Information Security Assignment: PII Strategy Proposal For DAS MyLicence Portal
Question
Task:
Scenario
The Department of Administrative Services (DAS) provides a number of services to other departments in an Australian State Government. These services include HR and personnel management, payroll, contract tendering management, contractor management, and procurement. These services have all been provided from the Department’s own data centres.
As a result of a change in Government policy, DAS is moving to a “Shared Services” approach. This approach will mean that DAS will centralise a number of services for the whole of Government (WofG). This means that each Department or Agency that runs one of these services for its own users, will be required to migrate its data to DAS so that it can be consolidated into the DAS centralised database. DAS will then provide these consolidated services to all other Departments and Agencies within the Government.
The Government has now decided that they want to centralise the application and renewal of licences from a number of different agencies into one single portal. The portal will be branded as MyLicence. The Government’s strategy is that the process of licence application or renewal for virtually all licences follows an almost identical workflow, even though some of the data may differ for different types of licences. Their aim is to have a single workflow for all licences, with some additional steps in case of special requirements for a particular type of licence.
The Government also sees the opportunity to gain a better view of what licences each citizen holds, and wants to link that data to other data that they hold about each citizen. In order to achieve this, the Government plans to encourage citizens to register on the MyLicence portal and create their own informal digital identity. This will allow all the licences, renewal dates, and other associated information for that digital identity to be available for viewing on a single page. This data, particularly when linked to a citizen’s digital identity, can then be used for more effective planning and decision making by Government and other public agencies.
The plan also has the advantage of simplifying the process of acquiring and renewing licences for its citizens so that they only need to go to a single web portal to acquire the licenses that they require.
The Government proposes, in line with its “Cloud First” policy, to use a public cloud provider to host the MyLicence portal, processing and databases. The Government also wants to ensure that all data remains on Australian soil so that it can ensure that data sovereignty does not cause any issues with MyLicence. However the Government is also committed to ensuring that the MyLicence portal makes maximum use of all the possible advantages of the public cloud.
Tasks to be covered in this information security assignment
After your successful engagement to provide a security and privacy risk assessment for the DAS, you have again been engaged to develop a Personally Identifiable Information (PII) privacy and personal data protection strategy for the MyLicence portal.
You are to write a report that proposes appropriate policies for DAS in the following areas:
- Develop a PII strategy proposal for the DAS MyLicence portal. The strategy should consider the threats and risks to both Privacy and data protection for the PII data collected in the MyLicence portal as well as possible controls to mitigate the identified risks.
- Develop a strategy to protect the informal Digital Identity that a user may create in the MyLicence portal. You should consider both the privacy and data protection aspects for a digital identity as well as possible controls to mitigate the identified risks.
- Develop a strategy to ensure data sovereignty for the MyLicence portal
Answer
Introduction to the context of information security assignment
There are some of the major improvements that have been in the field of technology. The business organizations and agencies are making a transition to the latest technology so that they may be able to provide improved services to the customers. The similar decision has been taken by the Department of Administrative Services, DAS. It is a Government department based in Australia and DAS has decided to use the shared services approach. As per this approach, there will be centralized database and the cloud services & platforms used by the department and all of its associated agencies. The cloud-based web portal that will be used by DAS will be referred as MyLicense Portal(Chang, 2015). When the user will log in to this portal, there will be a temporary digital identity that will be generated. In the entire process it is possible that the information privacy is poorly implicated.
The report covers the three major aspects. It includes the strategy to preserve the Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on the MyLicense portal and the digital identities. It also includes the coverage of the concept of data sovereignty and determines the impacts of the migration on data sovereignty.
Privacy & Data Protection – MyLicense Portal
One of the most significant aspects that will be associated with the DAS and its migration to the cloud services will be the information privacy and security. There are some of the inherent properties of the cloud that can play a major role in the promotion of information security risks and threats. The properties, such as resource sharing and multi-tenancy will expose the PII on the MyLicense portal to various forms of security issues and threats.
Risks & Threat Identification
|
ID |
Risk/Threat |
Brief Summary of the Risk |
|
1 |
Data Breaches and Leakage |
The information on the MyLicense portal will be shared over the cloud platforms. It would be possible that the unauthorized entities gain access to the data resulting in unauthorized breaches and data leaks(Cheung & Weber, 2015). |
|
2 |
Data Alteration |
The dynamic database will be used with the MyLicense portal as there will be numerous real-time services that will be involved and provided to the end-users. There can be unauthorized modifications to the data that may be done. |
|
3 |
Misconfigured Cloud Storage |
There can be issues around the configuration of the cloud settings and servers. There may be mismatched access management or misconfigured data access that may lead to the violation of the privacy of PII |
|
4 |
DoS Attack |
The MyLicense portal will be exposed to the denial of service attack and the execution of the attack will make the system unavailable to the end-users(Gordon, 2016). |
|
5 |
Malicious Codes |
The attackers may launch the malicious codes on the MyLicense portal to cause negative implications on the information access or network availability or for monitoring the system activities. |
|
6 |
Social Engineering Attacks |
The social engineering attacks, such as phishing attacks may be executed to gain access to the PII on the MyLicense portal. The confidential details of the customers will be accessed by tricking the customers. |
Risk/Threat analysis
The analysis of the risks is done on the basis of the qualitative analysis technique. To analyse the risks, the probability and impact matrix is used as depicted below. Using the values of probability and impact, the risk level is determined.
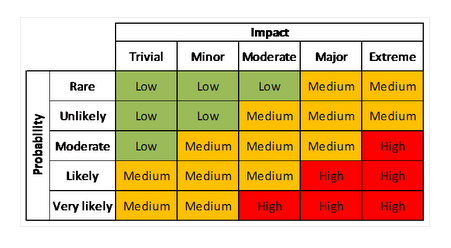
Probability-Impact Matrix
|
ID |
Risk/Threat |
Probability |
Impact |
Risk Level |
|
1 |
Data Breaches and Leakage |
Likely |
Major |
High |
|
2 |
Data Alteration |
Unlikely |
Moderate |
Medium |
|
3 |
Misconfigured Cloud Storage |
Rare |
Major |
Medium |
|
4 |
DoS Attack |
Moderate |
Major |
Medium |
|
5 |
Malicious Codes |
Likely |
Major |
High |
|
6 |
Social Engineering Attacks |
Likely |
Major |
High |
Risk Controls and Mitigation
There are various controls that are present and must be implemented so that the PII associated with the MyLicense portal can be prevented and kept protected at all times. The mapping of the security risks identified is done with the security controls and measures that may be used.
|
ID |
Risk/Threat |
Brief Summary of the Risk |
Risk Level |
Controls for Risk Mitigation |
|
1 |
Data Breaches and Leakage |
The information on the MyLicense portal will be shared over the cloud platforms. It would be possible that the unauthorized entities gain access to the data resulting in unauthorized breaches and data leaks. |
High |
Perimeter firewall shall be installed by DAS along with the inclusion of multi-factors authentication so that the unauthorized access does not occur. |
|
2 |
Data Alteration |
The dynamic database will be used with the MyLicense portal as there will be numerous real-time services that will be involved and provided to the end-users. There can be unauthorized modifications to the data that may be done. |
Medium |
The use of automated backups must be done for the DAS databases. The use of geodiversity shall be done wherein the physical location of the cloud servers and databases must not be on a common location(Kumar, 2016). |
|
3 |
Misconfigured Cloud Storage |
There can be issues around the configuration of the cloud settings and servers. There may be mismatched access management or misconfigured data access that may lead to the violation of the privacy of PII |
Medium |
The use of third-party tools must be done to ensure that the configuration of the cloud settings is effectively done. The automated verifications and alerts will be issued by these tools and it will provide the ability to effectively configure the cloud settings. |
|
4 |
DoS Attack |
The MyLicense portal will be exposed to the denial of service attack and the execution of the attack will make the system unavailable to the end-users. |
Medium |
The intrusion detection systems shall be installed and these shall be regularly monitored. There shall be limits applied on the source rates. Also, the use of firewalls must be done to prevent these attacks. |
|
5 |
Malicious Codes |
The attackers may launch the malicious codes on the MyLicense portal to cause negative implications on the information access or network availability or for monitoring the system activities(Macropoulos& Martin, 2015). |
High |
The use of anti-malware packages shall be done along with the access control using multi-factor authentication. There shall also be use of network and perimeter firewalls. The system updates shall be regularly checked and installed. |
|
6 |
Social Engineering Attacks |
The social engineering attacks, such as phishing attacks may be executed to gain access to the PII on the MyLicense portal. The confidential details of the customers will be accessed by tricking the customers. |
High |
There are automated anti-phishing tools that are present that must be used on the portal. The employees of DAS shall be educated and made aware on the social engineering techniques so that the proper utilizations and implementations can be done. |
Digital Identities
The digital identities refer to the unique identities that are created on the digital mediums so that the verification and validation of the users can be done. The digital identities are useful in the identification of the users and makes sure that the access control is implemented on the system. However, there can be specific security risks and issues that may be associated with the digital identities.
Digital Identifies – Risks and Issues
The digital identity will be created by the MyLicense portal as soon as the user will register on the portal. The user will be able to make use of these digital identities in order to access the system in the future(Meetei, 2017). However, there can be various risks that may be associated with these digital identities.
Risks & Threat Identification
|
2 |
Account Hijacking |
If the attackers succeed in guessing the passwords, it will be possible for them to easily break in to the account and hijack the user details(Millard, 2015). |
|
3 |
Database Injection Attacks |
The digital identities and the corresponding information will be stored in the centralized database for DAS. There are database injection attacks that may be executed on the system with the use of the malicious queries. |
|
4 |
Eavesdropping Attacks |
The cloud networks that will be used by the DAS may be monitored by the attackers and the digital identities may be acquired and misused in this manner. |
|
5 |
Malicious Codes |
The attackers may launch the malicious codes on the MyLicense portal to cause negative implications on the information access or network availability or for monitoring the system activities. |
|
6 |
Social Engineering Attacks |
The social engineering attacks, such as phishing attacks may be executed to gain access to the digital identities. The impersonation techniques or the tricking of the users may be done to carry out these attacks. |
Risk/Threat Analysis
The analysis of the risks is done on the basis of the qualitative analysis technique. To analyse the risks, the probability and impact matrix is used. Using the values of probability and impact, the risk level is determined.
|
ID |
Risk/Threat |
Probability |
Impact |
Risk Level |
|
1 |
Brute/Force Attacks |
Moderate |
Major |
Medium |
|
2 |
Account Hijacking |
Moderate |
Major |
Medium |
|
3 |
Database Injection Attacks |
Unlikely |
Major |
Medium |
|
4 |
Eavesdropping Attacks |
Likely |
Major |
High |
|
5 |
Malicious Codes |
Likely |
Major |
High |
|
6 |
Social Engineering Attacks |
Likely |
Major |
High |
Risk Controls and Mitigation
The risks associated with the digital identities can be avoided with the aid of the numerous control techniques that have been developed.
|
ID |
Risk/Threat |
Brief Summary of the Risk |
Risk Level |
Controls for Mitigation |
|
1 |
Brute/Force Attacks |
The digital identity that will be generated will require the user to create a password. There will be default password that the system will generate. It is possible that the users put weaker passwords or do not change the default passwords(Qin et al., 2018). The guessing of these passwords will be easily done by the attackers. |
Medium |
Multi-factor authentication shall be used on the portal wherein the digital identity verification shall be done and it shall be followed by the use of the biometrics recognition or the one-time password to validate the user identity. |
|
2 |
Account Hijacking |
If the attackers succeed in guessing the passwords, it will be possible for them to easily break in to the account and hijack the user details. |
Medium |
Multi-factor authentication shall be used on the portal wherein the digital identity verification shall be done and it shall be followed by the use of the biometrics recognition or the one-time password to validate the user identity. |
|
3 |
Database Injection Attacks |
The digital identities and the corresponding information will be stored in the centralized database for DAS. There are database injection attacks that may be executed on the system with the use of the malicious queries. |
Medium |
The use of parameterized queries shall be avoided. Also, there shall be automated backup tools used to safeguard the database. The access control on the database shall also be improved(Sari, 2015). |
|
4 |
Eavesdropping Attacks |
The cloud networks that will be used by the DAS may be monitored by the attackers and the digital identities may be acquired and misused in this manner. |
High |
The intrusion detection systems shall be installed and these shall be regularly monitored. There shall be limits applied on the source rates. Also, the use of firewalls must be done to prevent these attacks. |
|
5 |
Malicious Codes |
The attackers may launch the malicious codes on the MyLicense portal to cause negative implications on the information access or network availability or for monitoring the system activities. |
High |
The use of anti-malware packages shall be done along with the access control using multi-factor authentication. There shall also be use of network and perimeter firewalls. The system updates shall be regularly checked and installed. |
|
6 |
Social Engineering Attacks |
The social engineering attacks, such as phishing attacks may be executed to gain access to the digital identities. The impersonation techniques or the tricking of the users may be done to carry out these attacks. |
High |
There are automated anti-phishing tools that are present that must be used on the portal. The employees of DAS shall be educated and made aware on the social engineering techniques so that the proper utilizations and implementations can be done(Zanoon, 2015). |
Data Sovereignty
There are different aspects that are associated with the decision that is taken by DAS. Data is the primary asset that is involved in the process and there are measures that must be taken to preserve all the properties and aspects associated with the data. One of the most significant aspects is data sovereignty(Vatanparast, 2020). It is the concept that aims to maintain the compliance of the data sets and associated mechanisms as per the application laws and regulations.
In the present times of cloud technologies and mediums, it is very challenging to preserve the data sovereignty. This is because the cloud networks are restricted with the geographical boundaries. The data sets can travel from one part of the globe to the other within seconds. As a result, there are a few data sovereignty issues that can arise and are explored. These shall be properly handled and managed by DAS so that the avoidance of the issues is possible.
Issues on Data Sovereignty
DAS is the Australian department and the services that are provided on the MyLicense portal are primarily for the Australian citizens. However, it is possible that these users access the portal from other locations apart from Australia. The flow of the data can be carried out from one country to the other. One of the major issues will be the handling of the data as per the location of the user. The location-based services cannot be kept activated at all times as these may result in the negative implications on the security and privacy. Also, the frequently changing location of the user will result in the complexities in determining the regulatory and legal laws that may apply(Vaile, 2019). All of these aspects may lead to the generation of the non-compliance towards the defined laws and regulations. The inability of DAS to comply with the applicable regulations can also result in the legal obligations and the implications of the same can be critical.
The concept of data sovereignty has gained a lot of significance after the development of the cloud platforms. There are still regulations and legislations that are still being developed. The continuously changing regulations lead to additional complexities and confusions. As a result, there may be inability to properly develop the data sovereignty strategies.
Security Issues and Concerns
There are security issues that can also occur and cause negative implications on the concept of data sovereignty for DAS. The data on the MyLicense portal will be shared over the cloud stages. It would be conceivable that the unapproved elements access the information bringing about the issues around breaching and leaking of the data. The dynamic database will be utilized with the MyLicense portal as there will be various real-time benefits that will be included and given to the end-users. There can be unauthorized adjustments to the information that might be finished. There can be issues around the design of the cloud settings and servers. There might be poor access management or misconfigured information access that may prompt the infringement of the security of PII(Nugraha et al., 2015). The MyLicense portal will be presented to the availability attacks and issues, such as DoS attacks. The execution of the security issue will make the system inaccessible to the end-users. The malicious entities may dispatch the malicious codes on the MyLicense portal to cause negative ramifications on the data access or network availability or for monitoring the system exercises.
The social engineering attacks, for example, phishing attacks might be executed to access the PII on the MyLicense portal. The classified subtleties of the clients will be accessed by deceiving the clients. The digital identity that will be produced will require the user to make a password. There will be default password that the system will create. It is conceivable that the users put more vulnerable passwords or don't change the default passwords. The guessing of these passwords will be effortlessly done by the malevolent entities. Once the attackers succeed in guessing the passwords, they will be able to handily break in to the account and capture the user details. There are database injection attacks that might be executed on the system with the utilization of the malicious queries. The cloud networks that will be utilized by the DAS might be accessed by the attackers and the digital information might be procured and abused.
Control Measures & Techniques
There are some of the mechanisms that can be adopted to make sure that the issues around data sovereignty do not occur and can be avoided. There shall be identification of the applicable laws and regulations that must be done as the first step. The primary focus will be on the Australian laws and guidelines and it shall then follow the internationally applicable laws and regulations(Oguamanam, 2018). The determination of these will enable the management and administration of DAS to develop the effective techniques and mechanisms for preserving data sovereignty.
There are also a number of security controls and techniques that have been developed. The utilization and implementation of these techniques must be done so that the issues around information security and privacy are managed. This will automatically lead to the improvements and effective management of data sovereignty.
Conclusion
The decision of DAS to migrate to the cloud platforms is in accordance with the current times. However, there are certain aspects around information security and privacy that must be considered by the department. There are security and privacy attacks that may occur on the PII. It shall be made sure that the avoidance of such issues is done with the use of the administrative and logical controls. There can also be issues of data sovereignty that may occur and the identification and adherence with the applicable laws shall be done to avoid these issues.
References
Chang, H. (2015). Privacy Regulatory Model for the Cloud: A Case Study. IEEE Cloud Computing, 2(3), 67–72. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcc.2015.57
Cheung, A. S. Y., & Weber, R. H. (2015). Privacy and legal issues in cloud computing. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Gordon, A. (2016). The Hybrid Cloud Security Professional. Information security assignment IEEE Cloud Computing, 3(1), 82–86. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcc.2016.21
Kumar, R. (2016). Cloud computing and security issue. International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science. https://doi.org/10.18535/ijecs/v5i11.18
Macropoulos, C., & Martin, K. M. (2015). Balancing Privacy and Surveillance in the Cloud. IEEE Cloud Computing, 2(4), 14–21. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcc.2015.85
Meetei, M. Z. (2017). Mathematical model of security approaches on cloud computing. International Journal of Cloud Computing, 6(3), 187. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijcc.2017.086710
Millard, C. (2015). Forced Localization of Cloud Services: Is Privacy the Real Driver? IEEE Cloud Computing, 2(2), 10–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcc.2015.37
Nugraha, Y., Kautsarina, &Sastrosubroto, A. S. (2015). Towards Data Sovereignty in Cyberspace. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2610314
Oguamanam, C. (2018). ABS: Big Data, Data Sovereignty and Digitization: A New Indigenous Research Landscape. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3326282
Qin, Z., Weng, J., Cui, Y., & Ren, K. (2018). Privacy-Preserving Image Processing in the Cloud. IEEE Cloud Computing, 5(2), 48–57. https://doi.org/10.1109/mcc.2018.022171667
Sari, A. (2015). A Review of Anomaly Detection Systems in Cloud Networks and Survey of Cloud Security Measures in Cloud Storage Applications. Journal of Information Security, 06(02), 142–154. https://doi.org/10.4236/jis.2015.62015
Vaile, D. (2019). Data sovereignty and the cloud – a structured bibliography. Journal of Telecommunications and the Digital Economy, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.18080/jtde.v1n1.223
Vatanparast, R. (2020). Data and the Elasticity of Sovereignty. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3609579
Zanoon, N. (2015). Toward Cloud Computing: Security and Performance. International Journal on Cloud Computing: Services and Architecture, 5(5/6), 17–26. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijccsa.2015.5602












