How can businesses use customer involvement and brand reputation assignment research methods to develop effective brand sustainability models
Question
Task: How can businesses use customer involvement and brand reputation assignment research methods to develop effective brand sustainability models
Answer
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Research background
This customer involvement and brand reputation assignment explores whether Opposing “physical experience enhancement”, social media customer engagement guarantees organisational or brand-based customers’ emotional impact through specific motivation drivers. Cognitive nuance influence is a significant advantage stimulated through social media, with a higher “social media” user engagement in the digitalisation age worldwide. Cambra-Fierro et al. (2021) stated that the “Marketing Science Institute” highlighted “brand differentiation through customer experience” as a 2020-22 priority, where strategic management would priorly require regression mapping of the involved variables; in this study: customer engagement and brand reputation. Choi and Burnham (2020) observe that “self-expressed brand perception” exhibits a substantial impact on “voluntary sharing behaviour” and individual brand reputation. This chapter considers the contextual background, identifying the rationale and problem statement for forming this study's Aim, objective and question. This chapter pinpoints the current issues in customer engagement's link to brand reputation in the USA, incorporating the utility and prioritising social media. The research questions will guide the succeeding chapters in reaching a satisfactory analytical result and influence the variables' perceptions.
1.2 customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentResearch Rationale
The customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch shows Social media is gaining extensive market interest, with brands investing in “digital marketing strategies” such as campaigns, interactive advertisements and customer feedback time-scaling. The graph below represents the brand impression and reputation built by U.S. retail brands in 2020, showing “205 million cross-platform actions” for the emerging brand Fashion Nova, followed closely by Playstation with 130.2 million “social media user actions”. Statista (2022) states that social media is a vital marketing channel. USA brands use marketing tools, advertisement and sponsorship features of social media platforms to increase exposure, boost brand awareness and improve sales.
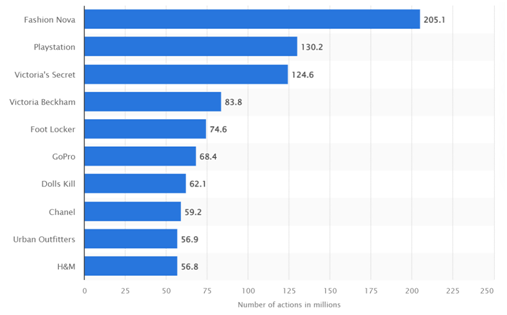
Figure 1.1: Social media's leading U.S. retail brands, 2020
(Source: Statista, 2021)
The figure above also identified higher website traffic, with active user engagement and increased product purchase-intent development through social media activeness. This study focuses on the impact relation and quantitative aspects of the interlinked variables of customer engagement and brand reputation, prioritising social media utility in USA businesses. de Oliveira Santini et al. (2020) opine that U.S. brands majority use social media as active brand leverage in gaining user activities, involvement and market awareness. This digital distribution and user-engagement medium are deemed a functional platform for linking customer engagement and brand reputation as direct and dependent variables. This research is expected to shed light upon this hypothesis, establishing a regression analysis-induced result for determining the link's characteristics and influence. De Keyser et al. (2020) postulated that touchpoints, feedback systems, escalations, goals, customer-centric service customisation, and impression alert are strategic focuses for organisational customer engagement, requiring process analysis for increased traffic and indirect influence on higher retention rates.
1.3 Aim and Objectives
1.3.1 customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentAim
The research aim is to analyse the interlink and relationship characteristics between customer engagement and brand reputation concerning social media usage and strategy influence in the USA.
1.3.2 Objectives
Supporting the research aim, the following are the objectives determined in this study:
To clarify critical theories and models related to “social media” customer engagement linking to brand reputation.
To analyse US-consumer perception of brand reputation through active social media engagement and increased brand awareness.
The customer involvement and brand reputation assignment will determine the dependent and independent influence factors of the customer-brand communication and profit link.
To strategise practical, cost-effective recommendations for U.S. brands' growth and reputation relevance using “social media customer engagement”.
1.4 Research Questions
1. What are the “social media” customer engagement theories linked to brand reputation
2. How is US-consumer perception of brand reputation impacted through active social media engagement
3. What are the customer-brand communication and profit link dependent and independent variables
4. What are some cost-effective recommendations for U.S. brands' reputation relevance using “social media customer engagement”
1.5 Problem Statement
Existing social media-administered customer engagement frameworks do not adequately account for impacting links to brand reputation and market relevance.
The brand development core constructs-customer engagement and brand reputation linked to social media utility- constitute the digitalisation trends of the U.S. industry. Vohra and Bhardwaj (2019) state that customer engagement frameworks are prioritised as high-responsive and have immediate impacts on company sales and fiscal year revenue predictions. A study examining a synthesised TAM framework determined motivation drivers of young customers being impactful in the behavioural management of brand engagement on “social media sites” (Florenthal, 2019). This denotes the likelihood of incorporating a predictive STP model with customer-influence variables impacting long-term brand reputation growth. However, more data information-based analytical study is required for brands to develop innovative strategies involving customer engagement and their impacting scopes on brand reputation.
1.6 Significance of the Research
Thiscustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment research is significant due to the scope of new analytical perceptions on the relationship development of social media-based customer engagement. Brand reputation is crucial for maintaining a brand reputation in a competitive market, and the digitalisation age has brought in subsequent systematic and operational changes in all U.S. organisations.Vinerean and Opreana (2021) opine that providing “omnichannel customer engagement”, leveraging chatbot capabilities, gamification, and social media lean, are essential research areas due to their credibility in improving customer traffic and subsequent brand impression. Through this research, a real-time respondent analysis is expected to provide a more profound link establishment, with suggestions and recommendations opening-up future research opportunities. The research significance also aligns with the fast-changing customer demands and industrial markets in the USA, prioritising long-term relevance strategies of link assessment, reflection and brand image positioning.
1.7 Summary
This chapter states preliminary studies on interlinking customer engagement and brand reputation using social media in the U.S. as a primary issue. Digitalisation is becoming irreplaceable in current technical and multi-dimensional strategies elements of global industries, using high “active user counts” as catalysts of brand improvement. Without adequate recognition of all dependent variables and influence factor interlinking. The customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch background encompasses the rising dependency on social media in company management and market improvement, paving customer engagement predictions. The sound reasoning propositioned in the background and research rationale situate social media as a crucial brand strategy, with digitalisation embedded in all industrial settings. The research objectives and questions introduced in this chapter are followed in the upcoming chapters for factual relevance, analysis, a questionnaire and analysis. The introduction has determined the research significance, which has noted newer innovative branding strategies as an inventive scope.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
Consumers have been overly active and using several social media platforms recently, for which the brands in the USA are also focusing on allocating their advertisements and campaigns through the social media platform. By using the social media platform, they are trying to increase the brand communication level with the customers through a specific social media platform which is expanding their customer engagement rate on the other social media platforms. This is referred to as a spillover effect that has been caused due to the direct effect. In the case of the brands, it has been seen that these advertisements and the campaigns have a long-term effect which enables the brands to increase their interaction level with the customers in the future, which will help the brands to sustain their customers within the market of USA. This effect is known as the carryover effect of the marketing strategy. For enhancing business growth, customer engagement and proper communication are becoming essential for the organisation leveraging technological advancement to build a better rapport with the customers (GuillenJr, 2018). Hence, the brands use social media platforms to facilitate customer engagement and make them invaluable for their business.
2.2 Using social media platforms as a branding strategy
From the previous customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch, it has been identified that the technological improvements and evolvements that have been taking place have brought significant changes within the branding and the marketing strategies that the business organisations of the USA are adopting since the social media platform is emerging as the new way of attracting new customers. Therefore the emerging new social media platform is considered to be highly effective for the marketing strategies and the promotional activities that are being adopted by the USA organisations and have also contributed to reducing the marketing cost that the companies were investing in order to advertise their product as the number of social media users are regularly using the business organisations and leveraging the social media platform as the most helpful site to capture a large amount of audience and to influence their perception regarding the branding value and the usefulness of the product that they're selling. Therefore, social media platforms have been seen to be effective in contributing to the purchasing decision-making of USA customers. It has been seen that social media platforms have been indirectly influencing the perception of the customers, which is considered to be implemented by the USA companies as their marketing strategy. Hence these companies are becoming highly advanced in order to cope with the evolution of technology for their business growth. The purpose with which the USA organisations use the social media marketing strategy, as pointed out by Waluya, Iqbal and Indradewa (2019), has been considered to be influencing the customers and their perceptions regarding the product and the brand value of the organisations, which helps them to enhance the purchasing decision through the help of the attractive contents that the organisations are providing through their blogs or their posts in their social media platform. Hence the social media platform is being used as a medium for creating awareness among the customers of the USA regarding the brand and its product. It is being pointed out by Kim and Chao (2019) that social media marketing is used as a tool for increasing the effectiveness of the marketing strategies of these brands, which has brought significant changes within the business operations and the marketing strategies that are being implemented by the business and as also contributed in enhancing the communication between the customers and the companies within the USA market which is further resulted into enhancing customer engagement and increasing brand loyalty. As per the statistics are given by witaa et al. (2018), it has been seen that in the future, 40% of the total investment that the USA companies are making will be invested in marketing strategies which will help them to earn new customers and will help them to increase their sales revenue. The organisation is using social media platforms in order to gain a competitive advantage within the market. It has been pointed out that through the help of customised ads, companies might be able to reach out to a large number of targeted audiences.
2.2 Theoretical framework for enhancing customer engagement using social media to increase brand reputation
As opined by Dam and Dam (2021), to increase customer satisfaction levels, business organisations have been focusing on creating Strategies for social media interactions that will help them meet the customer's expectations, and the companies social media presence will increase the customer interaction level. As society is evolving highly, the ways different brands adopt are also changing to keep the audiences connected to the brand.
(i)Customer’s responses: The youth, along with the adult generations residing in the USA, are now majorly hooked to online surfing in their free time hence the post that the companies or the brand are sharing are getting more responses which are helping these brands to enhance their engagement with the USA customers. While surfing these products, customers like or Wishlist these products or add them to their cart. This customer data from those residing within the USA market helps the companies to understand the customer's purchasing behaviour of the USA or their perceptions of the brand about which product they prioritise to what they like the most. This information is invaluable to the brand, which helps them to improve their offerings to customers to generate value for the product. This data also helps the companies enhance the brand's perception in front of the customers. In this context, it can be seen that keeping regular track of the information regarding which post is getting more liked or which post is getting more shared by the USA customers will help the brand to understand what the customers are expecting from the brand. In this context, one of the most important examples is if the measures that the brands are taking in order to enhance their corporate social responsibility are getting more view from the customers or the initiatives that the companies are taking to provide sustainable and eco-friendly products to the customers are getting more liked by the customers, it will help the brands to understand what the customer's exact needs are and will be able to work accordingly to meet their expectation level.
(ii) Customer’s review on the brand: It has been seen that the customer's review can either break or make the brand reputation for the companies situated in the USA since the customer's reviews are considered to be vital assets for the companies. It has been observed from the survey that almost 32% of customers, as pointed out by Raza et al. (2018), give their reviews of the product or the services that they purchase as a way in order to interact with the brand through the help of the social media platform. These reviews given by the customers of the USA are of high value since the companies can get an inside of the customer's perceptions regarding the brand from the reviews. Through the help of this review, the companies will get a vital chance to understand what the customers like about the product or what they dislike. This will give them ample opportunity to improvise their product so that they can improve their product for the customer's future purchasing. It is also seen that the customer's review that they leave after purchasing product lessons plays an essential role in encouraging the other customers regarding their decision-making for buying the product. The brand is using this response plan of the customers with the help of the review in order to manage their brand practices. The reviews shared by the existing customers within the USA borders help the other potential customer of the companies from the USA to gain information regarding the product mentioned by Dash, Kiefer and Paul (2021) to help them evaluate whether they want to make the purchase. Therefore, positive feedback from existing customershelps the companies or the brand to enhance the brand reputation within the market. In contrast, negative feedback might result in the USA-based company's deteriorating brand reputation. But it has also been seen that the companies use this feedback as vital information through which they get an idea on how to enhance their product. It also uses this as a platform for improving customer engagement. It is seen that a significant response from the existing customer might also help the companies to convert a customer who has purchased only once into a customer making repetitive purchasing. This will help the brand in order to develop its reputation within the USA market.
(iii) Content sharing: As mentioned above, the customers are also involved in sharing the post that the brand shares help the company reach out to a broader audience and contributes to increasing the company's customer base. As the customers share the post that the brands share on the social media platform, it helps influence the other customers of the USA to make their purchasing decisions. Therefore, sharing the brand's content with existing customers has influenced several people's purchasing decisions that they know. Hence it is seen that the level of influence that the sharing of posts by the customers have on the other USA audience has been high compared to the ads provided by the brands over the social media platform. Išorait (2018) mentioned that the existing customers share this content. It also helps the companies create their value proposition among a broader range of audiences, thereby allowing them to enhance their market image and brand reputation within the USA. This indicates that the social media platform in the USA has been contributing highly to increasing customer engagement with the brand, which is mentioned by Durmaz, Çavuolu and Özer (2018) to have contributed to increasing the brand reputation and also has contributed towards making the customers loyal towards the brand.
(iv) Following influencers: One of the most significant initiatives the brand is taking to increase its brand reputation is its collaborations with influencers in the USA. As shown by Ahmad et al. (2019), this collaboration helps the brand significantly impact the customer's perceptions and the way they view the brand and its product. It has been seen that collaborating with the correct influencers who support the value and vision of the companies might help the brand increase its value proposition and engage a considerable number of USA customers with the brand. This will also contribute to strengthening the brand's relationship with the customers of the USA. It is stated by Hermanda, Sumarwan and Tinaprillia (2019) that through the help of influencers who match the value of the brand, the companies will be able to connect easily to the target audience and will also be able to present the brand perfectly, which will enhance the way the customers perceive the brand. This will help the customers believe the brand blindly and help the companies increase their sales rate and take their place in the market.
2.4 Conceptual framework for regular customer interaction through social media in building up perceptions about the brand
It has been seen from the article of Mohammed and Rashid (2018) that the marketing strategies of the brand through the help of the social media platform have positively impacted the business effectiveness and influenced the customer's perception. The social media platform within the USA has significantly contributed to gaining popularity and increasing value proposition to the business organisation, which has contributed to the overall business growth. This popularity and growing brand reputation have influenced the customer's perception of the product that is being provided by the companies and also the way they perceive the brand. As seen, the number of social media users in the USA is increasing day by day the business organisations are also focusing on captivating this vast audience who are highly active on the social media platform in order to improve their marketing strategies. Through the help of the social media platform, the brand can provide timely and effective responses to customers' queries and help them make their purchasing decisions. As per past customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch, it has been seen that social media marketing has influenced the brand in order to gain the first of the customers and also to increase the customer's loyalty level towards the brand full stop; therefore, through the help of this advanced marketing solution the brand or the business organisations of USA have been able to enhance the be the customer perceives the brand which has also contributed in improving the decision making ability of the customers which is made the purchasing process more accessible. It is evident that through the increased customer perception regarding the brand's value, the companies are able to increase their sales revenue by grabbing an increasing number of customers. As opined by Mohamad et al. (2022), social media marketing and the way the customer seeds the brand work hand in hand to increase the brand's reputation within the market that they are operating. Therefore, by enhancing the customer's perception and also strengthening their marketing strategies using the social media platform, the companies are able to increase the awareness level among the customers and also are able to create brand value within the market.
From a broader perspective, it can be seen that the social media platform used in the USA can be used for both the purpose of data dispersion as well as a data connection. The social media network is considered an intriguing means for data dissemination regarding the brand. In this context, it can be seen that when customers are making purchasing decisions regarding high-price value items, they are looking for additional information to be 100% assured about the product before making the purchase. At this point, It is seen that the social media platform provides USA-based customers with ample information regarding the product and its usefulness. These data also provide the customer with a significant awareness regarding the brand value, which might also increase the customers' interest level for their future purchases (Išorait, 2018). It has been seen that previous customers' reviews have given a significant role in influencing the customer's perception of the brand and its product while making purchase decisions. Therefore, the increasing number of product audits being made online contributes to providing the customer with true purchasing power regarding the product.
The conceptual framework which is being followed here is given below:
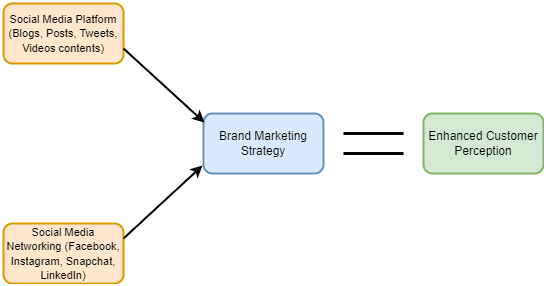
Figure 2.1: Conceptual framework for enhancing customer's perception regarding brand reputation through the social media platform
(Source: Mohammed and Rashid, 2018)
2.5 Disadvantages of social media as customer engagement and brand reputation tool
Social media marketing, as Oneiu (2020) opines, reflects a “relaxed fashion” of marketing, which is focused more on user-specific digital communication and engagement rather than brand interests and improved reputation recognition. Users search for brands, even high-end popular brands, on social media, in cases where they were aware of the brand priorly. Here, the brand reputation or market interest does not depend on the marketing tools' ability to attract an audience without brand awareness but to introduce marketing campaigns and repost features for loyal consumers. Another disadvantage of using social media as a bridge between customer engagement and brand reputation is the heavy advertisement reliance (Quesenberry, 2020). It can either lead to an authentic target market “interest and engagement rise” or bring about an inorganic high follower count without any engagement or impact on reputation. Muninger et al. (2022) state that the low ROI and high time consumption exhibited by effective “social media marketing” schemes result in time and cost overrun due to continuous investments and long-term departmental improvement for growth prospects.
2.6 Literature Gap
The literature review conducted in this study experienced varying contextual disadvantages, which hindered more informative customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch. The linking and dependency coefficient analysis of customer engagement and brand reputation is a newer R&D topic, with universities and other academic disciplines prioritising brand image and customer satisfaction in separate strategic spectrums. Further, the following disadvantage of choosing this topic is the ever-changing and rapidly deconstructing consumer interest, increasing procurement pressure and product availability while retaining quality, which provided the researcher with a volatile trend predictability and uncertainty. Being the latest research topic, peer-reviewed information was limited in determining the influence of brand reputation on “customer purchase behaviour”, which is aligned with increased engagement.
2.7 Summary
Consequently, it has been seen that the coordination between the brand product and the information provided through the social media platform helps in influencing the purchasing decision of the customers by evaluating the different brand and their consequences in terms of their facilities and usefulness. In order to make the evaluation, the customers can use the shopping sites or the service sides of the brand in order to gain the customer's review or their messages regarding the product or the brand, which might help the companies to influence the sales volume. In this regard, it is being stated by Siddiqui et al. (2021) believe that the impact of the internet or social media platforms within the market USA regarding the value of the word of mouth that comes from the existing customers of the brand contributes to amplifying the brand's value and also in recreating the customer's behaviour.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Introduction
This chapter highlights the varying methods under Saunder’s research onion used to determine a time-bound research “analysis and findings” process. The customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch onion’s stage-based structural division has assisted the research in narrowing down specific tools and approaches required in multi-step illustrations. Melnikovas (2018) opines that the “research onion” theoretical concept is a “research methodology construction” basics, determining essential future research prospectus. This chapter explains the step-by-step methodology used in this dissertation to build a comparative and reliable analytical assessment of “social media customer engagement” and brand reputation links. It also navigates the assistance and disadvantages experienced while using each strategy research onion stage, justifying utility.
3.2 Research Philosophy
As proposed under the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch onion model below, pragmatism research philosophy was implemented in this study due to its epistemological cognition and emotion-dimension relativeness. According to Cachero-Martínez and Vázquez-Casielles (2021), customer-specific factors mainly cater to their emotional and behavioural mannerisms to advertisement attraction and product consumer decision-making. However, for ensuring strategic productivity, pragmatism is the analytical tool incorporated by companies for their consumer and brand data structure. Considering these factors, pragmatism philosophy formed the actions, observations and further analysis of this study.
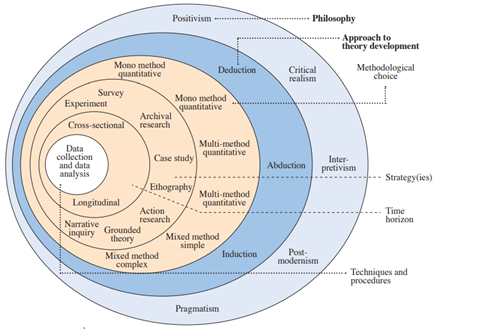
Figure 3.1: Saunders’s Research Onion
(Source: Melnikovas, 2018)
The above figure determines the different methodology layers. Pragmatism assisted in identifying the rational drivers of social media-based customer engagement and its link establishment with the latter. It positioned the U.S. social media as a practical management tool applicable to operational and external corporate influences. Majeed (2019) notes this philosophy's rigorous and wide-ranged applicability, allowing extensive data set and relevant information criticism to devise low-risk, non-preferential practical outcomes.
3.3 Research Approach
The "Abductive-deductive research approach” has been applied in this study, aligning with pragmatism. While finalising the research philosophy, the following approach was easier to pinpoint because of the technical practicability exhibited by both processes. Mitchell and Education (2019) state that abductive inference in known premises uses testable conclusion generation for a specific-general variable interaction. This approach has helped to acquire “rich contextual details from the data analysis, with the application liberty of a user-centric expert evidence-integration design.
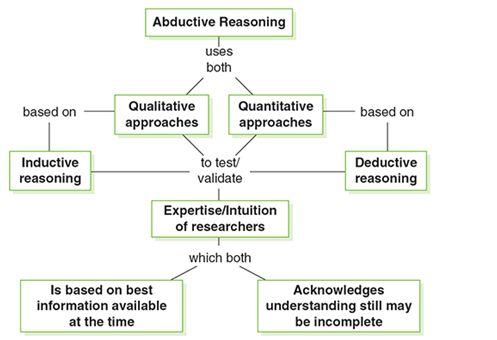
Figure 3.2: Abductive reasoning approach framework
(Source: Self-created by the author)
The flowchart above represents the application prospects of the abduction approach, showing comparative vast methodology suitability. While the reasoning uses qualitative and quantitative approaches for validation testing, thiscustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment research focuses on deductive reasoning as a researcher's intuition for applicability and outcome expectations. Cramer-Petersen et al. (2019) suggest an abductive-deductive approach as a counteractive affordable reasoning pattern that engages with idea generation dominance. This approach has allowed the study to verify the primary influence sources of the chosen organisational variables.
3.4 Research Design
“Mono-method quantitative design” is applied in the study for gaining real-time primary data information as a relevant factor to pragmatism usage in the research methodology. Quantitative design added contextual objectivity to the subject matter, critically aligning the variables and their interlinking social media strategy factor. This customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch design specifically depends upon numerical and variable position concretisation, allocating the "effect and cause” of all subsets and driven through data analysis methods (Wynn and Maier, 2022). The figure below is an interpretation framework implemented in research studies for extracting the conclusive assessment of proposed objectives.
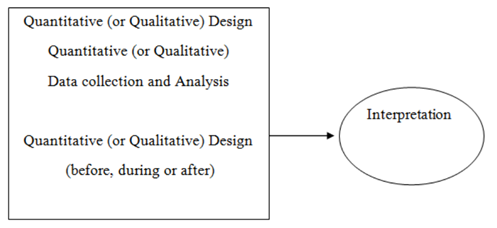
Figure 3.3: Embedded customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch design framework
(Source: Subedi, 2016)
Maintaining primary data reliability through pragmatism, quantitative design has assisted the research in gaining comparatively more reliable preliminary data. As stated in the problem statement, the lack of interlinking between the chosen variables, there has been limited primary research before. The utility of this embedded “research design framework” enabled methodology usage in a compact, low-cost analysis backed by preliminary data. Cox (2019) suggests that the objective measurement requirements and mathematical and statistical analysis certainty expected under pragmatism are approachable through quantitive design.
3.5 customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentResearch Strategy
A survey has been conducted as the research strategy for collecting primary data due to its comparatively lesser resource-sensitive application. Based on the applicability of the preceding methodology approaches, questionnaires would require resourcing or factual backup. Surveys comprise close-end and open-end questions based on the surveyor’s project intent (Hurley et al., 2021). This strategy has helped establish a “source and drivers” relationship between social media and increased customer engagement and traffic. Additionally, it has directed the potential of a directly proportional relationship between customer engagement and brand reputation.
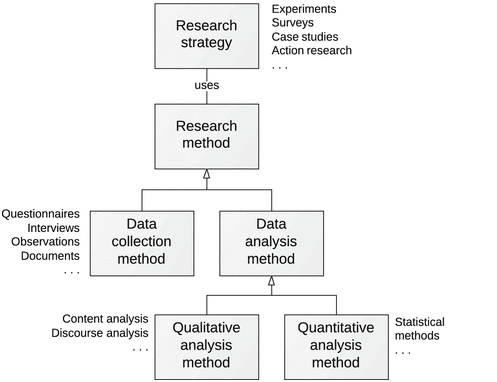
Figure 3.4: Research strategies model
(Source: Bueger and Gadinger, 2018)
The above diagram shows the successive procedures of a research strategy, directing the pathway towards a successful research conclusion. According to the author, research surveys are segmented into experiments, action research, surveys and case studies as the fundamental methodological elements of the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentprimary research. In this customer involvement and brand reputation assignment, the survey exponentially decreases literature gaps and barriers, standing as a result-based information mapping as another available data source.
3.6 Time Horizon
A cross-sectional time horizon has been implemented in this customer involvement and brand reputation
assignmentresearch, with the chosen data being assessed from USA’s “active social media” users. Kesmodel (2018) identifies cross-sectional studies to be effective for students performing time-specific surveys, providing accessible data accumulation and subset determination. Implementing this time horizon has assigned the researcher to collect data from the above-mentioned pre-determined sources. The purpose has not been to develop a long-term respondent movement of brand reputation and customer engagement interest. The focus was to determine a present-time response based on till-date social media influence and experience in association with these variables.
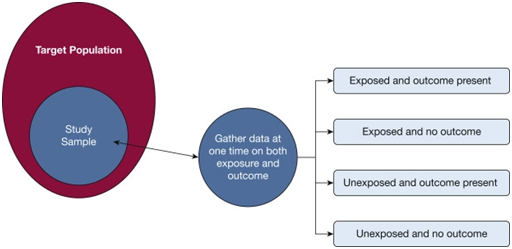
Figure 3.5: Cross-sectional time horizon
(Source: Wang and Cheng, 2020)
The image above identifies the varying types of Cross-sectional time horizons applicable to a quantitative study. According to the survey analysis requirement in this study, a retrospective study has been conducted where individuals, based on their variable utility, have been compared over a fixed timeline. In a retrospective study, the analysis depends on the reactive variability of components or population subsets, devoid of any future impact (Stiers et al., 2020). While prospective study develops a predictive statistical assessment, retrospective assessment has assisted in determining the variable influence factors based on the exact survey timeline and one-time response.
3.7 Data Collection
Primary data collection was incorporated in this study, with the utility of reliable, numerical and personally accumulated sources of information collection. For “primary data collection”, a self-administered questionnaire survey was undertaken with active users of different social media accounts. This data collection process was proposed at first for collecting more real-time information against the inaccessibility risk of secondary data (Parhizkar et al., 2020). However, during the process, the intent was shifted to analysing the impacting factors and reliability of the survey respondents. Articles and company finance reports collected in the literature review served as prevalently established information standpoints and peer-reviewed journal analysis reliability for building the favourable foreground to analysis extracted from the primary information from survey questionnaires. These data provided evidential backup to any insights or opinions from the preliminary data review.
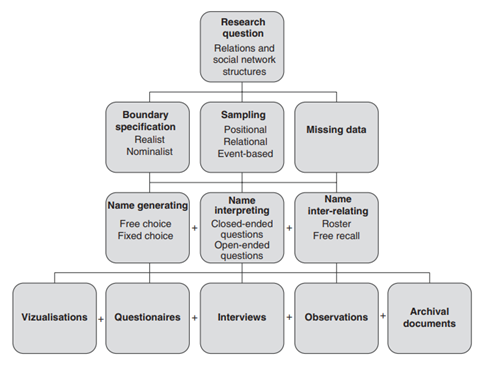
Figure 3.6: Data collection schematic guideline
(Source: Längler et al., 2019)
The figure above is the workflow diagram of a schematic guideline for the chosen data collection methodology. Sahin and Öztürk (2019) opine that the clarity of sampling lists and procedures enables the appropriate application of questionnaires, further adding name generation.A self-administered questionnaire survey was administered as the sole data collection process, comprising data from within U.K.'s customer retention and engagement observation criteria. Braekman et al. (2018) used this survey form to successfully conduct an unmanipulated, well-responsive data collection, commenting on the higher participation rate and lack of aversion of potential participants in the absence of a physically present or observing interviewer.
3.8 Sampling
A “non-probability convenience sampling strategy” was applied in this study as a risk avoidance application to fully-representative sample unavailability. Stratton (2021) suggested non-profitability sampling as an inexpensive, quick-responsive and easily applicable data-obtaining process as the requirement absence of a “complete survey frame”. The implementation of a convenience sampling strategy in this method allowed the researchers to proceed with easy-to-contact, non-random individuals. The sampling comprised 100 respondents from different age groups and social backgrounds. Individuals without background context-based profiling were approached with the survey through Google Forms distributed all over “social media platforms”. Social media platforms were utilised to ensure that the population subset chosen is at least aware of the context's source without influencing their responses.
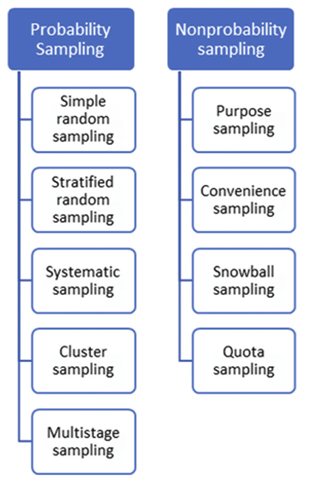
Figure 3.7: Sampling methods in customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch
(Source: Self-created by the author)
The above figure shows the different probability and non-probability sampling methods, among which non-random sampling has been implemented in the study. The population subset chosen for analysis has been as per the researcher’s discretion and subjective impression of data collection expectations. According to the 2021 Statista survey, the total 4th Quarter 2021 “active users’ activity” reached approximately 4.2 billion, with 82% of the U.S. population indulging in more extended screentime/day (Dixon, 2022). Reflecting upon this utility rise, distributing survey questionnaire forms through such mediums was deemed an appropriate method by the researcher.
3.9 Data Analysis
The regression analysis has been implemented as the primary data analysis method through the SPSS application incorporated with the survey data set. Brook and Arnold (2018) opine that regression analysis is crucial for informed decision-making, reducing customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch-analysis costs and targeting chosen samples in a coherent and statistically well-devised manner. It was introduced as the next part of a quantitative “data analysis method” as a software-specific utility for data relation establishment. It assisted in determining the coherent relationship between the two variables: customer engagement and brand reputation. The subset procured in the research sampling has been processed through SPSS for categorical number-based analysed data, deterring the link and ratio establishment between different dependent and independent variables in this study.
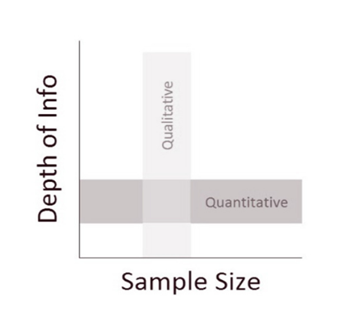
Figure 3.8: Data analysis requirements
(Source: Warren, 2020)
The figure above highlights the requirements of data analysis requirements in relation to information depth and sample size. Due to the limited population subset information, a maximised sample size is analysed in this study. According to Desboulets (2018), regression analysis is a highly cost-effective and fast-processed information relation establishment appropriate for scholars and researchers. Considering that, data analysis procurement has been subject to strategically determining the interrelation between the variables focused on in this study. Quantitative study and data analytics have helped to position an informed analysis of a non-random sample.
3.10 Accessibility, Reliability and Validity
The articles and peer-reviewed journals have been chosen for universally accessible sources, which are all in the English language, to ensure futurecustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment research interests of academic readers worldwide. This paper has been conducted in English to ensure readers from all universal disciplines can access and understand the comparative materials and determinants considered in this study. Furthermore, all sources collected and cited in this study have been collected from authentic and reliable mediums to ensure subject information reliability. Moreland (2018) opined that the reliability and validity ofcustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment research are based on strategic information source knowledge and objective guarantee. All the outside information sources have been appropriately referenced and cited throughout the work. The population subset selected for the analysis has been approached through standard mediums.
3.11 Ethical Consideration
Thecustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment researcher has dutifully abided by all the regulations under the “Data Protection Act 2018 (DPA)”, ensuring no privacy and personal information breach of the respondents. The survey forms included details regarding the survey purpose, publication fields,university source and contact number for clarity. The ethical consideration of secondary sources has been maintained, ensuring no plagiarism or copyright embellishment. Fleming and Zegwaard (2018) noted that researchers must guarantee follow-up and respect ethical consideration, considering no breach, force, or missing crucial information or falsification. The participants in the close-ended survey were provided priorly with all information regarding consented, voluntary participation, anonymous entries on choice, and removal of personal data information from survey responses at any point under the GDPR (Truong et al., 2021). The study accounted for a detailed checklist of all data protection and storage encryption facilities for providing absolute privacy and confidentiality guarantees to all the participants.
3.12 customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentResearch Timeline
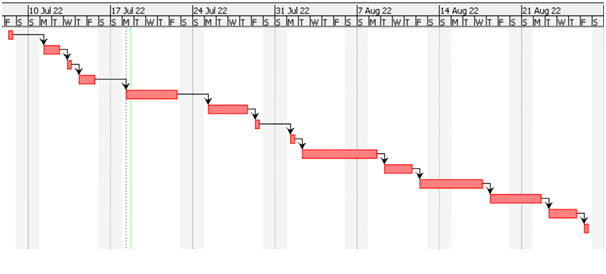
Figure 3.9: Research Timeline
(Source: Refer to Appendix I)
The research is expected to involve 1.5 months of step-by-step analysis, data collection, studying, findings and discussion analysis. The figure above identifies the entire research timeline starting from 8th July 2022 and finally being submitted on 26th August 2022. The first step, “Developing Aim and Objectives”, began on 11th July for a 2 days duration, prioritising research expectations and the above section's impact on the entire study topic [Refer to Appendix I]. The most time-consuming step is the “survey questionnaire development”, which was completed by 22nd July 2022, with 100 respondents' answers for findings and the discussion section. Other areas required 4 days for completion, between 25th July 2022 and 28th July 2022, marking 4 days for the Literature review’s initial draft. The image highlights literature gaps identification and study expectations impact for on day on 29th July 2022. There are, in total, 14 primary activities, with the last one denoting paper completion, where the preliminary survey conduction took place between 14th July 2022 to 15th July 2022.
3.13 Summary
Due to its epistemological relativism and emotion-dimension relativeness, the pragmatic research philosophy was used in this study, as suggested by the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch onion model below. Customer-specific characteristics primarily address their behavioural and emotional tendencies to attract consumers to advertisements and influence their purchase decisions. On the other hand, pragmatism is the analytical tool businesses use for their customer and brand data structure to ensure strategic productivity. Pragmatism philosophy guided this study's activities, observations, and subsequent analysis in light of these elements. The various techniques used to establish a time-bound research “analysis and findings” process are highlighted in this chapter under Saunders' research onion. The dissertation's comparative and trustworthy analytical examination of the linkages between “social media customer involvement” and brand reputation is described in detail in this chapter.
Chapter 4: Research findings and Discussion
According to the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch-based accumulated data regarding the exploding link between customer engagement and brand reputation in the age of social media in the USA, there are multiple aspects of evaluations taking place. One of the significant findings coming into the orientation or observations is accepting that the most common individuals who have responded to the research are between 21 and 30 years old. Based on this, it can be stated that the most significant number of social media-imposed social media-biased customers associated with the present scenario are the ones within the agent of 21 to 30 years.
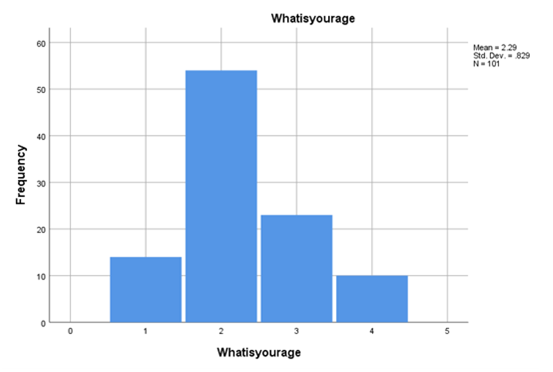
Figure 4.1: Age range of responders
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Moving forward to the evaluation, there is a divisible aspect of gender-based evaluations. Critical states that almost 58.6% of respondents are female and tend to be impressed by the influential movements of social media and the big brands decorating or increasing its renowned atmosphere for business operations. Even findings are coming in where the weight of individuals who get imposed who get biased being male through the help of social media represented by social media presented evaluations are 35.4%. It can also be stated that the number of responders associated with the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch study is female, and the number is white for females rather than males. Even the potential reputation building for any business brand or customer engagement development for the business plan as a decisive criterion for female customers due to the higher rate of social media usage is being identified through this research orientation.
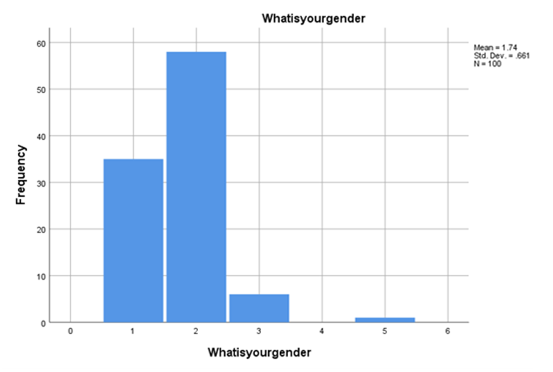
Figure 4.2: Gender bases
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Now moving forward to evaluating the amount of time an individual spends on social media platforms from the 100 participants we have boat it or who have been selected for the complement of thecustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment research as given the responses and the evaluation has come in based on that. The most influential fact of consideration coming into the assessment is the percentage of states held by every particular proposition assigned to individuals. According to the findings, it can be stated that almost 26.3 individuals or more than 26 individuals use social media for more than 5 hours a day associated with all the ads and brand base scenarios along with completing other personal activities.According to the regression results aligned with these variables in Figure 4.2, the standard deviation is marked at .661. On the other hand, 21.2% of respondents voted in favour of using social media 6 hours plus a day, which is quite an effect of an abbreviation because it is not an easy task to use a social media platform for more than 6 hours. Even this generates a strong probability of being influenced by social media advertising or social media-based brand product mobility acquisition. According to the finding, it is found that 30.3% of respondents used to use social media platforms for more than two hours or for close to 2 hours which is very influential and adequate to see. Even this can also be stated that the individuals who are working professionals are primarily included in this 30% who use social media for only 2 hours a day.
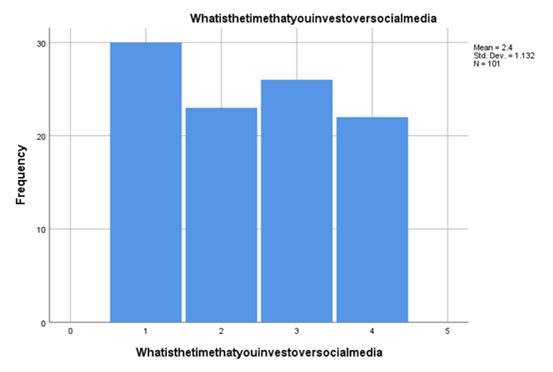
Figure 4.3: Time of social media usage
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Based on this subsequent evaluation, the most probable or most effective platform for the completion of activities like generating a more significant amount of customer engagement and brand reputation development in the age of social media gets accomplished. In this part, according to the evaluation(Figure 4.3), it is evaluated that the highest amount of social media engagement tends to take place on the social media platform Instagram, with the variables highlighting a 1.132 standard deviation and 2.4 mean value. Schielzeth et al. (2020) opined that a Std. Deviation above 1 is considerably high, representing the above mean data points, which is the case in Figure 4.3 results. So, it is pretty influential that any brand willing to market its product or develop a good brand reputation needs to have a significant Instagram handle. Along with this, it is imperative that the organisation also give more excellent value to the social media platform Facebook as it is also used by 29.7% of the responders with more than 2.93 billion users around the globe. As the number is staggering, so does the impact-making ability of both social media platforms are also very impactful. Even it is also found that 21.8% of individuals used to operate Twitter the most apart from all the other social media platforms, so there is a thick possibility of utilising Twitter-based marketing or brand value generation.
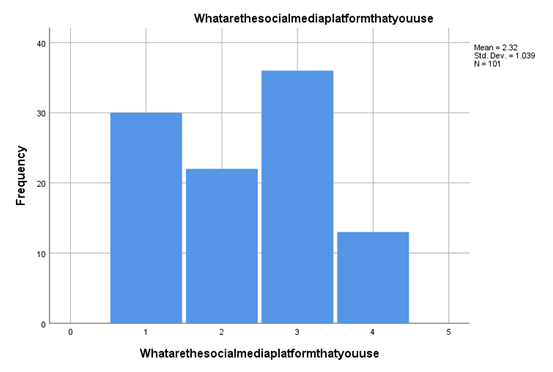
Figure 4.4: Most used social media platform
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Along with this perception of brand marketing and awareness generation for the brand, reputation has been identified through the evaluation of thiscustomer involvement and brand reputation assignment research. According to customer perception, it is determined that more than 75% of customers or precisely 75.8 per cent of customers, believe that social media is the leading marketing platform in the present global scenario for all organisations operating with greater significance and opportunities. Along with this, those who don't believe that social media is a leading marketing platform have their own set of doubts associated with this because digital marketing is completed through radio channels, television and others and is not a part of social media accounts.
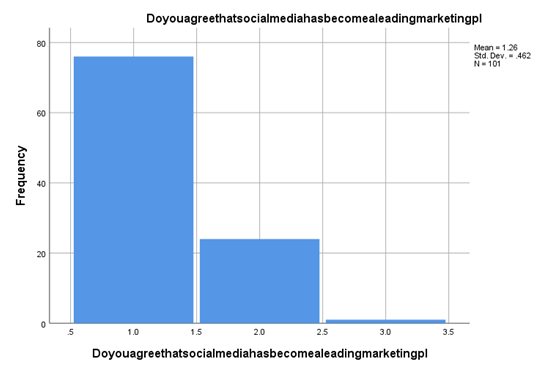
Figure 4.5: Social media as a marketing platform
(Source: Self-created by the author)
Even though findings are coming into the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch, it is available whether encouraging social media marketing is impactful for the customer's perspective development or not. The best resource-based identification suggests that almost 76.5% of customers believe that social media is efficient enough to develop marketing content or context in the customer's mind to benefit the organisation. Along with this, it can also be stated that the consumer also believes social media has the benefit of making an impactful or developing impact on the customer perspective for any brand (Sánchez-Casado, Artal-Tur and Tomaseti-Solano, 2019). This signifies that any customer brand having the efficiency of developing a more significant amount of social media value to its name can generate a more substantial amount of customer engagement in its own business and create a more considerable amount of brand reputation. On the other hand, it can also be stated that any brand that can develop a more significant amount of brand reputation can generate tremendous customer engagement.
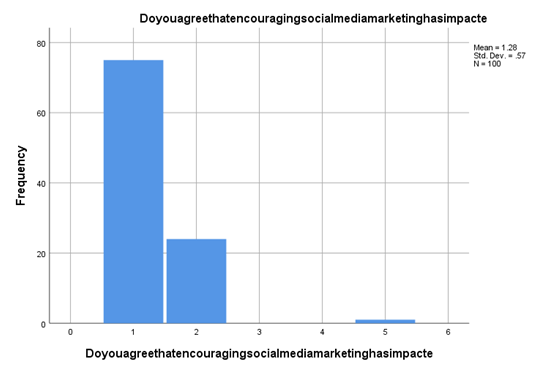
Figure 4.6: Social media in customer perspective development
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Another significant finding from the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch clearly states that there are different dimensions of understanding between the customers related to the efficiency of social media to generate a higher amount of sales for any organisation. According to the findings, only 13% of the respondents or customers believe that social media can not generate a more significant amount of sales and revenue for the organisation (Salomon and Brown, 2019). And another 11% of individuals or customers believe that social media is inadequate for developing sales channels or for organisations. On the other hand, more than 20% of individuals feel that social media is the gateway to more significant sales for new organisations. Along with this, it is also required to be established or stated that 35% more individuals have their say that social media can be used as a platform for sales and reputation for small businesses. Based on the evaluation, it can be stated that social media is efficient enough for small and medium enterprises to encompass or generate more significant sales.
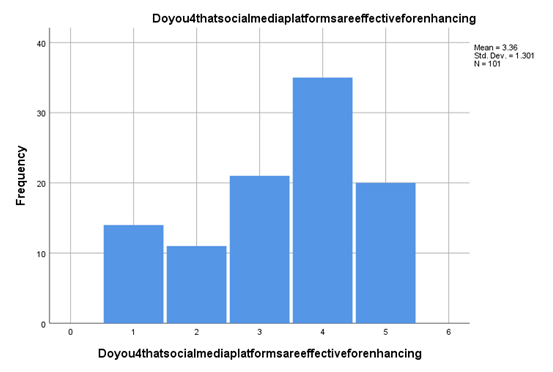
Figure 4.7: Social media & its sales generation ability
(Source: Created by the researcher)
According to customers' beliefs, social media is one of the platforms which can be used for positive and negative marketing, too (Liu, Shin and Burns, 2021). As any brand can develop its reputation through social media, there is also another chance coming in where the brand can lose its reputation without taking a scarce set of time. According to 52% of the customers, opportunities are coming into the path of the customers when it can diversify its customer base through social media but also can lose its reputation through a not efficient move taken for the benefit of the organisation or intentionally taken for more help. So along with having benefits, there is a more significant amount of risk associated with social media too.
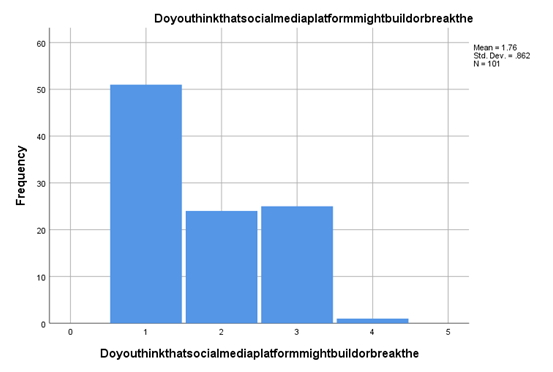
Figure 4.8: Social media & its risks
(Source: Created by the researcher)
According to the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch-oriented data and validation of the data, it is pretty efficient that more than 56% of respondents believe that social media influences customer purchasing decisions. So it can mistake it that any individual willing to buy any dress or shop for any product from the organisation is based on their decision through the help of a few social media welfare activities or any activities running in the present social media forms (Li, Teng and Chen, 2020). The brand having the ability to run its business with a solid proposition towards social media overviews on new trends associated with social media gets an efficient chance to accumulate a more significant amount of customers and the purchasing decision of the customer working in its favour.
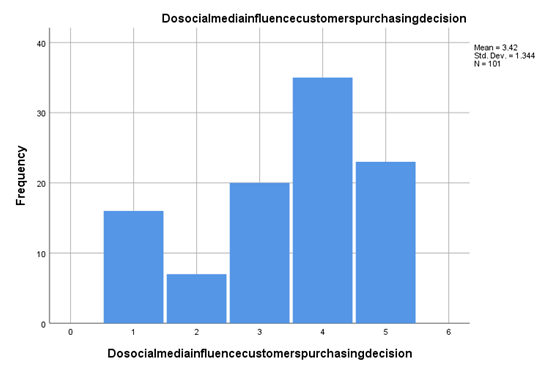
Figure 4.9: Social media influence on customer purchasing decision
(Source: Created by the researcher)
According to the understanding of the customer perception and evaluation, it can clearly be stated that the customers are the responders associated with this research believes the fact that with the impact-making ability of social media, the new customer-based organisations are much more into a more significant investment over marketing strategies associated with social media. The brands believe the more they can invest in social media, the more brands can earn from it (de Oliveira Santini et al., 2020). So there are probably opportunities where this social media can be utilised as the best marketing platform for the brands based on customer perspective and the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch overview associated with these findings.
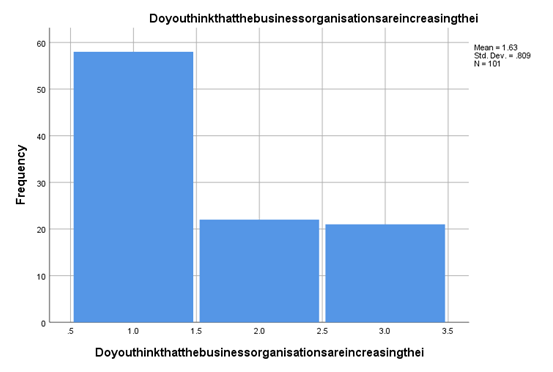
Figure 4.10: Social media marketing investments by brands
(Source: Created by the researcher)
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendation
5.1 Conclusion
This chapter speculates upon the “data information collection” and secondary data incurred in the study, bringing forward a conclusive assessment. The objectives are analysed here in a link to the information extracted in the analysis and literature review. According to Chapter 1.2, the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch aimed to determine the association between customer engagement and brand reputation in relation to the digitalisation prospects of social media. Chapter 2 analysed all secondary information sources, stabilising a relationship between the variables. The significance of the conceptual framework is directed toward procuring a clear diagram-based perception of the interrelated factors and their study scope. Chapters 3 and 4 were this study's main methodological strategies and SPSS findings. This chapter is essential as a subjective and analytical assessment of research expectations and modes of completion.
5.2 Linking the customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentObjectives
5.2.1 Linking with Objective 1
Chapter 2.1 states the rising screentime and activity of “social media users” worldwide is influencing USA brands to adopt these tools for their product management and advertisement. In Chapter 2.2, “social media intervention," theories and engagement strategies are implemented by businesses to increase market interest and online traffic. Hinson et al. (2019) opine that “customer engagement theory” is a practical and highly responsive theoretical framework impacting customer behaviour and brand interest. Chapter 2.2 from the literature review also aligns modes and strategic models affecting customer response to increasing purchase motivation in the USA marketing policies, as is also observed in Figure 4.7. Therefore, the direct impact of “customer engagement theories” is observed to impact customer retention, increased marketing sales, loyalty and eventually reputation, linking this observation with Objective 1.
5.2.2 Linking with Objective 2
Chapter 2.2 points out the utility of contact sharing and customers’ brand reviews are elemental in gaining brand market interest upon proper customer retention. Mason et al. (2021) opine that, following the user traffic rise in “social media platforms” during COvid-19 restrictions, marketing strategies have prospectively shifted to this medium. Customer engagement in such advertisement modes is fuelled by high-quality visuals, brand awareness, market interest, product variation and online presence, aligned with Figure 4.3 analysis. US Gen Z and Millenials form the primary online crowd for brands to gain competitive positions in. Speculating on the consequential impact of customer interest on engagement and follow-up increase in brand revenue, Objective 2 can be appropriately linked to these sections.
5.2.3 Linking with Objective 3
According to Chapter 4 observations, 76.5% of respondents believed in social media's efficiency in procuring marketing materials essential for customer engagement. The regression analysis initiated with 100 respondents and 10 questions also showed that 52% of consumers agreed that a brand's workplace and product availability diversification extensively impacted their preference, holding the brand's reputation high. The results from Chapter 4 can be appropriately linked with Objective 4, highlighting the directly proportional relationship between the two variables.
5.2.4 Linking with Objective 4
Chapter 2.4 shows that social media platform in the United States has contributed significantly to the business organisation's popularity and rising value offer, which has helped overall business growth. This popularity and expanding brand reputation have impacted customers' perceptions of the products offered by the companies, as well as how they perceive the brand. As can be seen, the number of online users in the United States is growing by the day, and businesses are focusing on capturing this large audience which is a highly heavy users media outlet, in order to better their marketing efforts. The brand can provide timely and practical solutions to client concerns and assist them in making purchasing decisions by utilising the social media platform. Hence, this chapter can be suitably linked with Objective 4 as an improvement recommendation.
5.3 Recommendations
An essential recommendation is the inclusion of a customer-brand engagement programme, where customers can openly engage with the development prospects of the brand. The improvement of brand reputation is dependent on the customer base's perception of the brand's market value, responsibility and product/service quality. Therefore, change management is also recommended, adding sustainable measures and consumer market transparency into the framework. Customers feel social media is effective enough to create advertising messages or context in the marketplace that will benefit the organisation. Customer media marketing is the dominating marketing tool in the world's current setting for all organisations operating with greater relevance and potential, according to customer opinion. The final recommendation is to add quarterly operational assessment planning where the link's impact will be monitored for influence and troubleshooting. Keeping the survey questions simple, with the inclusion of survey pre-test, rating-scale question inclusion and audience consideration improvement are further recommended.
5.4 Research Limitations
Insufficient customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch materials on the chosen subject matter limited the expected output of the study, with rising incoherence in link bridging between the variables mentioned. The study lacked a more concretised and well-established secondary method implementation for source-information reliability. Brand reputation is vital to industry-specific market interest and relevance, requiring the strategic identification of all impacting components for structured growth. According to the data provided and analysed, regression analysis using SPSS required a more specific data subset for predictive validity. The research has been conducted under time-bound and low-cost procedures, therefore, limiting the delivery expectations appropriate for this subject matter. Questionnaire surveys are often perceived to be unreliable due to respondents' dishonesty, incomplete fill-ups and data manipulation (Mechanic, 2021). This added to the pre-conceived scepticism around digital survey options using social media distribution modes. Lastly, an important research limitation has been the limited reach and answering of the proposed research questions opening up the possibilities for more structured and well-planned future research.
5.5 Future Scope
The incompetencies and limitations of this customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearch, adding the research questions still inadequately answered, exhibited the scope for more informed and documented future research. The lack of proper subject-based information led to a limited and scarcely factual literature review, mainly depending upon the questionnaire survey for analysis. However, adding this research has added a newfound opportunity for the disciplinary approach of upcoming researchers with the same field interest. Another scope is the research introduction of this context in the academic sphere, leading to R&D investments for brand management development and the U.S. industrial progression. The scope of utilising social media to influence and attract customer engagement and, as causation, improve brand reputation is a highly realistic and innovative idea. Investments would motivate more researchers and professionals to raise their interest in this subject, providing the scope for study progress in the upcoming 2-3 years. The research questions and results are an opportunity for other customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentresearchers to find a bringing stance into their field's application development.
Reference List
Ahmad, A.H., Idris, I., Mason, C. and Chow, S.K., (2019). The impact of young celebrity endorsements in social media advertisements and brand image on the purchase intention of young consumers. International Journal of Financial Research, customer involvement and brand reputation assignment10(5), pp.54-65.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Arman-Haji-Ahmad/publication/336471644_The_Impact_of_Young_Celebrity_Endorsements_in_Social_Media_Advertisements
_and_Brand_Image_Towards_the_Purchase_Intention_of_Young_Consumers/links/5da1e8e745851553ff8c14ba/The-Impact-of-Young-Celebrity-Endorsements-in-Social-Media-Advertisements-and-Brand-Image-Towards-the-Purchase-Intention-of-Young-Consumers.pdf
Braekman, E., Berete, F., Charafeddine, R., Demarest, S., Drieskens, S., Gisle, L., ... and Van Hal, G. (2018). Measurement agreement of the self-administered questionnaire of the Belgian Health Interview Survey: Paper-and-pencil versus web-based mode. PLoS One, 13(5), e0197434. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/articleid=10.1371/journal.pone.0197434
Brook, R. J., and Arnold, G. C. (2018). Applied regression analysis and experimental design. CRC Press. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.1201/9781315137674/applied-regression-analysis-experimental-design-richard-brook-gregory-arnold
Bueger, C., and Gadinger, F. (2018). Doing praxiography: Research strategies, methods and techniques. In International practice theory (pp. 131-161). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-73350-0_6
Cachero-Martínez, S., and Vázquez-Casielles, R. (2021). Building consumer loyalty through e-shopping experiences: The mediating role of emotions. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 60, 102481. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969698921000473
Cambra-Fierro, J. J., Fuentes-Blasco, M., Huerta-Álvarez, R., and Olavarría, A. (2021). Customer-based brand equity and customer engagement in experiential services: insights from an emerging economy. Service Business, 15(3), 467-491. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11628-021-00448-7
Choi, L., and Burnham, T. (2020). Brand reputation and customer voluntary sharing behavior: the intervening roles of self-expressive brand perceptions and status-seeking. Journal of Product & Brand Management, 30(4), 565-578. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JPBM-12-2019-2670/full/html
Cox, K. A. (2019). Quantitative research designs. Research Design and Methods: An Applied Guide for the Scholar-Practitioner. https://books.google.com/bookshl=en&lr=&id=DgKPDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT109&dq=quantitative+research
+design&ots=dCkYgcSR2y&sig=_5gh5QEsB5UR9J8rpAWurEubfKU
Cramer-Petersen, C. L., Christensen, B. T., and Ahmed-Kristensen, S. (2019). Empirically analysing design reasoning patterns: Abductive-deductive reasoning patterns dominate design idea generation. Design Studies, customer involvement and brand reputation assignment60, 39-70. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142694X1830067X
DAM, S.M. and DAM, T.C., (2021). Relationships between service quality, brand image, customer satisfaction, and customer loyalty. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 8(3), pp.585-593.https://www.koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO202106438543453.pdf
Dash, G., Kiefer, K. and Paul, J., (2021). Marketing-to-Millennials: Marketing 4.0, customer satisfaction and purchase intention. Journal of business research, 122, pp.608-620.https://e-tarjome.com/storage/btn_uploaded/2021-01-26/1611643625_11963-etarjome%20English.pdf
De Keyser, A., Verleye, K., Lemon, K. N., Keiningham, T. L., and Klaus, P. (2020). Moving the customer experience field forward: introducing the touchpoints, context, qualities (TCQ) nomenclature. Journal of Service Research, 23(4), 433-455. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1094670520928390
de Oliveira Santini, F., Ladeira, W.J., Pinto, D.C., Herter, M.M., Sampaio, C.H. and Babin, B.J. (2020). Customer engagement in social media: a framework and meta-analysis. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48(6), pp.1211-1228. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11747-020-00731-5
Desboulets, L. D. D. (2018). A review on variable selection in regression analysis. Econometrics, 6(4), 45. https://www.mdpi.com/370092
Dixon, S. (2022). Percentage of U.S. population who currently use any social media from 2008 to 2021. Statista. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/273476/percentage-of-us-population-with-a-social-network-profile/#:~:text=Share%20of%20U.S.%20population%20who%20use%20social%20media%202008%2D2021
&text=This%20equals%20approximately%20223%20million%20U.S.%20social%20media%20users%20as%20of%202
020.&text=According%20to%20estimates%2C%20the%20number,4.2%20billion%20in%20January%202021. [Accessed 17th July 2022]
Durmaz, Y., Çavuolu, S. and Özer, Ö., (2018). The effect of brand image and brand benefit on customer loyalty: the case of Turkey. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(5), pp.528-540.https://www.bingol.edu.tr/documents/tam%20metin(10).pdf
Fleming, J., and Zegwaard, K. E. (2018). Methodologies, Methods and Ethical Considerations for Conducting Research in Work-Integrated Learning. International Journal of Work-Integrated Learning, 19(3), 205-213. https://eric.ed.gov/id=EJ1196755
Florenthal, B. (2019). Young consumers’ motivational drivers of brand engagement behavior on social media sites: A synthesised U&G and TAM framework. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JRIM-05-2018-0064/full/html
GuillenJr, N.B., (2018). Understanding the effect of Facebook in the relationship of self-concept and brand image on smartphone brand satisfaction. ISSN No. 2362-7832, p.418.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ian-Benedict-Mia/publication/341368933_Assessing_the_impacts_of_green_supply_chain_management_and_frugal_
product_innovation_to_the_sustainability_of_social_enterprises_in_the_Gawad_Kalinga_Enchanted_Farm
/links/5ebcb09e92851c11a8677f46/Assessing-the-impacts-of-green-supply-chain-management-and-frugal-product-innovation-to-the-sustainability-of-social-enterprises-in-the-Gawad-Kalinga-Enchanted-Farm.pdf#page=423
Hermanda, A., Sumarwan, U. and Tinaprillia, N., (2019). The effect of social media influencer on brand image, self-concept, and purchase intention. Journal of Consumer Sciences, 4(2), pp.76-89.https://jurnal.ipb.ac.id/index.php/jcs/article/download/26525/17503
Hinson, R., Boateng, H., Renner, A., and Kosiba, J. P. B. (2019). Antecedents and consequences of customer engagement on Facebook: An attachment theory perspective. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, customer involvement and brand reputation assignment13(2), 204-226. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JRIM-04-2018-0059/full/html
Hurley, E., Dietrich, T., and Rundle-Thiele, S. (2021). Integrating theory in co-design: an abductive approach. Australasian Marketing Journal, 29(1), 66-77. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1839334921998541
Išorait, M., (2018). Brand image development. Eco Forum Journal, 7(1), pp.1-6.https://www.ceeol.com/content-files/document-1087626.pdf
Išorait, M., (2018). Brand Image Theoretical Aspects. Integrated Journal of Business and Economics, 2(1), pp.116-122.https://caritulisan.com/media/255742-brand-image-theoretical-aspects-305e74e4.pdf
Kesmodel, U. S. (2018). Crosssectional studies–what are they good for. Acta obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, 97(4), 388-393. https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/aogs.13331
Kim, R.B. and Chao, Y., (2019). Effects of brand experience, brand image and trust on brand building process: The case of Chinese millennial generation consumers. Journal of International Studies, 12(3).https://jois.eu/files/1_670_Kim_Chao.pdf
Längler, M., Brouwer, J., and Gruber, H. (2019). Data collection for mixed method approaches in social network analysis. In Mixed Methods Social Network Analysis (pp. 25-37). Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780429056826-4/data-collection-mixed-method-approaches-social-network-analysis-manuel-l%C3%A4ngler-jasperina-brouwer-hans-gruber
Li, M.W., Teng, H.Y. and Chen, C.Y., (2020). Unlocking the customer engagement-brand loyalty relationship in tourism social media: The roles of brand attachment and customer trust. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 44, pp.184-192. https://e-tarjome.com/storage/btn_uploaded/2020-11-15/1605418866_11581-etarjome%20English.pdf
Liu, X., Shin, H. and Burns, A.C., (2021). Examining the impact of luxury brand's social media marketing on customer engagement: Using big data analytics and natural language processing. Journal of Business Research, 125, pp.815-826. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Andres-Artal-Tur/publication/331447979_Social_Media_Customers'_Experience_and_Hotel_Loyalty_Programs/links/
5cfe31d24585157d15a00fc8/Social-Media-Customers-Experience-and-Hotel-Loyalty-Programs.pdf
Majeed, M. H. (2019). Pragmatist inquiry in to consumer behaviour research. Philosophy of Management, 18(2), 189-201. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40926-018-0103-4
Mason, A. N., Narcum, J., and Mason, K. (2021). Social media marketing gains importance after Covid-19. Cogent Business & Management, 8(1), 1870797. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/23311975.2020.1870797
Mechanic, M. (2021). Jackpot: How the Super-Rich Really Live—and How Their Wealth Harms Us All. Simon and Schuster.customer involvement and brand reputation assignmenthttps://books.google.co.in/bookshl=en&lr=&id=9vvtDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=Questionnaire
+surveys+are+often+perceived+to+be+unreliable+due+to+respondents%27+dishonesty,+incomplete+fillups+and
+data+manipulation.&ots=knfJdxz1cK&sig=rawgJDru7TDnQ6RHGSUZoIaisDc
Melnikovas, A. (2018). Towards an explicit research methodology: Adapting research onion model for futures studies. Journal of Futures Studies, 23(2), 29-44. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Aleksandras-Melnikovas/publication/333388233_Towards_an_explicit_research_methodology_Adapting_research_onion_
model_for_futures_studies/links/5d47c8404585153e593cfbec/Towards-an-explicit-research-methodology-Adapting-research-onion-model-for-futures-studies.pdf_sg%5B0%5D=started_experiment_milestone&origin=journalDetail
Mitchell, A., and Education, A. E. (2018, July). A review of mixed methods, pragmatism and abduction techniques. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Research Methods for Business & Management Studies (pp. 269-277). https://books.google.com/bookshl=en&lr=&id=gU9mDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA269&dq=inductive+approach
+in+pragmatism&ots=Eug6aYlXPY&sig=wJ0bRpY52krQCZ8GpsUkBklmiVw
Mohamad, B., Abdullah, S.N., Akanmu, M.D. and Raji, R.A., (2022). To What Extent Are Credibility and Attractiveness of Social Media Influencer Important in Developing Positive Brand Image and Customer Attitude. In Mixed Methods Perspectives on Communication and Social Media Research (pp. 180-201). Routledge.https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781003265887-14/extent-credibility-attractiveness-social-media-influencer-important-developing-positive-brand-image-customer-attitude-bahtiar-mohamad-siti-norain-abdullah-muslim-diekola-akanmu-ridwan-adetunji-raji
Mohammed, A. and Rashid, B., (2018). A conceptual model of corporate social responsibility dimensions, brand image, and customer satisfaction in Malaysian hotel industry. Kasetsart Journal of social sciences, 39(2), pp.358-364.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452315118302182
Moreland, C. (2018). Chasing transparency: Using disparate impact analysis to assess the (in) accessibility of dual enrollment composition. Writing assessment, social justice, and the advancement of opportunity, 171-199. https://wac.colostate.edu/books/assessment/chapter5.pdf
Muninger, M. I., Mahr, D., and Hammedi, W. (2022). Social media use: A review of innovation management practices. Journal of Business Research, 143, 140-156. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296322000510
Oneiu, D. D. (2020). The Impact of Social Media Adoption by Companies. Digital Transformation. Studia Universitatis Vasile Goldi Arad, Seria tiine Economice, 30(2), 83-96. https://sciendo.com/downloadpdf/journals/sues/30/2/article-p83.xml
Parhizkar, T., Hogenboom, S., Vinnem, J. E., and Utne, I. B. (2020). Data-driven approach to risk management and decision support for dynamic positioning systems. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 201, 106964. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0951832019307318
Quesenberry, K. A. (2020). Social media strategy: Marketing, advertising, and public relations in the consumer revolution. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. https://books.google.com/bookshl=en&lr=&id=QWTyDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR3&dq=Another+disadvantage
+of+using+social+media+as+a+bridge+between+customer+engagement+and+brand+reputation+is+the+heavy
+advertisement+reliance+&ots=BtrmVpBLoN&sig=Kp74u5kCeeo_DW5dFH_2wlZwb50
Raza, M., Frooghi, R., Abd Rani, S.H.B. and Qureshi, M.A., (2018). Impact of brand equity drivers on purchase intention: A moderating effect of entrepreneurial marketing. South Asian Journal of Management Sciences, 12(1), pp.69-92.https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0bd6/371adec14d56eccd01a7aea2e3e52ab812ca.pdf
Sahin, M. D., and Öztürk, G. (2019). Mixed Method Research: Theoretical Foundations, Designs and Its Use in Educational Research. International Journal of Contemporary Educational Research, 6(2), 301-310. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/880619
Salomon, I. and Brown, C.S., (2019). The selfie generation: Examining the relationship between social media use and early adolescent body image. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 39(4), pp.539-560. https://uknowledge.uky.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgiarticle=1117&context=psychology_etds
Sánchez-Casado, N., Artal-Tur, A. and Tomaseti-Solano, E., (2019). Social Media, Customers' Experience, and Hotel Loyalty Programs. Tourism Analysis, 24(1), pp.27-41. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Andres-Artal-Tur/publication/331447979_Social_Media_Customers'_Experience_and_Hotel_Loyalty_Programs/links/
5cfe
31d24585157d15a00fc8/Social-Media-Customers-Experience-and-Hotel-Loyalty-Programs.pdf
Schielzeth, H., Dingemanse, N. J., Nakagawa, S., Westneat, D. F., Allegue, H., Teplitsky, C., ... and ArayaAjoy, Y. G. (2020). Robustness of linear mixedeffects models to violations of distributional assumptions. Methods in ecology and evolution, customer involvement and brand reputation assignment11(9), 1141-1152. https://besjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/2041-210X.13434
Siddiqui, M.S., Siddiqui, U.A., Khan, M.A., Alkandi, I.G., Saxena, A.K. and Siddiqui, J.H., (2021). Creating electronic word of mouth credibility through social networking sites and determining its impact on brand image and online purchase intentions in India. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(4), pp.1008-1024.https://www.mdpi.com/0718-1876/16/4/57/pdf
Statista (2021). Leading retail brands in the United States on social media in 2020, by user engagement. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/257762/us-retailers-ranked-by-social-media-engagement/ [Accessed 18th July 2022]
Statista (2022). Brands on social media - statistics & facts. Available at: https://www.statista.com/topics/2057/brands-on-social-media/#topicHeader__wrapper [Accessed 18th July 2022]
Stratton, S. J. (2021). Population research: convenience sampling strategies. Prehospital and disaster Medicine, 36(4), 373-374. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/prehospital-and-disaster-medicine/article/population-research-convenience-sampling-strategies/B0D519269C76DB5BFFBFB84ED7031267
Subedi, D. (2016). Explanatory sequential mixed method design as the third research community of knowledge claim. American Journal of Educational Research, 4(7), 570-577. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/downloaddoi=10.1.1.1079.177&rep=rep1&type=pdf
witaa, M., Gamrot, W., Reformat, B. and Biliska-Reformat, K., (2018).The influence of brand awareness and brand image on brand equity–an empirical study of logistics service providers. Journal of Economics & Management, 33, pp.96-119.http://cejsh.icm.edu.pl/cejsh/element/bwmeta1.element.cejsh-751d3eb1-92f8-46dc-8a1d-9edeefe4a20f/c/06.pdf
Truong, N., Sun, K., Wang, S., Guitton, F., and Guo, Y. (2021). Privacy preservation in federated learning: An insightful survey from the GDPR perspective. Computers & Security, 110, 102402. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167404821002261
Vinerean, S., and Opreana, A. (2021). Measuring customer engagement in social media marketing: A higher-order model. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(7), 2633-2654. https://www.mdpi.com/0718-1876/16/7/145
Vohra, A., and Bhardwaj, N. (2019). Customer engagement in an e-commerce brand community: An empirical comparison of alternate models. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/JRIM-01-2018-0003/full/html
Waluya, A.I., Iqbal, M.A. and Indradewa, R., (2019). How product quality, brand image, and customer satisfaction affect the purchase decisions of Indonesian automotive customers. International Journal of Services, Economics and Management, 10(2), pp.177-193.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rhian-Indradewa/publication/335227247_How_product_quality_brand_image_and_customer_satisfaction_affect_
the_purchase_decisions_of_Indonesian_automotive_customers/links/5dce0a40299bf1b74b425dec/How-product-quality-brand-image-and-customer-satisfaction-affect-the-purchase-decisions-of-Indonesian-automotive-customers.pdf
Wang, X., and Cheng, Z. (2020). Cross-sectional studies: strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations. Chest, 158(1), S65-S71. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012369220304621
Warren, K. (2020). Qualitative Data Analysis Methods 101: The “Big 6” Methods + Examples. Available at: https://gradcoach.com/qualitative-data-analysis-methods/ [Accessed 18th July 2022]
Wynn, D. C., and Maier, A. M. (2022). Feedback systems in the design and development process. Research in Engineering Design, customer involvement and brand reputation assignment1-34. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00163-022-00386-z
Appendices
Appendix I: customer involvement and brand reputation assignmentResearch Timeline
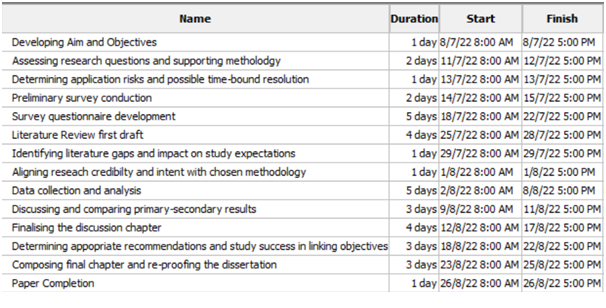
(Source: Self-created by the author)












