Smith, T.R., &Tesvic, J., 2020. The curse of ‘The Lucky Country’: In search of economic antidotes to COVID-19.Economics assignment McKinsey & Company. Retrieved from [https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/asia-pacific/the-curse-of-the-lucky-country-in-search-of-economic-antidotes-to-covid-19#] Elsbach, K.D. &Stigliani, I., 2018. Design thinking and organizational culture: A review and framework for future research. Journal of Management, 44(6), pp.2274-2306.https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206317744252
Nicola, M., Alsafi, Z., Sohrabi, C., Kerwan, A., Al-Jabir, A., Iosifidis, C., Agha, M. and Agha, R. 2020). The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19): A review. International journal of surgery (London, England), 78, 185.DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.018 Prideaux, B., Thompson, M. &Pabel, A., 2020. Lessons from COVID-19 can prepare global tourism for the economic transformation needed to combat climate change. Tourism Geographies, pp.1-12.https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2020.1762117
PWC, 2020. COVID-19: from health issue to economic crisis. PWC Australia. Retrieved from [https://www.pwc.com.au/important-problems/australia-rebooted-resetting-economy-after-covid-19/economic-recovery-factors-forces.html]
Williams, A., Kennedy, S., Philipp, F. & Whiteman, G., 2017. Systems thinking: A review of sustainability management research. Journal of Cleaner Production, 148, pp.866-881.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.002












