Healthcare Assignment: How Behavioral Contributions Develop Type 2 Diabetes?
Question
Task:
Healthcare Assignment Task: For your chosen health condition (TYPE 2 DIABETES) you are required to discuss potential intervention strategies to address an element of behaviour change through the application of one of the health behaviour models addressed in the unit (Theory of Planned Behaviour, Transtheoretical Model, Health Belief Model or Protection Motivation Theory). There are three elements to this assignment. Firstly, the assignment needs to define the health behaviour within the context of the selected health condition as a rationale for intervention. Secondly, the assignment should provide a critical review of factors that may contribute to predicting health behaviour change in the context of a health behaviour model, as well as clearly outlining potential barriers. Finally, the assignment needs to provide an evidence-based implementation plan to effect behaviour change
Answer
Introduction
Type 2 Diabetes, taken in the present context of healthcare assignment, is a growing concern as it is detrimental to the individual's health. Mortality and morbidity are rapidly increasing due to the presence of this disease. It is currently affecting over 26 million individuals in the US. Earlier, Type 2 Diabetes was incurable, and nowadays, it has several treatments available (Fedcourt.gov.au, 2021). Despite several interventions available, the concern is that individuals are not relieved, as it is a recurring disease. Apart from medicines, drugs, insulin and surgery are used to treat this disease. Additional effort is made by the psychologist to treat this disease by examining the behavioral pattern of the individuals. Thus, in this study, an attempt is made to understand how behavioral contributions develop this disease and how it can be mitigated by using health belief models and theory. The model's effectiveness will be depicted in the form of an intervention plan developed from these models to mitigate the disease and its impact.
Rationale
To understand what the disease is, it is necessary to understand what makes it rise. As opined by Kalra et al., (2018) the occurrence of disease occurs when the cells of humans are damaged and destroyed due to infection. This leads to an illness and sometimes loss of death. On the contrary, it is opined by Kivimäki and Steptoe (2018), disease refers to a psychological disorder in the human that affects multiple areas of life. What in this process happens is that it creates disorders and distress to a person who tends to develop these symptoms and disease. At present, a disorder in the human lifestyle is majorly responsible for the occurrence of Type 2 diabetes. It has been found that Type 2 diabetes occurs due to anxiety disorders (Fedcourt.gov.au, 2021). It is traditionally proved that anxiety is associated with poor metabolic outcomes, which lead to increased medical complications such as D2M. On the other hand, it is found that increased stress is responsible for developing D2M. This is due to the fact that stress leads to increased blood sugar levels and glycated hemoglobin levels (Guy et al., 2019). As opined by Thernlund, an individual having a stressful experience continuous of 2 years can develop D2M. It is evident that psychological stress is the indirect cause of Diabetes as it leads to fluctuating blood sugar levels in people.
The associated potential complications with Diabetes are heart & blood disease. It is associated with the increased risk of stroke, kidney failure, high blood pressure, heart attack, narrowing blood vessels and others. It is undeniable that Diabetes has a severe impact on human health (Vancampfort et al., 2017). The other disease is nerve damage in limbs. The thing to be noted is that what the individual believes is disease occurs due to uncertainty, but one cannot forget that it is the result of what we act to or it the result of individual actions. In the current era, many changes have taken place, and the lifestyles of individuals have also been changed. The major reason for the occurrence of Diabetes is found to be disorders in eating, sleeping problems, hostility, anger and others. It is evident that treating Diabetes costs millions of dollars, and it is recurring again due to the fact that it needs super control over it (Vancampfort et al., 2017).
Health Professionals believe that to cure the disease when it becomes critical; it is better to prevent it before when the reason for the occurrence is known. They believe that when the disorder and human behavior is recognized, it will be easy to control the disease without spending millions on diabetes treatment or on medical treatment such as Metformin. At present, it has become easy to determine what really leads to the generation of Diabetes in humans. This is the reason they suggest treating diseases by examining the behavior of the individuals through disorder occurrence. It is opined by (Vancampfort et al., 2017), there is a connection between disorder and health behavior. It is true there is a behavior contribution to Diabetes, and it is found to be mitigated when the individuals have control over their worse lifestyle. It has been found that Diabetes type 2 has affected the world worse, and there is a need for intervention to be taken so that it would be cured. As per the Center for Disease Control, it has stated that 11% of men and 10% of women above 20 years are affected by T2D (Sanches et al., 2017).
The centre has estimated that if this left to be untreated, there is a chance that it would increase to 54% more in future. Many factors and interventions have been determined for the rise of T2D. However, an intervention to treat such a disease is a failure. Day by day, cases associated with Diabetes are occurring (Fedcourt.gov.au, 2021). It has been found that different individuals have different reasons for developing Diabetes. Earlier it tended to develop in the older patients as the behavior pattern of the individuals have changed this has reached to the children and youth as well. Reasons in children for Diabetes are determined as sedentary lifestyle, poor glucose regulations and physical inactivity (Kivimäki & Steptoe, 2018). On the other hand, pregnant women are the victims of Diabetes due to hormonal misbalance, stress and poor diet intake. In the older ones, the reason for developing the disease is due to an increase in insulin resistance. This disability leads to a severe effect of Diabetes.
Model application for possible course of actions undertaking
As opined by Zuhriyah et al., (2018), Diabetes is curable when the individuals control the disorder in human behavior. Various theories and models have been developed to treat and support the disease to be cured. The different types of health models provide an insight into the facts, the causes for the occurrence of disease and ways to mitigate this. Currently, Diabetes is growing rapidly due to changes in behavior and occurrence of disorder in the individual, and it has been estimated that it will remain to be increased (Sanches et al., 2017). The effort of the health practitioner is to provide the ways through models and theories so that necessary intervention can be adopted to mitigate the severity of the disease. The behavioral change models describe that public health must aim at preventing disease and promote better and quality of life (Livi et al., 2017). In addition, it focuses on elaborating the environmental conditions causing such disease through which individuals can become healthy via intervening at the community, institutional and societal level. Health practitioners have introduced an effective health model that helps the patient to overcome the disease presence. One of them is the Health Belief Model (Zuhriyah et al., 2018).
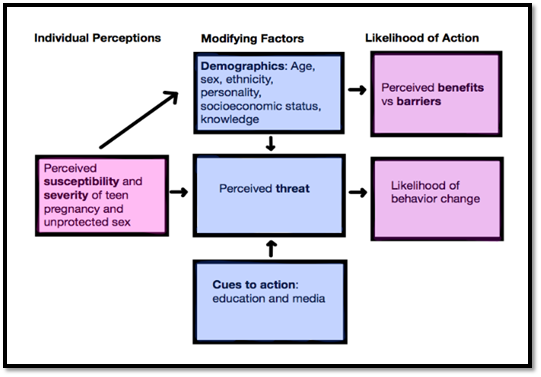
Figure 1: Health Belief Model
Source: (Den Braver et al., 2017)
The health belief model was introduced in the 1950s. It was developed by social scientists in the "Public Health Service" US. The core purpose for developing this model is to understand the reason why people fail to adopt disease prevention strategies or why people fear for screening tests to have early disease detection. This model has great and effective usage. This elaborates that it is the personal threats of the individual that becomes the reason for occurring illness, and it is the individual belief that leads to having effectiveness to overcome illness by changing in behavior patterns (Sanches et al., 2017). The HBM is derived from psychological theory and behavior theory in order to avoid illness and cure illness. The HBM is built on the belief that the human course of action is subject to human's perception that leads to barriers and benefits associated with health behavior (Zuhriyah et al., 2018). The following are the six constructs of the health belief model that states the results of human behavior.
Perceived susceptibility- This means that humans get to have the disease with the perception of their own fear. In other words, it is assumed that humans have a wide variation of feelings due to personal vulnerability that develops into illness (Den Braver et al., 2017). This is that stage where a person is subjected to the perception of the risk of having an illness.
Perceived severity- This stage refers to the person's feeling of having seriousness in illness or feeling of disease untreated. This feeling or behavior includes medical consequences such as disability and death. On the other hand, social consequences such as social relationships and family life.
Perceived benefits- A stage refers to perceptions of having effectiveness in various actions that result from reducing the threat of having an illness (Den Braver et al., 2017). In this feeling, a person adopts a health benefits recommendation that helps to overcome the severity of disease.
Perceived barriers- An observation of obstacles in treating such illness. This refers to feelings of barriers such as cost in treating disease, dangerous, time-consuming, expensive, and inconvenient and others.
Cue to action- This refers to a stimulus, which is needed in triggering the decision-making process for accepting health recommendation action. These cues may be in the form of wheezing and chest pains (Den Braver et al., 2017).
Self-efficacy- A level of personal confidence is determined in this behavior to successfully treat the disease. Here, feelings generate to successfully deliver a behavior.
It is evident that this model has great support for its practice as it has been taking in the programmes for providing intervention plans to the people (Zuhriyah et al., 2018).
Intervention
Apart from all disorders discussed in the above study, it is understood that stress is the indirect cause of T2D and has a large impact on human health. Thus, stress management is understood to be one of the effective interventions that can prevent T2D. It is assumed that stress hormones are the reasons for insulin-producing cell disruption. It stops the proper functioning of blood sugar levels in the body. To balance the insulin secretion in the body, stress must be managed (Den Braver et al., 2017). When the stress is managed, individuals get performed well in daily life. Effective stress management helps the individual to activate those cells that help the body to function well. It has been observed that stress management not only treats Diabetes but has additional benefits from this, such as stress management provides better sleep, it helps to control weight, develop a tendency of individuals to resist disease. To prevent T2D, stress management is essential as it helps in glucose management of the individual's body (Den Braver et al., 2017). The three identified strategies have been depicted in this study that contributes to stress management:
- Relaxation to coping up with stressful environment
As opined by National Institutes of Health (2021), relaxation contributes to stress management. It is true that when stress hormones are released, it enhances blood pressure level and heart rate. Relaxation techniques may help the body to lower the blood pressure level and maintain heart rate that ultimately manages the stress. Relaxation techniques can be deep breathing, Meditation and others. - Exercising for better health outcomes
On the contrary, it is opined by Spruijt-Metz et al., (2014) stress can be managed with the adoption of exercise. Exercise pumps up the endorphins that reduce the negative impact of stress. Physical activity helps in boosting the production of good neurotransmitters that improves mood and ultimately reduces stress. - Proper intake of balanced diet
According to Den Braver et al., (2017), stress can be managed by having proper intake of a balanced diet. A proper balanced diet cuts the level of stress hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol and makes the body potential enough to manage the stress. It is evident that a healthy diet helps in countering the effect of stress via shoring up the immunity system & lowering blood pressure levels.
The identified strategies are better interventions in stress management and ultimately help the patients to overcome the severity of disease such as T2D (Zuhriyah et al., 2018).
Conclusion
It can be concluded that Diabetes is destroying the life of an individual and somewhere it creates difficulty in overcoming the disease. The study has highlighted the way Diabetes can occur in the individual and highlighted the findings with the help of which this disease can be cured. Stress management is identified as an effective intervention to prevent the occurrence of Diabetes. This has highlighted the three recommendations as relaxation to cope up with a stressful environment, exercising for better health outcomes and proper intake of a balanced diet. These three recommendations are helpful in mitigating the issues associated with Diabetes. Moreover, the study has highlighted the effective usage of the behavior change model over the individual to identify the fears and concerns regarding the adoption of health recommendation strategies.
References
Beran, M., Muzambi, R., Geraets, A., Albertorio, J., Adriaanse, M. C., Iversen, M. M., ... & European Depression in Diabetes (EDID) Research Consortium. (2021). The bidirectional longitudinal association between depressive symptoms and HbA1c: a systematic review and meta?analysis. Diabetic Medicine, e14671.http://oro.open.ac.uk/78741/1/78741.pdf
Bickett, A., & Tapp, H. (2016). Anxiety and Diabetes: innovative approaches to management in primary care. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 241(15), 1724-1731.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4999621/
Den Braver, N. R., de Vet, E. W. M. L., Duijzer, G., Ter Beek, J., Jansen, S. C., Hiddink, G. J., ... & Haveman-Nies, A. (2017). Determinants of lifestyle behavior change to prevent type 2 diabetes in high-risk individuals. International journal of behavioral nutrition and physical activity, 14(1), 1-11.https://ijbnpa.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12966-017-0532-9
Fedcourt.gov.au. (2021). Retrieved 7 October 2021, from http://www.fedcourt.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/29026/Corporate_Plan_2016-2020.pdf.
Guy, S. Z., Li, L., Thomson, P. C., & Hermesch, S. (2019). Quantifying the health challenges in an Australian piggery using medication records for the definition of disease resilience. Journal of animal science, 97(3), 1076-1089.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6396246/
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Health and Behavior: Research, a. (2021). Biobehavioral Factors in Health and Disease. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 7 October 2021, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK43737/.
Kalra, S., Jena, B. N., & Yeravdekar, R. (2018). Emotional and psychological needs of people with Diabetes. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 22(5), 696.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6166557/
Kivimäki, M., & Steptoe, A. (2018). Effects of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular disease. Healthcare assignment Nature Reviews Cardiology, 15(4), 215-229.https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10042807/1/Steptoe_Kivimaki%20%2526% 20Steptoe%20Nat%20Rev%20Cardiol.pdf
Livi, S., Zeri, F., & Baroni, R. (2017). Health beliefs affect the correct replacement of daily disposable contact lenses: predicting compliance with the Health Belief Model and the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Contact Lens and Anterior Eye, 40(1), 25-32.https://publications.aston.ac.uk/id/eprint/29600/1/Health_beliefs_affect_the_ correct_replacement_of_daily_disposable_contact_lenses.pdf
Sanches, C. P., Vianna, A. G. D., & de Carvalho Barreto, F. (2017). The impact of type 2 diabetes on bone metabolism. Diabetology & metabolic syndrome, 9(1), 1-7.https://dmsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13098-017-0278-1
Spruijt-Metz, D., O’Reilly, G. A., Cook, L., Page, K. A., & Quinn, C. (2014). Behavioral contributions to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Current diabetes reports, 14(4), 475.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4001920/
Type 2 Diabetes. National Institutes of Health (NIH). (2021). Retrieved 7 October 2021, from https://www.nih.gov/research-training/accelerating-medicines-partnership-amp/type-2-diabetes.
Vancampfort, D., Firth, J., Schuch, F. B., Rosenbaum, S., Mugisha, J., Hallgren, M., ... & Stubbs, B. (2017). Sedentary behavior and physical activity levels in people with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder: a global systematic review and meta?analysis. World Psychiatry, 16(3), 308-315.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/wps.20458
Zuhriyah, L., Cahayani, W. A., Rahayu, I. D., & Suprapto, R. P. (2018, October). Perception of medical students of ecopreneurship according to the health belief model. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 2019, No. 1, p. 030016). AIP Publishing LLC.https://aip.scitation.org/doi/pdf/10.1063/1.5061869












