Critical Analysis on HTC corporation case study
Question
QUESTION ONE
Using the lenses of resource-based and institution-based, nominate and justify what you believe will be the drivers of success for the business turnaround?
QUESTION TWO
Considering the competitive dynamics, how should HTC position for its future markets?
QUESTION THREE
Suggest market entry modes that HTC could consider when entering a new foreign market? What factors should be taken into account?
QUESTION FOUR
Propose a structure that might suit the company for its turnaround and justify. What relationships could it consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholders and how may these provide long-term benefit?
Answer
Introduction
The HTC corporation case study analysis considers the words of Heymanet al. (2019, p.275) that the business strategy relates to the decisions and actions that are taken by the business organizations for reaching the business goals and objectives. The present study is based on the HTC corporation case study, which is a Taiwanese company of consumer electronics. HTC has experienced a significant fall from a higher position in the respective industry and is now planning for a business turnaround. The present HTC corporation case study analysis identifies the drivers of success for HTC’s turnaround plan with the usage of the resource-based and institution-based view. The developed study based on the HTC corporation case study explains the way in which the company can position itself for the future and also highlights the modes of market entry.
?
Question1
Drivers of success for the business turnaround
From the analysis of the HTC corporation case study, it has been identified that although the share value of the company has reduced significantly as compared to the peak in the year 2011, the organization has still not lost hope and planning for business turnaround using the virtual reality technology-based products. According to Parolaet al., (2017, p.122) there are some critical factors that can help organizations in making the business turnaround successful. The resource-based view and the institution-based view models would help in describing and justifying these drivers in relation to HTC’s turnaround business plan.
Resource-based view
In recent research on HTC corporation case study, Schmitt et al., (2019, p.553) have explained that business turnarounds involve situations like loss of competitiveness, experiencing a threat of sustenance, and regaining a competitive advantage in the market. Therefore, it is vital to consider the resources that help organizations in gaining a competitive advantage when accessing the drivers of recovery. It has been identified in regards to the HTC corporation case study that successful business turnaround plans are based on resources that possess four major characteristics; value, rarity, inimitability, and non-substitutability. Therefore in order to drive the success of the business turnaround plan at HTC, the top management has to ensure that their resources are rare, valuable, inimitable and non-substitutable. Virtual reality has become one of the big technological trends in the consumer electronics market.

Figure.1: Resource-based view (Source: Rajaramet al., 2018, p.10)
However, the HTC corporation case studyanalysis has helped in identifying that although the technology virtual reality that the company is utilizing is valuable and rare among the other organizations in the same industry, it is not inimitable and non-substitutable. For instance, the computer organisation Sony is also planning to adopt virtual reality to upgrade its products to lead over HTC. Therefore, such product diversification strategy with imitable and substitutable resources cannot allow the company to gain long term competitive advantage in the market. Other important resources for the company that can drive the turnaround plan into success are knowledge regarding marketing and business strategy (Liang et al., 2018, p.315). As per the readings of the HTC corporation case study, patents are another important resource for the organisation that can enable it to make its products inimitable, pardoning the sustained competitive advantage in the market making the turnaround successful.
Institution-based view
According to Wild and Lockett (2016, p.850), institution-based view models concentrate on the dynamic relationships between organizations and institutions and visualize strategic decisions based on the existing interaction. The Institution-based view demonstrates that strategic decision making in organizations is not only decided by the situation of the industry and capabilities of the organizations but also by the formal and informal controls of a specific institutional situation. From the perspective of the institution-based view, the success of HTC’s turnaround plan can be explained based on the three major drivers that are resources and capabilities of the company, industry-based competition, and institutional transitions and conditions that result in the formation of strategic choices.
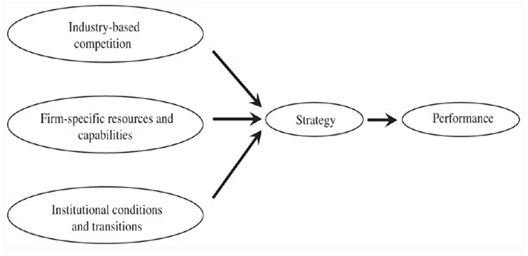
Figure.2:
Institution-based view
(Source: Jensen et al., 2016, p.170)
From the HTC corporation case study, it has been identified that the poor decision making business strategies implemented by HTC is one of the reasons behind its failure from the top position. In order to lead in the market in the presence of top competitors like Apple and Samsung, HTC has greatly focused on diversification. However, the random and frequent product diversification without the analysis of risks has led the company to increase confusion among the consumers regarding the distinct and unique features of each product resulting in huge loss. For the mod lack of adequate financial resources due to huge loss has also been identified to be one of the major reasons behind its failure (Hung and Tseng, 2017, p.811). Therefore, the analysis of the risks in the context of HTC corporation case study in the institutional conditions, industry-based competition, and financial resources are key drivers for the turnaround plan of HTC. ?
Question 2
The existing competitive dynamics
From the HTC corporation case study, it has been identified that competitive dimensions in the foreign markets have eroded HTC from its premium pricing strategy as well as budget. In the US the company faced tough competition from premium Smartphone companies like Apple. Apart from that, Samsung also dominated other foreign markets (Woulfin and Weiner, 2019, p.233). The HTC corporation case study depicts that Chinese Smartphone organizations have also played a critical role in enhancing the overall competitive dynamics in the consumer electronics market by offering smart phones within the budget of the middle-class people. It has been identified that the foreign competitors were backed with huge support from the government, from the large consumer base with greater customer loyalty which makes the competition more intense for HTC (Tsai and Chang, 2018, p.111).
Figure.3: Revenue source of Samsung
(Source: The HTC corporation case study)
The different Chinese Smartphone companies that have launched smart phones within the budget are Xiami, Oppo, Huwai. It has been identified that the majority of the consumers are now preferred using budget Chinese smartphones instead of home-grown brands like HTC. As a result, the competitive dynamics in the domestic market has also changed (Chen and Ann, 2016, p.241). As the loyalty of the customers has greatly reduced in the home market, and in the foreign market, customers are also loyal to the other organizations; HTC faces a tough competition despite offering quality products.
Ways to position the company for the future
From the analysis on HTC corporation case study of the existing competition in the global Smartphone industry, it can be explained that HTC originally implemented a premium pricing strategy. However, due to the existence of the top players like Apple and Samsung that release updated smart phones every year, HTC has fallen short in the competition. On the other hand, the rise of the budget smartphones by the Chinese companies has also forced the company to launch smartphones in the low budget. The budget offerings of the Chinese organizations have grown and have emerged as a global leader that makes the turnaround strategy of HTC more difficult (Giachetti and Marchi, 2017, p.359). This implies that the positioning of the products offered by the company has been changed but still the company has not received adequate sales improvement. From the analysis of the HTC corporation case study, it can be said that the number of key players within the premium pricing range is lower than the low budget Smartphone range.
According to Iyeret al., (2019, p.35) the premium-priced products of high brands are more effective in the case of HTC to win consumer loyalty and satisfaction as compared to its budget brands. Therefore, in the future, the company can be suggested to apply the premium pricing strategy based on the high quality of its products to compete with the low number of premium Smartphone companies. Apart from the premium pricing strategy, the company is also suggested to focus on the launch of limited products as the highly diversified product range of HTC are misleading and confusing for the consumers. Thereby the company is strongly recommended to reposition its strategy in relation to pricing and product (Lindsay et al., 2017, p.141). ?
Question 3
What are the different types of market entry modes considered in the HTC corporation case study?
Shenet al., (2017, p.446), in recent research on HTC corporation case study has mentioned five major types of market entry modes that are used by organizations for expanding their businesses into the international markets. From the case analysis, it has been identified that HTC has made a decision regarding expansion into the Chinese market; however, the decision regarding the market entry mode was not very effective for the company. HTC had made a partnership with China Mobile to expand into China. However, a poor marketing strategy has caused the ineffectiveness of the concerned organization in the China market. Licensing and franchising is a major type of market entry mode that causes fast entry into the international market with low risk. As per the statement of Taheriet al., (2017, p.89) licensing and franchising entry mode require low price and risk and therefore facilitates easy market expansion. The acquisition strategy is another important market entry mode for international expansion that offers fast market entry. In cross-border acquisitions, an existing business takes over another business that operates in a foreign market in a similar industry. Business acquisitions are felt in the Smartphone industry as it provides the opportunity to the quick establishment in the new market (Schwenset al., 2018, p.21). Partnership and strategic alliances is another way to enter the new market. In this type of market entry mode, businesses are required to make a partnership with local organisations and sign a contractual agreement regarding the activities.
Suggested market entry mode for HTC
From the analysis of the HTC corporation case study, it has been identified that HTC has made strategic alliances with China mobile in order to expand into China. This particular strategy was not beneficial for the company as there were problems in integration between the two corporate environments (Game and Apfelthaler, 2016, p.222). The agreement between the two companies limited the marketing functions of HTC resulting in poor sales. Considering the advantages and disadvantages of the different market entry modes HTC can be suggested to focus on business acquisition and franchising strategy. The business acquisition strategy followed in the HTC corporation case studywould enable HTC to enter in a target market in less time and take the opportunity of the established operations. However, the cost of business-acquisition strategy implementation is relatively higher than the other market entry strategy that is franchising. If the company chooses a franchising strategy to enter into the new market it would face lower risks and it would have to spend a lower cost (Grünig and Morschett, 2017, p.112). Moreover, the HTC corporation case study considered to develop the present study also signifies that it would promote fast entry into the target market. However, by applying a franchising strategy the company can have less control over the stores in the target market and phase issues relating to regulation and legal system.
Factors to be considered
HTC has to consider the regulation and legal aspects relating to different market entry routes in the target international markets before choosing to expand the business with a specific strategy. In an acquisition strategy, HTC would have to identify the strengths and weaknesses of another organization on which the acquisition would be done. The strengths of the target company would help in the fast establishment in the new market. Apart from the company would also be required to carry out a detailed risk analysis associated with a specific market entry route in the target market so that the possible strategies can be taken to mitigate the risks (Taheriet al., 2017, p.89).
?
Question 4
The proposed structure along with justification
From the business case of HTC, it is perceived that the concerned organization is hoping the implementation of the turnaround plan would restore its profitability, sales and brand recognition. However, for making the plan a success the company is not only required to focus on the pricing and product strategy but also have to pay attention to the way in which the organization is structured and governed. Currently, the company uses a matrix organizational structure. According to Shenet al., (2017, p.446), a matrix organizational structure involves a series of issues and confusion regarding reporting to the multiple managers.
In the functional organizational structure, a top-down organizational flowchart is followed for information flow within the organization. In a functional structure, the elements of the organizations are generally divided into smaller groups based on particular functional areas like marketing, finance, and IT. The implementation of a functional structure is justified for HTC as a specialization of the department helps the employees focusing on work. Moreover, the structure also enhances productivity through specialism. As the organization operates globally, HTC is recommended to use a centralized structure over a decentralized structure. As opined by Chen and Ann, (2016, p.241) a centralized structure helps business organizations make an efficient decision based on the vision and mission. The implementation of a decentralized structure can be disadvantageous for HTC as multiple opinions from different people can complicate the decision-making process.
Relationships to consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholders According to Woulfin and Weiner, (2019, p.233), for business organizations it is very important to secure long-term relationships with institutions within the industry for generating a valuable stream of revenue. There are different ways in which an organization can develop a relationship with the industry partners. In the HTC corporation case study, it is important to develop a relationship focusing its poor relationship with stakeholders. By maintaining the high standard of its products and quality HTC can focus on developing a strong relationship with its partner organizations. Moreover, this strategy would also help the company in building a strong relationship with its customers that are the major stakeholder of any company. In the opinion of Grünig and Morschett, (2017, p.112) to function in an appropriate manner within the consumer electronics industry, organizations must develop a strong interaction with the suppliers. Therefore, a trust-based and respectful relationship with the suppliers can help HTC in gaining sustained competitive advantage in the market. It has been identified that the poor marketing strategies of HTC are one of the reasons behind its failure from the top position in the consumer electronics market. Apart from that, the HTC corporation case study has also highlighted that the organisation was unable to deliver an appropriate message to the customers. Therefore, the company can be recommended to develop a strong relationship with customers using modern-day marketing techniques. Social media marketing is one of the best closed digital marketing strategies which can be used by HTC to develop a strong customer base and encounter the highest sales of its products. ?
Relationships to consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholders
Conclusion
From the above HTC corporation case study analysis, it can be concluded that the business turnaround strategy in HTC depended on its resources and the company needs to focus on the value, rarity and uniqueness of the resources. Moreover, the study also suggested the company utilize premium pricing along with the limitation of product diversification to compete effectively with its turnaround strategy. HTC has been suggested to focus on acquisition and franchising strategy for entering into new markets. Moreover, a centralized structure has been proposed to the company due to its effectiveness in business decision making. HTC would be also required to develop a strong relationship within the industry and with the stakeholders with a major focus on the marketing aspects to make the turnaround plan successful.?
Relationships to consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholders
References
Chen, C.M. and Ann, B.Y., 2016. Efficiencies vs. importance-performance analysis for the leading smartphone brands of Apple, Samsung and HTC.HTC corporation case studyTotal Quality Management & Business Excellence, 27(3-4), pp.227-249.
Game, R. and Apfelthaler, G., 2016. Attitude and its role in SME internationalisation: why do firms commit to advanced foreign market entry modes?.European Journal of International Management, 10(2), pp.221-248.
Giachetti, C. and Marchi, G., 2017. Successive changes in leadership in the worldwide mobile phone industry: The role of windows of opportunity and firms’ competitive action. Research Policy, 46(2), pp.352-364.
Grünig, R. and Morschett, D., 2017. Determining the Market Entry Modes.In Developing International Strategies (pp. 105-123).Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Relationships to consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholders
Relationships to consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholders Guadalupe, M., Li, H. and Wulf, J., 2014. Who lives in the C-suite? Organizational structure and the division of labor in top management.Management Science, 60(4), pp.824-844.
Relationships to consolidate within its industry and with other stakeholdeHeyman, F., Norbäck, P.J. and Persson, L., 2019. The turnaround of the Swedish economy: lessons from large business sector reforms. The World Bank Research Observer, 34(2), pp.274-308.
Hung, S.C. and Tseng, Y.C., 2017.Extending the LLL framework through an institution-based view: Acer as a dragon multinational.Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 34(4), pp.799-821.
Iyer, P., Davari, A., Zolfagharian, M. and Paswan, A., 2019.HTC corporation case study Market orientation, positioning strategy and brand perforial Marketing Management, 81, pp.30-39.
Jensen, J.A., Cobbs, J.B. and Turner, B.A., 2016. Evaluating sponsorship through the lens of the resource-based view: The potential for sustained competitive advantage.Business Horizons, 59(2), pp.163-173.Liang, X., Barker, V.L. and Schepker, D.J., 2018. Chief executive cognition, turnaround strategy and turnaround attempts of declining firms. Journal of Change Management, 18(4), pp.304-326.
Lindsay, V., Rod, M. and Ashill, N., 2017. Institutional and resource configurations associated with different SME foreign market entry modes. Industrial Marketing Management, 66, pp.130-144.Malone, T.W., 1987. Modeling coordination in organizations and markets.Management science, 33(10), pp.1317-1332.
Mansfield, R., 1973. Bureaucracy and centralization: An examination of organizational structure. Administrative Science Quarterly, pp.477-488.
Moch, M.K. and Morse, E.V., 1977. Size, centralization and organizational adoption of innovations.American sociological review, pp.716-725.
Parola, F., Risitano, M., Ferretti, M. and Panetti, E., 2017. The drivers of port competitiveness: a critical review. Transport Reviews, 37(1), pp.116-138.
Rajaram, R., Singh, A.M. and Sewpersadh, N.S., 2018. Business rescue: Adapt or die. South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences, 21(1), pp.1-13.
Schmitt, A., Raub, S., Schmid, S. and Harrigan, K.R., 2019. Changing tires on a moving car: the role of timing in hospitality and service turnaround processes. HTC corporation case studyInternational Journal of Hospitality Management, 77, pp.549-561.
Schwens, C., Zapkau, F.B., Brouthers, K.D. and Hollender, L., 2018. Limits to international entry mode learning in SMEs.Journal of International Business Studies, 49(7), pp.809-831.mance.Industrial Marketing Management, 81, pp.16-29.
Shen, Z., Puig, F. and Paul, J., 2017. Foreign market entry mode research: A review and research agenda. The International Trade Journal, 31(5), pp.429-456.
Taheri, S., Moradi, M.R., Manafzadeh, M.A., Ghaderi, E. and Mowlaie, S., 2017. The Effect of Types of Market Entry Modes on Organizational Design in Hotels in Tehran Province.Journal of Ecophysiology and Occupational Health, 17(3/4), pp.87-92.
Tsai, W.L. and Chang, P.T., 2018. Combining data envelopment analysis and competitive dynamic theory for exploring global smartphone manu-facturers' performance.JABS, 4(2), pp.109-125.
Wild, A. and Lockett, A., 2016. Turnaround and failure: Resource weaknesses and the rise and fall of Jarvis. Business History, 58(6), pp.829-857.
Woulfin, S.L. and Weiner, J., 2019. Triggering change: An investigation of the logics of turnaround leadership.HTC corporation case studyEducation and Urban Society, 51(2), pp.222-246.












