Team communication assignment: An Annotated Bibliography
Question
Task:
Finance Assignment Case Scenario:
Marina Costas has been referred to you by a mutual friend as she needs some assistance to sort out her investments and superannuation accounts. During your initial meeting, Marina provides you with the following information about her current personal situation and financial position.
Marina turned 47 years old in June 2020. She separated from her husband of 13 years in 2016 with their divorce and property settlement being finalised in 2017. Marina is enjoying her new “single life” and has no family to support financially. She is also not looking for a serious relationship at this point in her life and wants to set things up to ensure she is financial independent. Although COVID has caused some issues with how she works, Marina’s employment is secure and she currently earns a good salary of $105,000 plus employer superannuation guarantee contributions working as a marketing manager.
She owns and lives in a townhouse in Mount Druitt, which was bought when she separated from her husband. She purchased this property in 2016 for $290,000. Marina believes the property is worth approximately $460,000 today as one of the neighbours sold their unit in January for that price. There is currently no mortgage on this property and Marina takes great comfort knowing that in the worst-case scenario she owns her own home and will have a place to live. Marina has her personal contents insured with GIO, with cover in place for $55,000. The building is insured through the strata.
Before he died 2 years ago, Marina’s father gave her his boat, which he said “was a great investment”. The last time Marina got the boat valued, she was told it was worth somewhere between $35,000 and $38,000. Although she rarely uses the boat she keeps it in memory of her late father who took her fishing often as a child. It costs her $250 a month in mooring fees and $3000 annually for maintenance.
Marina is quite concerned about debt although she has a credit card, (limit $20,000), which she uses to pay all of her living expenses to take advantage of the frequent flyer points. She has an automatic debit set up to ensure this is paid off each month before having to pay any interest.
Marina’s car is an 8 year old Toyota Corolla, which is insured comprehensively for $8,000. Marina would like to buy herself a new car and thinks there should be some bargains due to the current economic conditions. While she is not yet sure what sort of car she will buy, she does think she will need to spend about $40,000 in total. One of the main reasons that Marina is seeking advice from you is that her last surviving family member, her sister, recently passed away and as Marina was the sole beneficiary she will inherit substantial funds from her sister’s estate. Marina expects to be receiving $430,000 after all the estate expenses are accounted for and have been told the funds will be available in October or November 2021. Marina is not sure what to do with these funds when she gets them. She has been considering an investment property but is not sure if that is an appropriate investment option as she has read recently that property prices have been falling in Sydney.
Marina keeps about $10,000 in her every day bank account so there is cash available if needed, as well as holding a further $15,000 in a 3 month term deposit with the Commonwealth Bank that she just lets rollover for another term each time it matures. The interest is paid to her normal bank account each maturity and the current term deposit has an interest rate of 0.65%pa.
Since paying off the mortgage, Marina has used any spare funds from the divorce settlement and savings to build a share portfolio. Marina admits she knows very little about shares and has really only bought shares in companies she knows. She is adamant about avoiding shares in any business involved in gambling. The one piece of advice she did follow was provided by a workmate who told her to set up a CommSec account and buy ten (10) different shares to make sure she would have a diversified portfolio. Marina’s portfolio currently includes the following:
- 49 BHP Group (BHP)
- 320 Commonwealth Bank (CBA)
- 600 Qantas (QAN)
- 560 AMP Ltd (AMP)
- 90 QBE Insurance (QBE)
- 40 Suncorp Group (SUN)
- 600 Telstra (TLS)
- 400 Macquarie Group (MQG)
- 490 Woolworths (WOW)
- 50 ANZ Bank (ANZ)
Last year Marina read about a new investment and although not really understanding it decided to “have a go” and invested $10,000. She has received a holding statement which shows she has 8,000 units in the Pengana Private Equity Trust. It says this investment is listed on the ASX with a stock code of PE1. She has not really had time to see how it has performed and is not really sure if it is a share or some other form of investment.
Marina has not been a big believer in superannuation, mainly as she does not really understand it, and just lets things continue as they have for some time. She has two superannuation accounts – one her employer pays into and the other one that just “sits there”. She would be happy to look at doing something with super if it is worthwhile and would be happy to discuss any suggestion you might have. She would like to better understand the tax benefits that she has heard superannuation has.
Her current employer pays into the Australian Super Balanced option. When Marina looked at the account online to prepare to meet with you, it showed a balance of $164,325. The other superannuation account is left over from a previous job, which she left several years ago. This account is with HostPlus Super in the Shares Plus option and has a current balance of $18,212. Asset allocations of these super funds can be located from each of the fund’s public websites.
As Marina is single, she does not see the need for large amounts of personal insurance cover. She does have the default insurance cover for Life and TPD in the Australian Super account which provides $50,000 for each option. Marina has put in place personal income protection to ensure she has an income in case she was to fall sick or is injured and this will provide 75% of her current salary until age 65 if she becomes eligible to claim benefits under this account. This cover is with MLC and provides a benefit after a 1 month waiting period.
As Marina is earning a good salary and can easily cover living expenses, she is not in need of additional income from investments. While not a top priority, Marina would like to structure her investments to take advantage of any tax advantages that may be available.
You have completed a risk profile with Marina and the result was that she is effectively a BALANCED investor. She wants a good return on her investments, but does not want to take a lot of risk. Your licensee has provided risk profile definitions, research and recommended asset allocations for three (3) different risk profiles which can be found below
- Conservative
- Balanced
- Growth
Students are required to read and analyse a case study for a potential client, Marina Costas.
You are required to produce an “Investment Report” addressing the goals, objectives and issues raised in the case study provided.
Answer
1. Current Situation and Goals and Objectives considered in the Finance assignment
Marina Costas is a single lady of 47 years having some difficulties in the financial management of the current wealth and also the sum of the amount expected to be received after the death of her last family member. She does not have a financial obligation or liability that she is required to fulfil, but she wants to be financial independent in the sense that she has enough reserves in case she falls sick or meets any uncertainties due to which she is unable to work for a while. Thus, here are the details of her current earnings and expenses incurred.
Her primary source of income currently is her salary income being $105000 plus the superannuation amount contributed by the employer. She lives in a house owned by her, so she does not have to pay any mortgage or rent to others. For security purpose, she has taken building insurance for $55000 per annum. She has also got a boat of her dad on which she has to bear the maintenance cost of $3000 per annum and mooring fees of $3000 per annum ($250 per month). She has also got her car which she wants to replace, but current insurance cost is $8000 per annum. She keeps $10000 in her bank account to meet any contingencies and has made a term deposit of $15000 which gives her an interest of 0.65% per annum. She has also made investment in shares of various companies of which she is aware. She does not have any idea about investing in the shares market but has created 10 stocks to diversify the investment. She also holds 8000 units of the Pengana Private Equity Trust, purchased for $10000. She does not have any idea about this investment also being done by her. The superannuation funds in which her employers contribute has totalled to $164325 from the current employer and $18212 from the previous employers. Thus, she is financially active in investing her funds on the basis of random advice from various sources. She has also invested in some options where she is not aware of the benefits of her investment.
She is expecting to receive $430000 as an inheritance after her sister’s death. She does not want to spend this amount on a random basis without understanding about the benefits and obligation of choosing any given option of investment. Her main motive is to get the tax benefit from her investment along with maximum return at moderate risk being associated with it.
2. Current Personal Net worth Statement
The net worth includes all the assets as reduced by the liabilities that the individual have (Davydov 2016). It is net assets owned by the individual and helps to get the current financial position of the person. In the given case Marina Costas has been using her surplus funds by investing in various areas. In the calculation of the net worth the assets owned for personal purpose as well as for investment purpose shall come in. She has no fixed liability undertaken by her thus all the investment and property held by her will come under her net worth.
|
Net Worth Statement |
|
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
House Property |
$ 4,60,000.00 |
|
Boat |
$ 38,000.00 |
|
Car |
$ 40,000.00 |
|
Bank Account |
$ 10,000.00 |
|
Term Deposit |
$ 15,000.00 |
|
Investment in Shares |
$ 1,32,271.78 |
|
Superannuation 1 |
$ 1,64,325.00 |
|
Superannuation 2 |
$ 18,212.00 |
|
Less: Mortgage Loan Other liabilities |
$ NiL |
|
Total |
$ 8,77,808.78 |
|
|
|
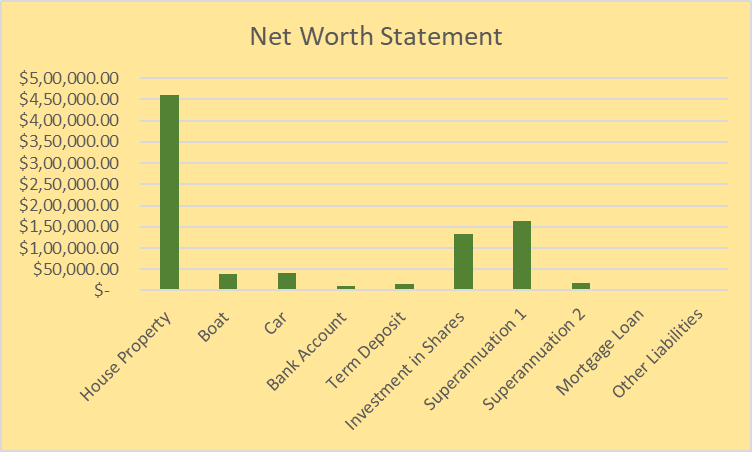
The net worth is calculated using the latest market price of the assets irrespective of the cost of acquisition. The most valuable asset held by her is her house that is more than 50% of the total net worth. The second most valuable asset is the employer’s contribution to the superannuation funds. The only investment which she has really done is in the shares of the Australian Equities. The only investments which she has made in the PE1 shares are also consist of Australian equities. She has only invested in shares known to her so the exposures to the global equities are nil. The little amount is also deposited in the short term deposit having nominal interest income. This are the most secure form of investment with fixed income and less risk associated with it. The little amount is kept in the bank account to keep the liquid cash for meeting any contingencies. Original cost of the car and depreciation is not available so we have considered replaceable cost as value of the car. (Deegan 2016)
3. Current Portfolio Asset Allocation
The current asset allocation is shown below.
|
Asset Allocation |
||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Percent |
|
Bank Account |
$ 10,000.00 |
2.94% |
|
Term Deposit |
$ 15,000.00 |
4.41% |
|
Investment in Shares |
$ 1,32,271.78 |
38.93% |
|
Superannuation Fund |
$ 1,82,537.00 |
53.72% |
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
$ 3,39,808.78 |
100.00% |
|
|
|
|
|
Sl No. |
Shares Portfolio |
No. of Shares |
Price |
Market Value |
|
1 |
BHP Group |
49 |
47.72 |
$ 2,338.28 |
|
2 |
Commonwealth Bank |
320 |
98.01 |
$ 31,363.20 |
|
3 |
Qantas Airways Limited |
600 |
4.76 |
$ 2,856.00 |
|
4 |
AMP Ltd |
560 |
1.12 |
$ 627.20 |
|
5 |
QBE Insurance |
90 |
10.59 |
$ 953.10 |
|
6 |
Suncrop Group |
40 |
10.60 |
$ 424.00 |
|
7 |
Telstra |
600 |
3.42 |
$ 2,052.00 |
|
8 |
Macquarie Group |
400 |
151.41 |
$ 60,564.00 |
|
9 |
Woolworths |
490 |
41.35 |
$ 20,261.50 |
|
10 |
ANZ Bank |
50 |
27.85 |
$ 1,392.50 |
|
11 |
Pengana Pvt Equity Trust (PE1) |
8000 |
1.18 |
$ 9,440.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL |
|
|
$ 1,32,271.78 |
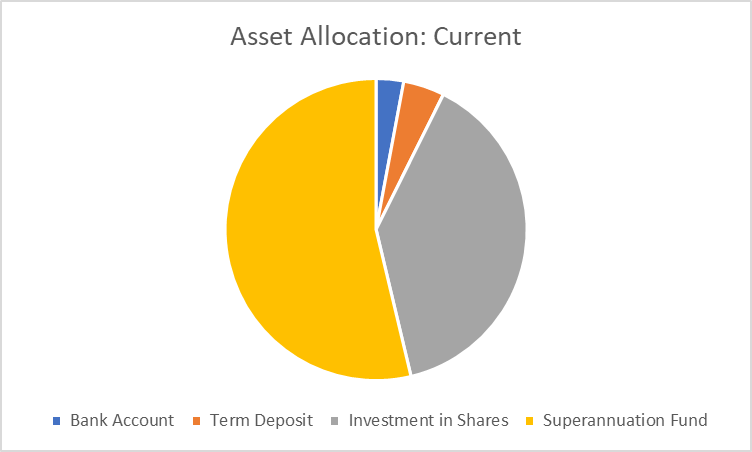
In the portfolio of the investments being done, the personal assets are not included, and thus, only those assets are involved which acquired with the intention to earn interest income or capital appreciation are only taken into consideration (Shuli 2011). Thus, the house property, car and boat, which are personal assets, are not included. The second house, if she purchases and keeps it not for the living purpose but letting it out then that house shall form the property investment and be allocated accordingly.
In her current portfolio, the exposure to the domestic sector can only be seen, and international exposures are avoided. She is not aware of the available options and corresponding risk and rewards associated with them, so she has not invested in any international funds. The companies in which equity the investment has been are having their head office in Australia, but the operations are carried out in other parts of the world also. The risk and rewards of investing in the equities are high, and she has invested in them without having much knowledge about the same. She is not planning to withdraw the invested amount in the short term period so the overall average return of the stocks shall be available to her. The benefit of diversification is also their which will reduce the chance of reducing the capital invested (Hitchner 2016). She has been categorized as a balanced investor as she has invested the amount of approx 39% in the equities comprising of the global and Australian equities (19+19=38%). Her investments in the property being global or international are nil as compared to the average percent being 8% (6+2=8%).
The main area where the money is kept in investment is the compulsory contribution in the superannuation funds. It is to be noted here that she has her funds in two different accounts (Mersland & Urgeghe 2013). The account fees are being paid in both the accounts, which are an additional cost which she is incurring. If she consolidates both the account fees will be charged for the single account only. Further she is not doing any voluntary contribution to the fund, which would have helped her with the tax benefits. This is the only investment in which she gets tax relief and must contribute further to enhance the rewards.
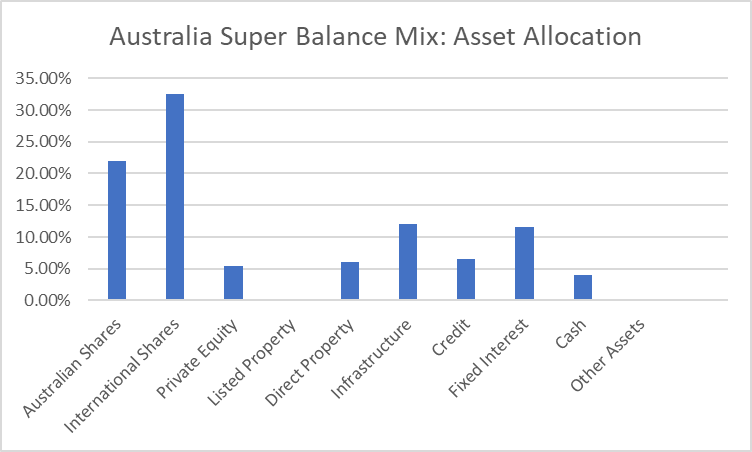
The other investment consists of the Australian fixed interest comprising the short term deposit of 3 months and maintaining the minimum balance at bank account to maintain the liquidity. The balance with the bank account shall be considered as cash in the asset allocation.
|
Australian Super Balanced Mixed |
|
|
Assets |
Allocation |
|
Australian Shares |
22.00% |
|
International Shares |
32.50% |
|
Private Equity |
5.50% |
|
Listed Property |
0.00% |
|
Direct Property |
6.00% |
|
Infrastructure |
12.00% |
|
Credit |
6.50% |
|
Fixed Interest |
11.50% |
|
Cash |
4.00% |
|
Other Assets |
0.00% |
|
|
|
|
HotPlus |
|
|
Assets |
Allocation |
|
Australian Shares |
21.00% |
|
International Shares- Developed |
21.00% |
|
International Shares- Emerging |
8.00% |
|
Property |
13.00% |
|
Infrastructure |
12.00% |
|
Private Equity |
8.00% |
|
Credit |
7.00% |
|
Alternatives |
5.00% |
|
Cash |
5.00% |
|
|
|
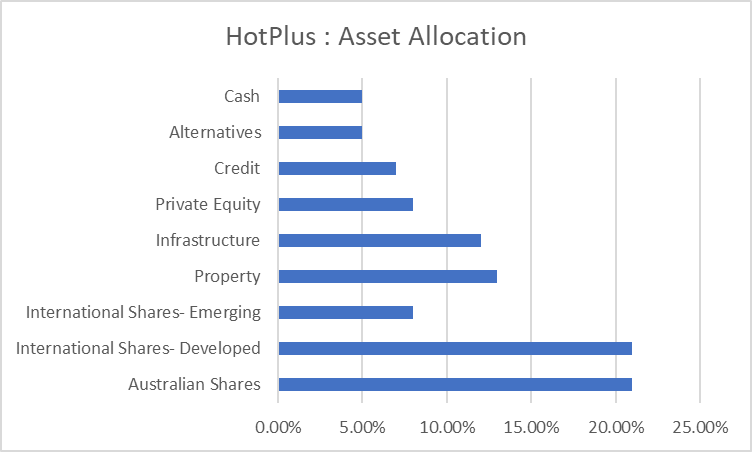
4. Investment opportunity
It can direct investment in several investment opportunities or invest in different portfolio fund available in the market based on risk, thus in this type of portfolio fund, the fund manager invests the money of the investor on different assets and make a portfolio (Welsh 2007).
Thus, the following are several investment opportunities if Maria wants to invest on its own:
Australian Equities: These are equity markets where an investor invests in the equity shares of the companies listed in the Australian stock exchange, which is done through the trading platform (Morecroft 2015).
Global Equities: These are equity market where an investor invest in the equity shares of the companies listed outside Australian stock exchange and this is done through trading platform (Coetsee 2010)
Australian property: Investment in residential or commercial properties in Australia for rental income or capital appreciation Global property: Investment in residential or commercial properties in Countries outside Australia for rental income or capital appreciation (Pucheta-Martiinez, M & Garcia-Meca, 2019)
Listed infrastructure: It is the time of investment where the big companies engaged in infrastructure are listed in the Australian or Global market (Pucheta-Martiinez, M & Garcia-Meca, 2019)
Alternatives: Alternative plan such as superannuation plan, also known as “super”, is the money set from the income by the employer or even the employee can additionally contribute on the same, and this amount is set aside for use when an employee retires from work (Sherman 2015). Thus, it is a retirement plan, and the amount is received on retirement. Investment in a superannuation fund reduces the taxable income on the year of investment, but it is taxable in the year when the amount is received (Coetsee 2010). Australian Fixed interest: These are an investment in fixed deposits of Australian Banks, government bonds or other secured fixed interest-bearing securities of an Australian company or financial institution (Carlon 2019)
Global Fixed Interest: These are an investment in fixed deposits in other than Australian Banks, government bonds or other secured fixed interest-bearing securities of other than Australian company or financial institution (Carlon 2019) Cash: cash in bank or hand for liquidity.
5. Recommendations and proposed portfolio and asset allocation
Marina is about to receive $ 430,000 in the month of October – November 2021 from inherit substantial funds from her sister’s estate and thus she has lots of investment opportunity in individual securities or in form of portfolio fund. Marina has expressed her willingness that as she is earning a good salary and can easily cover living expenses thus she is willing to structure her investment to take any tax advantage and make her current and proposed portfolio as a balanced portfolio.
Currently the portfolio of Marina is a growth and balanced portfolio where there is 39% equity investment, 54% investment in superannuation fund, 4% in short term deposit and remaining 3% in cash. Thus $430,000 which is to be invested in October and November shall has the following asset allocation based on the requirement of Marina Costas
|
Asset Allocation (proposed $430,000) |
||
|
Particulars |
Amount |
Percent |
|
Investment in Fixed interest |
$ 1,40,000.00 |
32% |
|
Investment in properties |
$ 1,15,000.00 |
27% |
|
Investment in Shares |
$ 1,50,000.00 |
35% |
|
Superannuation Fund |
$ 25,000.00 |
6% |
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
$ 4,00,000.00 |
100% |
|
|
|
|
In the above proposed investment we shall recommend Investment in Fixed deposit of $140,000.00 for interest income and for secured investment, Investment in properties of $ 115,000.00 for rental income and capital appreciation as Marina is willing to invest in properties but due to falling in price in properties she is afraid of investing but considering the fact that in falling price it is the correct time to invest so Marina should invest 27% of the proposed amount in investment in properties, Investment in shares could be recommended for $150,000.00 to maintain a portfolio a growth portfolio and to keep portfolio growing and lastly investment in superannuation fund of $ 25,000 as gain additional tax benefit.
Thus, considering the current and proposed investment the asset allocation and percentage of asset allocation is shown in the table below
|
Asset Allocation (Current + Proposed) |
||||
|
Particulars |
Current |
Proposed |
Total |
Percent |
|
Bank Account |
$ 10,000.00 |
$ 10,000.00 |
1% |
|
|
Investment in Fixed Deposit |
$ 15,000.00 |
$ 1,40,000.00 |
$ 1,55,000.00 |
20% |
|
Investment in Shares |
$ 1,32,271.78 |
$ 1,50,000.00 |
$ 2,82,271.78 |
37% |
|
Superannuation Fund |
$ 1,82,537.00 |
$ 25,000.00 |
$ 2,07,537.00 |
27% |
|
Investment in Properties |
$ 1,15,000.00 |
$ 1,15,000.00 |
15% |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Total |
$3,39,808.78 |
$ 4,30,000.00 |
$ 7,69,808.78 |
100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
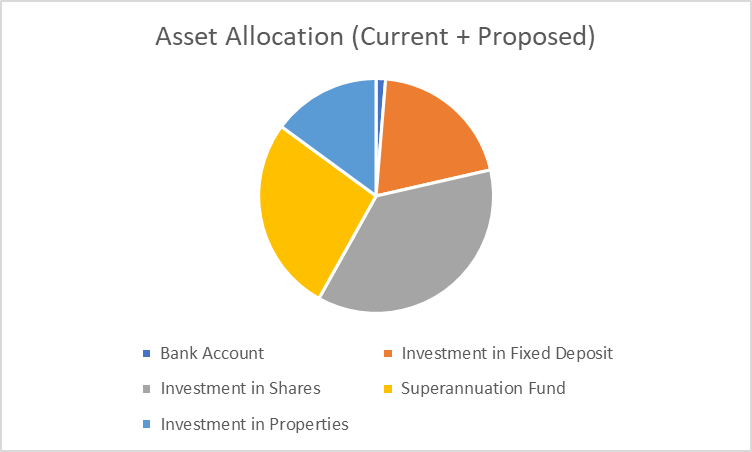
In the above table, the investment amount is allocated to make the portfolio a Balanced portfolio. In the above table, the Investment in fixed deposit is 20% of the total Investment which include of short-term deposit of 2% and the remaining 18% as fixed deposit for interest income, Investment in shares is maintained at 37% of the total portfolio size, and for that, we had made an additional investment in the share of $150,000. Thus this is done in Australian or Global Equities. Investment in a superannuation fund is 27%. This gives a tax benefit to the employee and provides money after retirement. Thus, being a single lady, she needs money to survive. Thus, her retirement plans should be firm and secured for living expenses, so additionally, $25,000 has been invested in the fund, keeping in mind the upper limit of employees contribution in such funds. Marina can also invest in Australian properties or Global properties for rental income or capital appreciation; thus this Investment will also help Marina after her retirement
Thus, the above portfolio, after considering the current and proposed, is balanced with the additional tax advantage and asset allocation in different assets.
6. Conclusion
The investment options are huge and should be chosen keeping in mind the available risk appetite and rewards as per the prevailing economic conditions. As she is having a balanced approach in her investment plans that are good as she will not be driven by any high reward promising stock and go for higher risk. She is financially satisfied with her income and spending habits but wants to ensure that the prudent investment decision may be taken based on the detailed knowledge of areas of investment.
In the given case the net saving she is having annually after paying off her major expenses is only $36000 out of which around $20000 is spend in the other miscellaneous day to day expenses.
|
Particulars |
Amount |
|
Salary Received |
$ 1,05,000.00 |
|
Building Insurance Charge |
$ 55,000.00 |
|
Mooring Fees |
$ 3,000.00 |
|
Maintenance Boat |
$ 3,000.00 |
|
Car Insurance Charge |
$ 8,000.00 |
|
|
|
|
Total |
$ 36,000.00 |
|
|
|
The appreciation in the value of the property held has been high, approximating to around 12% pa, who is the highest of all alternatives since due to covid situation, the share market is showing volatility.
Her credit card limit is $20000, which, if fully utilized, only $16000 per annum will be available for the investment purpose. She has not contributed any amount as a voluntary contribution to the superannuation fund. She shall also make a rule to invest a fixed amount in a superannuation fund, which will have a dual impact on earning and tax relief. She shall postpone, if possible, the purchase of a new car, or she might have to use the funds received from the inheritance of her sister. This shall otherwise be done with the reduction in the investment in the term deposits for the time being.
References
Carlon, S., 2019, Financial accounting: reporting, analysis and decision making, 6th ed. Milton, QLD John Wiley and Sons Australia, Ltd
Coetsee, D 2010, ‘The role of accounting theory in the development of accounting principles’, Meditari Accountancy Research, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 1-16.
Davydov, D 2016, ‘Debt structure and corporate performance in emerging markets’, Research in International Business and Finance, vol. 38, pp. 299-311. Deegan, C. M 2016, Financial accounting, McGraw-Hill Education.
Hitchner, J. R 2016, Financial valuation, John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Mersland, R & Urgeghe, L 2013, ‘International Debt Financing and Performance of Microfinance Institutions’, Strategic Change, vol. 22, pp. 36-47, Morecroft, JD 2015, Strategic modelling and business dynamics: A feedback systems approach, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken,
Pucheta-Martiinez, M & Garcia-Meca, E 2019, ‘Monitoring, corporate performance and institutional directors’, Australian Accounting Review, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 208-219. doi:10.1111/auar.12262
Sherman, E 2015, A manager's guide to financial analysis : Powerful tools for analyzing the numbers and making the best decisions for your business, Ama Self-Study
Shuli, I 2011, ‘Earnings management and the quality of the financial reporting’, Perspective of Innovation in Economics and Buisness (PIEB), vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 45- 48.
Welsh, M. J 2007, ‘Financial accounting: An introduction to concepts, methods, and uses’, Issues in Accounting Education, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 343-344.












