Introduction To Strategic Human Resource Management
Question
Task:
Write a detailed assignment explaining the meaning, purpose, and functions of strategic Human Resource Management.
Answer
Introduction
Strategic Human Resource Management is the process of recruitment and selecting employee, providing orientation and induction, training and development, assessment of employee (performance of appraisal), providing compensation and benefits, motivating, maintaining proper relations with employees and with trade unions, maintaining employee’s safety, welfare and health measures in compliance with the laws formulated by the government. This assignment explains the meaning, purpose, and functions of strategic Human Resource Management.
Effect of Organizational Structure on Human Resource Strategies:
The organizational structure defines methods and techniques used for assigning, coordinating, and supervision of activities performed by employees at all levels of the management, for achieving organizational objectives. It also illustrates the flow of information across all functions of the organization (Katou, 2017).
For instance, a top-down approach is used in a centralised structure, whereas the authority and responsibility of making decisions is distributed among different levels of the management. Further, organizational structures are illustrated in the form of flowcharts and diagrams that look like a pyramid. Individuals with the highest authorities are displayed at the top and the lowest power and authority are shown at the bottom.
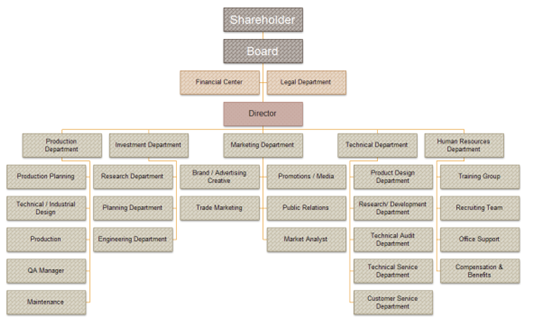
Figure 1: Organizational Structure.
Source: (Al-Sarayrah, et al., 2016)
As illustrated in Figure 1, shareholders have the highest authority as they have the power to appoint the Board of Directors (referred to as the Board). The Board comprises members representing the shareholders and devises business strategies. They are placed at the top of the flowchart as they have the maximum power and authority. Similarly, maintenance and customer service departments have low power and authority and hence, are placed at the bottom.
Organization structure stands for the appropriate planning of individuals operating for the corporation so that the business attains convinced objectives. The outline of association is shaped between individuals and the association. Diverse kinds of organizations are in existence for example Line, Serviceable, divisional, and line and operator matrix. The place of the HR section in the total organization setup is principally dependent on whether a specific component is minor or enormous. In minor organizations, there might not be a discrete HR subdivision and the human resource roles might be accompanied by the aid of a workplace manager. However, this is not the situation in superior organizations. In contemporary times, an organization has a chair and managing director as part of human resource management (HRM).
In an organization, HR organizational structure plays a vital part as the basis and other aligning resources is demarcated as a fragment of the business strategy stating the organization’s culture. The structure unswervingly affects the corporation’s skill to entice and maintain suitable HR aptitude. Subsequently, the effort of HR inspires the achievement of the organization in the forthcoming (Cooke, Xiao, and Chen, 2021). Its inspiration is within and outside the range of the HR roles as well. An operative organizational structure has its origins in the formation of an optimistic influence on commerce and that is why it is continuously aligned with an appropriate occupational strategy. It is aimed to appeal to their great executing people and make situations so that the development and expansion chances are also impacted. The contemporary research benefits to discover the requirements of the occupation so that significant assistance can be made to the commercial.
Effect of Organizational Culture on Human Resource Management Strategies
Organizational culture is referred to as the values and shared beliefs of the organization that shapes the character and attitude of employees. Further, the culture followed at the organization helps the employees to understand the types of goals to be achieved and methods that can be used for achieving their objectives. Thus, organizational culture is the motivation and attitude practiced at the organization for achieving its objectives. For example, manufacturing companies focus on delivering the highest quality products. Hence, this belief and perception are shared by each employee in the organization that enables them to achieve organizational objectives (Chams & Garcia-Blandon, 2018).
Culture is the manner of existence of individuals which is artificial by their standards, principles, approach, skill and discipline, types of insight, thoughts, and activities. In this way, culture clarifies how entities live and perform in a setting and how his/her opinions and acuity are shaped which move the reciprocal association between entities and setting in which he/she exists. Globalization has emphasized the cultural alterations within the association moving the enactment of it. Human resource practices like training, recruitment have a noteworthy influence due to cultural alterations.
Nowadays, human resource is reflected as the most important and dissimilar feature of organizations and quantity of actions are assumed. Lots of programs are applied to upsurge the efficiency of staff by supporting and obliging altering requirements. The significance of organizational culture has amplified. Trade culture influences the organization and the operative’s presentation. Multinational companies are endorsing commercial culture refining regulating, assimilating, and organizing their affiliates over the whole world. Yet these companies function in diverse cultures. There are robust indications to recommend the straight connection between corporations’ presentation and company culture. The factual examination of organizational culture is to rationalize with these approaches. MNC is, thus, aware to pay responsiveness to the appropriateness of commercial culture within their branches functioning in diverse national cultures to smooth enactment, chiefly HRM approach.
1) Impact on recruitment and selection
Organizations always look for selecting the best candidates as the quality workforce is an essential component of the organization. The workforce uses skills and expertise for completing their assigned tasks by following standard procedures prescribed by the management. This enables the firms to achieve the desired level of efficiency and productivity and increasing the competitiveness of the firm (Delery & Roumpi, 2017).
Although the skills and expertise of employees are considered while selecting the candidates, the motivation fit factor is used as an important differentiating factor in the selection process.
Motivation fit is classified as:
Job fit motivation:
This refers to the extent to which individuals find personally satisfying with the underlying responsibilities and job profiles in an organization. In short, it refers to the attractiveness of the job profile to attract individuals because of nature and type of activities performed. Further, the experience and expertise of candidates are evaluated during the selection process. Therefore, the interest shown by candidates is the first factor that is considered since motivation drives individuals to develop the required skills and expertise for performing tasks.
Organization fit motivation:
It is also referred to as “culture fit” since the compatibility of motivation and attributes of candidates are matched with shared values of the organization. The candidates are selected only if their attributes or motivation 'fit’ with organizational culture (Mousa & Othman, 2020).
Hence, these two types of motivation are considered since job fit motivation enables individuals to improve their performance which helps the firms to achieve efficiency and productivity. Whereas culture fit factor enables to select those candidates whose motivation and belief are as per the shared values of the organization. With the increasing complexity of organizational structures, such as increased diversity in the workplace, complex communication channels due to collaborations with foreign companies, and availability of flexible work conditions, it is essential to consider the culture fit factor in the selection process. This is because it helps to select only those candidates who share common values thereby ensuring that they remain with the firm for the long-term. Companies prefer long-term association with employees since recruitment and selection involves investing a huge amount of time and money. Thus, incurring recruitment and selection costs frequently results in increased expenses that hamper investing funds in more productive activities such as research and development.
2) Impact on Training and Development
It is well-established that training and development enable firms to develop the skills and expertise of the employees. Hence, the belief shared in the organization towards training and development impacts the performance of employees. This is because organizational structure and culture that fosters innovation and creativity tend to be more successful as new techniques and methods can be introduced. This is done by creating an environment of continuous learning and development that motivates employees to undertake research across all functions (Zehir, et al., 2016). Additionally, it is important to provide the latest information to employees during training since it enables the management to obtain accurate information.
3) Performance Management
Employee performance evaluation is considered an important function of organization that deals with evaluating contributions made by them for achieving organizational objectives. Under this, the HR department takes feedback from managers and supervisors related to employees’ performance and rate their contribution accordingly. In a centralised organizational structure, the feedback mechanism is bottom-up wherein the information collected from managers and supervisors is provided to the top management for assessment. Also, employees do not take active participation in the feedback process as they are informed about their performance either through face-to-face interviews or via emails. However, in a de-centralised structure, the HR department collaborates with department heads or senior managers for providing ratings, and hence, employees have the option of discussing with managers during the performance evaluation process (Funminiya, 2018).
Similarly, organizational culture that fosters an open-door policy and encourages employees to take active participation in the performance evaluation process helps to gain the trust and confidence of employees. Thus, employees feel motivated to improve their performance that helps the management to achieve its objectives. Also, using effective performance measures helps the management to align appropriate resources for training and learning programs since skills gaps can be identified accurately.
4) Compliance Management
The Human Resource department has the responsibility of maintaining statutes related to health and safety, employment legislation, equality act, provisions related to maintaining the privacy of data, and others. In this regard, organizational structure enables creating appropriate channels for providing information to local authorities. Also, the flow of information depends on the centralisation and de-centralisation of communication channel. For instance, a centralised structure controls the flow of information and hence, the management may not disclose complete information (Úbeda-García, et al., 2017).
On the other hand, a de-centralised and open communication structure enables to integration of various functions, and hence, appropriate information can be shared with authorities.
Similarly, culture fosters the attitude and belief of the management while maintaining compliance. A positive and encouraging culture promotes providing true facts to the government and accepts mistakes. Whereas negative cultural practices providing incorrect information related to compliance or hiding facts from the government. An example of 7-Eleven can be considered for wherein the management did not disclose information related to salaries provided to employees in Australia. It attracted huge fines and penalties for breach of contract of Wages Act.
From the above discussion, it can be evaluated that organizational culture and structure affect human resource strategies by ensuring that framework and policies are aligned with organizational objectives.
2) Human Resource Department and Finance are often considered as existing at the opposite ends because HR is concerned with people and value created by them for achieving business objectives while finance deals with calculating ROI (Return on Investment) on the amount spent on employees (Hitka, et al., 2020).
Additionally, the core values of these two functions also differ; HR values employees as the best asset available, whereas finance values assets that can be quantified. However, both HR and finance are inter-dependent since their objectives overlap with one another for achieving organizational objectives.
Importance of Finance for Human Resource
Finance aids in allocating capital to meet an institution's priorities while preserving a cost-revenue balance. HR hires, trains and motivates staffs to accomplish the same objectives. This field of HR is frequently the most costly for a company. Within a company, coordination between HR and finance is crucial (Collins, 2021). It will be impossible for the organizations to completely endorse organizational priorities if this does not happen. The HR and finance divisions cooperate to achieve a shared objective of increased performance and profitability. HR professionals also conduct activities that were previously considered to be economic.
Chief financial officers are in the same boat. Financial managers and HR managers must look beyond workers as expenses to see if they can boost profitability by exploiting human resources. HR needs the data that Finance collects and monitors to make the right economic choices. When seeking finances for programs, HR relies on unreliable prediction models, making it difficult to provide a viable return on investment results. HR and Financing will operate better as a system of checking and balancing. HR is in charge of the payroll side of things. If teams don't interact, there could be a slew of problems that cost the organization a lot of money.
As Finance makes significant funding cuts without informing HR, the company is also unwittingly exposed to legal action by workers and customers. Because of the negative impact and additional cost to the organization, contact should be encouraged. In today's market, a company that lacks HR and financing would fail to compete (Chams, and García-Blandón, 2019). In today's ever-changing economy, a modern company must have complete HR and financial support. The advantages are multiple, cutting supply, consumer loyalty, and profit to their highest levels.
A successful business strategy ensures that resources available to the organization are utilised to the maximum extent. In the case of Human Resource, financial resource or funds are utilised for:
- Recruiting and selecting appropriate candidates for various posts across all functions.
- Providing appropriate training and learning facilities for improving employee performance.
- Maintaining employee records for both utilising it for performance evaluation as well as for maintaining compliance (Papa, et al., 2018).
- Providing compensation and benefits for employees
1) Recruitment function
HR uses both internal and external recruitment approaches for hiring employees for filling vacancies in the organization. Funds are not required for internal recruitment as employees working in the organization are promoted or transferred for filling vacancies. However, they have to be appropriately compensated by providing monetary benefits such as increasing their pay or allowances. This enables to retain the talent within the organization and management ensures that they continue to contribute towards the growth and development of the organization (Rajapakse, 2017).
External recruitment involves using external sources such as posting job advertisements on media sources such as newspapers, online platforms and partnering with recruitment agencies for filling vacancies. This involves investing funds and hence, funds are required for paying for services offered by third parties. The management benefits by professional hiring agencies since they have knowledge and expertise in hiring personnel for various positions. Also, external sources enable collecting profiles of numerous eligible and talented individuals, thus, the management has the opportunity of selecting the best candidate for the job roles. Hence, it enhances the capability of the organization thereby increasing its competitiveness in the market.
2) Training and Development
HR requires funds for designing and developing training modules and for procuring related hardware and software such as computers, projectors, and other stationeries. Further, the appropriate number of manpower is required for conducting training and evaluating the results of the evaluation. Period evaluation enables organizations to ascertain the impact of training on the skills levels of the organization. Deriving this data enables policymakers to evaluate the effectiveness of funds used for training (Cooke, 2018).
The training modules can be modified based on the results obtained from performance evaluation. Hence, investing in training and development improves the performance of employees, thus, enhances the productivity of employees along with developing their skills for performing research.
3) Performance Evaluation and Management
Organizations conduct a periodic performance evaluation of employees by designing suitable performance criteria across all levels of management. Performance evaluation involves conducting interviews, taking feedback, and recording and storing records in a centralised database. All these require sufficient funds as both funds and resources are required for this purpose. Since performance evaluation motivates employees by providing incentives, bonuses, increments, and promotions. This motivates employees to improve their performance and builds trust and confidence among employees (Ekpo, et. al., 2017). Thus, obtaining sufficient funds will help to implement techniques that accurately determine the needs and aspirations of the employees and implement employee-friendly policies such as flexible work arrangements.
Hence, finance and HR departments coordinate with each other for developing policies that benefit organization so that overall objectives can be achieved.
Finance aids in allocating capital to meet an institution's priorities while preserving a cost-revenue balance. HR hires, trains and motivates staffs to accomplish the same objectives. This field of HR is frequently the most costly for a company. Within a company, coordination between HR and finance is crucial (Collins, 2021). It will be impossible for the organizations to completely endorse organizational priorities if this does not happen. The HR and finance divisions cooperate to achieve a shared objective of increased performance and profitability. HR professionals also conduct activities that were previously considered to be economic.
Chief financial officers are in the same boat. Financial managers and HR managers must look beyond workers as expenses to see if they can boost profitability by exploiting human resources. HR needs the data that Finance collects and monitors to make the right economic choices. When seeking finances for programs, HR relies on unreliable prediction models, making it difficult to provide a viable return on investment results. HR and Financing will operate better as a system of checking and balancing. HR is in charge of the payroll side of things. If teams don't interact, there could be a slew of problems that cost the organization a lot of money.
As Finance makes significant funding cuts without informing HR, the company is also unwittingly exposed to legal action by workers and customers. Because of the negative impact and additional cost to the organization, contact should be encouraged. In today's market, a company that lacks HR and financing would fail to compete (Chams, and García-Blandón, 2019). In today's ever-changing economy, a modern company must have complete HR and financial support. The advantages are multiple, cutting supply, consumer loyalty, and profit to their highest levels.
The factors affecting human resource management in a Coca-Cola
The Coca-Cola Company is a global beverage company located in the United States. The Coca-Cola Company has interests in energy drinks and syrups processing, retailing, and advertising.
The HRM of Coca-Cola gets affected by the factors as follows-
- Population and Workforce:
Human resource management is affected by population and workers since these are the pillars for an organization's external supply of human capital (Michael, 2019). Coca-Cola should distinguish between employees and community when assessing population and workers as a source of foreign human capital since only a portion of the population can work. - Workforce Market Condition:
The current state of the labor market of Coca-Cola demonstrates the need for and supply of labor. It affects recruiting and selection processes in human resource management. In the labor market, there are connections between employers and prospective workers. Since the workforce market covers all types of jobs, only the applicable workforce market is considered when looking for potential employees. - National Income:
The wage structure of Coca-Cola is affected by national income, especially as calculated in terms of per capita income. Each employer must adapt their pay structure to the macroeconomic climate. This is the explanation for the disparity in wage structures between developed and emerging nations. - Inflationary Pressures:
Inflationary pressures in a country impact the payment to be given to workers in addition to the national income. Employee compensation is related to the cost of living in most nations, either directly or indirectly. As a consequence when a country is subjected to rising inflation, the standard of living index rises, causing employers to increase worker pay. - Socio-Cultural Factors:
Socio-cultural influences include a wide variety of subjects and have an influence on many areas of the Coca-Cola industry, including human resource management (Herrera, and de las Heras-Rosas, 2020). Attitudes, values, preferences, aspirations, and customs of the community at a particular time are relevant from the perspective of human resource management. - Technological Factors:
Technological influences are the total of information that allows people to do things in different ways. These involve inventions and techniques that affect how goods and services are developed, manufactured, and distributed. Technology has two impacts on Coca-Cola: (i) determining the essence of workers, and (ii) shaping human resource management practices.
The HR department deals with recruiting and managing people and since organizations deal with communities with different backgrounds, the government takes the responsibility of ensuring that they are treated fairly. Hence, various statutory norms are enacted by the government for protecting the rights of people or employees working in companies across all sectors. Further, it is the responsibility of the HR department for maintaining these statutory requirements by drafting guidelines by aligning with the provisions enumerated by the government. For example, while finalising the compensation of employees, provisions of the National Minimum Wage Act must be considered by the management. Also, the HR department must maintain various records such as wage sheets, receipts, and attendance records of employees. These records are checked periodically and EasiClean plc may get penalised for non-compliance.Human resource management is governed by federal regulations, though small businesses may be exempt depending on their size. Each state has its own set of employment principles that regulate issues like record retention, workplace relations, criminal history, and even employee mileage reimbursement standards, in addition to federal legislation. As a result, HR professionals must be well-versed in the ever-changing world of employment law in order to reduce the company's liability in all aspects of HR.
The following are some of the legislations that must be considered by the management while devising HR strategies.
National Minimum Wage Act 1998: The salaries and wages have to be finalised as per the provisions;
- Apprentice: £4.15 per hour
- Below 18 years: £4.55 per hour
- 18 to 20 years: £6.45 per hour
- 21 to 24 years: £8.20 per hour
- Above 25 years: £8.72 per hour
Further, the HR should also include the following as working time while calculating the number of hours worked by employees; (Grimshaw, et. al., 2017)
- Machine breakdown time when employees cannot work without using equipment or machine
- Meetings with supervisors or other team members before, after, or during working hours.
- Travelling in connection with work or for training
The following are the activities that are not considered as normal working hours.
- Leaves taken by employees, holidays, or week-offs
- Travelling between work and home
- Employees not working but are present at the workplace and available for work
Employment Rights Act 1996: This act covers varieties of topics ranging from unfair dismissal, employment contracts, redundancy, and family-friendly leave. The HR policy has to consider providing statement of income in the form of pay slips, overtime sheets, and other employment documents as per the request raised by employees. This act also ensures employees for guaranteed and payment for their work and hence, an appropriate method of paying salary/wages has to be implemented so that employees are paid on time. Additionally, health and safety concerns have to be addressed by arranging for appropriate medical facilities (Wynn, 2016).
Employment Relations Act 1999: Provides rules and guidelines for trade union recognition, de-recognition, and industrial actions. The important aspect of this act is that it recognises trade unions as representatives of the employees and negotiating with the trade unions as part of collective bargaining. The HR policy should promote collective bargaining by including employees or their representatives in the decision-making process. Further, employees and their representatives have to be informed related to changes in the employment policies and procedures. The HR policy should ensure handling appropriate grievance handling procedure for resolving various employment issues faced by employees. Appropriate guidelines have to be provided for managers for resolving disputes within the specified duration (Vanstraelen & Schelleman, 2017). It not only ensures including employees in the decision-making process that builds trust and confidence among employees.
Part-time Workers (Prevention of Less Favourable Treatment) Regulations 2000: This act states that part-time employees be provided the same treatment as that of permanent employees. The HR strategy should promote equality across all levels of management and treat employees based on their merits. Part-time workers or interns should be provided with all details of employment, including pay and other remuneration. As in the case of regular employees, part-time employees, interns, and contract employees have the right to receive payslips and other employment documents. With the changes in the composition of employees due to globalisation, employment provisions have to accommodate changes in the business landscape. Hence, the HR strategy should be flexible enough so that changes can be included in the policy as and when required.
Anti-Discrimination Laws in Hiring
“Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964” prohibits discrimination against workers on the basis of "race, colour, faith, sex, or national origin." The regulations apply to employers who have 15 or more employees on the payroll every day for at least 20 weeks during the current or previous calendar year (Hayter, 2018).
Regulations Protecting Wages and Overtime
The “Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)”, which is updated on a regular basis, determines the federal minimum wage. Because many states have minimum wage laws that are higher than the federal minimum, HR professionals must ensure that the amount paid to employees is correct on a regular basis (Andrias, 2018). In addition to stringent child labour regulations, FLSA regulations mandate that all covered workers be paid overtime for any hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek.
Family and Medical Leave Provisions
For a range of reasons, including employees', spouses or serious illnesses of health, linking with a new baby, or a requirement for qualification related to active military service, Federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) allows skilled workers to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a year. Employees caring for a qualified service member are eligible for up to 26 weeks of leave (Code, 2019).
Disability and Medical Privacy Protections
Different federal regulations govern how an employer treats an employee who is disabled or chronically ill. Employers are prohibited from discriminating against workers under the American Disability Act on the basis of disability or perceived disability. Employers must also make adequate accommodations to enable workers to fulfill their work duties, and provide accommodations – such as interpreters - to enable disabled consumers to have access to the organization's products or services. The Act also encourages firms to modify their facilities to allow consumers to use them.
Issues related to identifying the impact of the law on Employment Practice
Considering equality during promotions: Certain categories of individuals are protected by the law such as women or the disabled. Hence, it is important to include them in creating a diverse workplace. However, managers may prefer other groups of employees because they feel that employees can work for a longer duration when compared to women or disabled. In this case, the management may consider productivity over ethical considerations, thus, creating the gap between policy formulation and implementation (Inyang, 2020).
Implementation of standard procedures during emergencies: In normal circumstances, the HR department ensures that appropriate guidelines and policies are followed as perthe statutes. However, during emergencies, the management may implement strategies for the survival of the organization during emergencies such as the recession. In this case, policies may be modified temporarily that gives more power to managers, including terminating employees. In such a position, the HR cannot prevent the management from making tough decisions since it impacts the survival of the firm (Merritt, et. al., 2019).
From the analysis, it can be stated that provisions of the employment act have to be maintained for ensuring that employees’ rights are protected. The HR policy should ensure that provisions are communicated to managers and employees so that business strategies can be developed accordingly. For example, EasiClean Plc may use advanced software and applications for processing payments so that salaries and wages can be disbursed on time. Similarly, automatic time recording systems can be placed for recording the number of hours worked by employees accurately so that there are no disputes with regard to payment of salaries and calculating overtime hours.
1) Strategic Human Resources Management Models
The strategic human resources management models are essential for EasiClean Plc as these models enable the management to develop an analytical framework for human resource management practices such as strategic choices, determine situational factors, competence, and managing stakeholders. These models legitimise HR practices, particularly in training and development as a distinct and futuristic approach enables to determine future requirements of the organization (Boon, et. al., 2018). For example, training and development may include using advanced technology so that the staff and employees can use software and applications appropriately, thus, increasing the productivity and efficiency of employees.
The HRM Models are;
- The Harvard model
The Harvard Model was developed by Beer et al (1984) at Harvard University and the authors referred to it as the map of HRM territory. This model acknowledges that multiple stakeholders exist within the organization and identifies stakeholders are; employees, communities, and the government. The Harvard model emphasizes the human side of Human Resource Management and operates with five critical components; interest of stakeholders, HRM outcomes, situational factors, HRM policies, and long-term consequences of the organization. Further, this model states that there is a correlation between stakeholders' interests and situational factors that have a greater impact on HRM policies implemented at the organization. These policies, when implemented effectively, leads to achieving desired HR objectives. Also, this framework divides HR outcomes into 4C’s which are competence, commitment, cost-effectiveness, and congruence (Boon, et. al., 2018).Organizations develop strategies for improving 4C's for achieving favourable results for individual and societal well-being, and organizational effectiveness. This model nurtures promotes implementing motivational practices and provides for general managers for getting involved while formulating HR strategies. This model is developed based on the perception that human resource enables the firms to gain a competitive advantage; hence, employees have to be considered as assets instead of considering them as costs centres. Thus, this model considers promoting employee-friendly policies that enable the firms to improve their performance and achieve overall objectives.
- Devanna Model – “Michigan Model or Matching Model”
This model was developed by Devanna and Fombrun Tichy in 1984 at the Michigan Business School. This model is also referred to as the "Matching Model of HRM" since this model emphasizes the hard side of human resource management. This is because the focus is on ensuring a "tight fit' between business strategies and HR strategies implemented at the organization. It considers matching the jobs performed in the organization should be matched with that of available human resources. Since integration has to be achieved between business and HR strategies, HR should involve calculating the quantity or number of employees or the staff required for achieving business objectives (Delery and Roumpi, 2017).As per this framework, business strategy is important since human resources are considered as any other resources present in the organization that must be utilised to the optimum extent for achieving organizational objectives. This model is based on the "product-market logic" that considers procuring cheap labour to gain higher profits. Also, the labour must be developed and exploited to the maximum extent by developing strategies that enable the management to exploit the full potential of employees.
The limitations of using the Michigan Model prompted firms to develop other HRM models that are flexible and acceptable to all. This is because the Michigan Model emphasized achieving business objectives strictly adhering to the principles of utilising available resources irrespective of their expertise in handling tasks. Also, the management is forced to achieve organizational objectives by reducing labour costs that arise due to Performance Related Pay, staff reduction, and structural re-organization. Additionally, the "Matching Model" considers that business strategy should be considered while performing four core HR functions;
- Selection: Matching jobs with available human resources (Delery and Roumpi, 2017).
- Appraisal: Performance management
- Rewards: The reward system should be developed for both short-term and long-term achievements and it must fit with the financial objectives of the firm.
- Development: Developing an efficient workforce through training and development programs.
The matching model emphasizes the "resource" aspect of HRM and the efficient utilisation of available manpower for realising organizational objectives. Although this model is criticized for considering only the benefits aspect of human resources and does not consider providing emotional support to employees. This is because by providing the required support, the management gains trust and confidence, thus, the required productivity and efficiency can be achieved.
Therefore, the “Matching Model” serves as the basis for developing future strategic HRM models that enable overcoming the drawbacks of this model.
- The Warwick Model
This model was developed by Andrew M. Pettigrew and Chris Hendry at the University of Warwick. This model is based on the Harvard Model and represents an analytical approach to Human Resource Management. This model focuses on five different elements;- The inner context includes leadership, culture, structure, and task-technology.
- The outer context consists of technical, political, and competitive forces.
- HRM context that represents HR outputs, definition, role, and organization.
- HRM content consists of reward systems, work systems, and employee relations.
- Business strategy content consisting of product market, general strategy, and company objectives (Harrison and Bazzy, 2017).
This framework is focused on achieving organizational growth and performance by maintaining a balance between internal and external context and using HRM content elements and context that enables implementing flexible policies.
- The Ulrich Model
This model was developed by Dave Ulrich in 1995 and organised key HR functions into; change agent, strategic partner, employee champion, and administrative expert. The important feature of this model is that it is focused on people working in the organization and the roles played by them for achieving overall business objectives. Although this model is not used extensively, it is an important milestone as it ensures creating favourable working conditions for motivating employees. In today's business context, this is highly relevant due to the dynamic nature of the business environment (Kaufman, 2020). - The ASTD Competency Model
This model was developed by the American Society for Training and Development in 2004 through a research process conducted by ASTD. This model is effective as it considers achieving performance against a credible set of descriptors. The framework contains three blocks or layers;- Foundational Level: This includes key competencies; managerial, personal, and inter-personal.
- Focus Level: In this level, Area of Expertise (AoE) is introduced that consists of improving the performance of employees, coaching, performance evaluation, and career planning (Kaufman, 2020).
- Execution Level: This considers four important professional roles; project manager, learning strategist, professional specialist, and business partner.
This model considers professional development as a key factor in achieving personal and business objectives. The key factor considered is the competencies that have to be developed by employees that enable them to exceed their performance and contribute towards the growth of organization (Tomicic-Pupek, et. al., 2017).
- The 5P’s Model
This model is a type of strategic HRM designed by Randall S. Schuler in 1992 and consists of five HRM aspects; purpose, processes, people, performance, and principles. This framework emphasizes aligning and balancing the five elements for achieving organizational objectives.This model defines;
- Purpose: This is the firm’s mission, vision, and objectives.
- Principles: These are defined as operational protocols that enable the management to achieve the objectives (Bozhinovska, 2019).
- Processes: This consist of systems, methods, and the firm's architecture
- People: Workforce appointed for performing various tasks as per the pre-defined processes and principles.
- Performance: Results that can be measured by using appropriate standards.
This HRM model focuses on achieving the long-term objectives and maintaining productivity and efficiency for a longer duration. Also, the outcomes depend on the performance of employees engaged in processes and guided by the purposes and principles of the organization.
- The HR value chain:
This is one of the most well-known HR styles. It is based on Paauwe and Richardson's (1997) work and adds complexity to the previous models in terms of how HR works. All achieved and calculated in HR can be split into two groups, according to the HR value chain: HRM activities and HRM outcomes. Recruitment, compensation, preparation, and succession planning are examples of day-to-day HRM activities (Poisat and Mey, 2017). The aims we aim to accomplish with HRM practises are known as HRM outcomes. - The HR Value Chain Advanced:
The HR value chain is very similar to this model, but there are two main differences. The balanced scorecard, for starters, determines organisational efficiency. The main performance metrics from a financial, consumer, and process perspective are all included in the balanced scorecard. Second, the model begins with a collection of human resource enablers. These enablers are critical to HR's success in the workplace. HR programmes, budgets, capable staff, and other main factors are all included. - The 8-box model by Paul Boselie:
The 8-box model depicts various internal and external factors that affect the efficacy of HR activities.The external general market context, the external population market context, the external general institutional context, and the external population institutional context are all discussed first. External factors influence the way HR is treated (Mala, 2020). The past, culture and technology of the company all influence how people communicate in HR, what they want to do, and how effective HR policies are. These two factors have an impact on HR policy.
- The Standard Causal Model of HRM:
The model comes from many similar models released in the 90s and early 2000s. The model demonstrates a causal chain that begins with the business plan and ends with improved financial results through HR processes. The model thus demonstrates how company success is guided by HR activities associated with organizational strategy. Under this model, HR can only be successful if its policy is consistent with its corporate strategy. The human resources plan is also extracted from the overarching plan.
2) Human resource management contributes to the achievement of the organization’s strategic plans
An HR manager performs a key role in the organization's strategic planning, which is in accordance with their vision. This involves their advocacy/relation to the workforce, as the employee's dedication and efficiency decide the company's success rate. HR tracks the capacity of the company and matches personnel in the right tasks to achieve strategic objectives with the implementation of efficient performance management programmes, predicting the types of positions required to achieve the strategic plan and adapting to the demographic shifts of the workforce. HR management also plays a pivotal role in improving employer-employee partnerships because they make a major contribution to training and development initiatives. This allows workers in the business to flourish and thereby increases employee satisfaction and productivity (Zardasht, Omed and Taha, 2020). The human resources management role contributes to ensuring employee satisfaction, company efficiency and success. It can provide the company with an obvious view of competitive advantage and greatly assist in the implementation of the organization’s strategic plans.
The scope of HR management is vast. All the activities of employees from entering into an organization to exit from the organization are the responsibility of HR management. Since every organization is made of people, HRM is all about helping EasiClean Plc in building a strong organization by acquiring the services of people (Kasekende, et. al., 2020).
Since every organization is made of people, HRM is all about helping the organization in building a strong organization by acquiring the services of people. Its HRM's responsibility for developing the skills of employees, motivate them to work with goal achieving strategy. To provide a well behaved, goal-oriented workforce to the organization, HRM work on various functions of human resource management.
Job analysis and Job design: Job Analysis is the process of determining and recording all the pertinent information about a specific job, including the tasks involved, the knowledge and skillset required to perform the job, the responsibilities attached to the job, and the abilities required to perform the job successfully. Job design is the next step after job analysis. Job design essentially involves integrating job responsibilities or content and certain qualifications that are required to perform the same. It outlines the job responsibilities very clearly and also helps in attracting the right candidates to the right job. HRM first analyses and design the job for the aspirants then go for the recruitment process (Muindi, 2017).
Recruitment and Selection: It involves interviewing, screening, and selecting well qualified and potential candidates according to the job requirement. This process is to obtain extremely well talent for the organization. The recruitment and selection process is one of the most important aspects of EasiClean Plc. The right employees can take EasiClean Plc business to new heights. The wrong ones can hurt business by missing sales, turning customers off, and creating a toxic workplace environment.
Orientation: This is an introductory stage in the process of new employee assimilation and a part of the continuous socialization process in EasiClean Plc. Major Objectives of orientation are to (1) gain employee commitment, (2) reduce employee's anxiety, (3) helps understanding organization's expectations, and (4) convey what they can expect from the job and the organization.
Strong Work Culture: Work culture plays an important role in extracting the best out of employees and making them stick to EasiClean Plc for a longer duration. The organization must offer a positive ambiance to the employees for them to concentrate on their work rather than interfering in each other's work. Work culture is a concept which deals in beliefs, thought processes, attitudes of the employees, Ideologies, and principles of EasiClean Plc (Boudlaie, et. al., 2020).
Employee Relation Management: Employee relationship management is a process that EasiClean Plc effectively manages all interactions with employees, ultimately to achieve the goals of its organization. Employee relationship management is an information system that supports the relationship between a company and its employees. Employee relationship management has focused on enabling employees to collaborate on typical managerial tasks with their employers by engaging inputs from both sides of the employment relationship (Harrison and Bazzy, 2017).
Apart from the above functions, HR performs various other functions for fulfilling organizational objectives.
Operative Functions: These are the core activities performed by the HR which are;
Recruitment: Recruitment is the most challenging process; it requires so much research about the candidates and job description, the right person for the right designation with enough knowledge
Training and Development: after selecting the candidate, HRM provides the training for fresher candidates. This function makes it easy for the employees to understand the working process and structure of the organization so they can do their jobs with much satisfaction.
Professional Development: It is an important function that provides the employee with an opportunity for growth by brushing their skills by organizing training seminars and functions (Nieves and Quintana, 2018).
Compensation and Benefits: Employees work better if there are some rewards and awards. People put their effort into rewards, which makes it easier to get the target at right time. Human resource management should provide the facilities like Working hour flexibility, timely vacation, Medical Insurance, house, and transport expenditures.
Performance Appraisal: Performance evolution is important to function for HR managers to ensure the growth of the company. Promotions and rewards are given to the candidates who perform better, this function helps the organization to get information about the employee that they are moving towards the goals and objectives of the organization or not, so that organization can find out the new area of improvement.
Managerial Functions: This involves planning and managing the workforce by implementing policies that enable the management to utilise the expertise of employees for achieving business objectives. These are;
Planning: Planning is a very important function where a strategic blueprint is created about all the activities of an organization. In this function goals and different approaches are prepared to obtain an organizational goal.
Organising: Organising means knowing the structure of the firm and making available required resources for the organization like a number of employees, designations, and their work process. All the functions of an organization can be distrusted by the respective people (Kasekende, et. al., 2020).
Directing: It is a function of HRM to direct the employees in such a way, by which they get inspiration and try hard to achieve their goals. In this process, managers try to find the employees' needs and award them with the same to motivate them towards the work.
Controlling: Controlling refers to managing the team, examining their work, and planning according to the organization need, checking organization goal is achieved or not (Muindi, 2017).
Advisory Functions: Along with planning and implementing appropriate strategies, HR also advices the management while formulating HR strategies.
Management Advice: The HR Manager is responsible to discuss all the policies with the authority about the business needs and employees' outputs. It includes the area of organization goal, available budget, revenue, required employees, working environment, that are responsible for high productivity (Boon, et. al., 2018).
Departmental advice: HR Manager advises the authorities of various departments in the organization on strategies about the current status and future requirements like creating new jobs, developing designations, organizing recruitment process, selecting candidates, and maintaining a positive environment for a positive result.
Hence, the HRM has the responsibility to analyze their hiring procedure to check what went right and find out the areas for improvement. Examining the hiring procedure on what basis a candidate is selected and another is rejected. The hiring procedure should follow strict rule and regulations to ensure no discrimination between candidates. Hiring should be according to the requirement and required qualities for the designation. And the applicant needs to perform to show his/her abilities for the post during the selection process.
1) Factors to be considered when preparing human resource management strategies
Every organization has its own culture. Almost everything that affects an organization's ability to compete and respond successfully to changes in the external environment – ultimately, the organization's success or failure – is an aspect of that culture. The internal factors determine how the organization moves forward, both as a self-contained organizational entity and in response to its external environment. An effective human resources department is necessary for the organization to be successful (Bozhinovska, 2019).
An HR department typically encounters a number of internal and external factors as part of its function.
External Factors- There is several factors that affect the day-to-day operations of HRM.
Government Regulations- Government regulations influence every process of the HR department, including hiring, training, compensation, termination, and much more. Without adhering to such regulations a company can be fined extensively which if it was bad enough could cause the company to shut down (Papa, et. al., 2018).
Economic Conditions- One of the biggest external influences is the shape of the current economy. Not only does it affect the talent pool, but it might affect your ability to hire anyone at all. One of the biggest ways to prepare against economic conditions is to not only know what's happening in the world but also create a plan for when there is an economic downturn. The most pressing issue in human resource planning is the amount of money available for wages, training, and equipment. External economics, on the other hand, is equally significant.
Technological Advancements- This is considered an external influence because when new technologies are introduced the HR department can start looking at how to downsize and look for ways to save money. Technology is revolutionizing the way one does business and not just from a consumer standpoint, but from an internal cost-savings way (Cooke, 2018).
Workforce Demographics- As an older generation retires and a new generation enters the workforce the human resources department must look for ways to attract this new set of candidates. They must hire in a different way and offer packages that work for this younger generation. At the same time, they must offer a work environment contusive to how this generation works.
- Social factors:
Social factors can have an effect on an organization's human resource planning. It's a smart idea to build in ways to open up new possibilities where there is a strong disparity of one social category (Bibi, Ahmad and Majid, 2018). - Legal factors
Employment law is the most relevant field of the legal system that has an impact on human resource planning, and it is constantly evolving. HR managers must remain updated on employment law and have access to an employment law expert if appropriate. Changes in employment law must be incorporated in corporate policy. - Labor market
People with talents and abilities can be tapped into the job market when and whenever the necessity arises. Despite the fact that many third-world countries have excess labour, skilled workers are in short supply. We should take steps to increase the number of skilled workers in the country. - Environmental factors
Environmental considerations may include the location of the company, the difficulty of recruiting sufficient workers, or changes in the environment that necessitate the hiring of more or fewer staff. - Technological factors
Companies must still be mindful of proficiencies and preparation needs when preparing human resources as emerging technology introduces new skill requirements (Agarwal and Al Qouyatahi, 2018). New products and services can also necessitate the hiring of highly qualified staff or the preparation of current workers to meet the demand. - Employment
The job market in a country has an effect on HRP. In countries where unemployment is higher, the government can put more pressure on the business to hire more workers. - Organizational changes
Occasionally, changes arise within the company. For instance, a company can diversify into new products or shut down operations in certain areas, among other things. In such situations, a company can recruit or fire employees based on the circumstances. - Technical changes in society
Technology progresses at a breakneck pace, necessitating the recruiting of new workers with the requisite skills. In some cases, the company may be able to maintain current workers and train them on the latest technologies, while in others, the company may be forced to fire existing employees and recruit new ones (Bondarouk, Parry and Furtmueller, 2017).
Internal Factors- A company’s internal factors directly impact the HRM decision making so as to profit and growth of the organization.
Company Mission: The firm's mission summarizes its purpose, values, and vision. When the HR department goes to fill staff positions, it can recruit, interview, and hire individuals who possess similar values (Funminiyi, 2018).
Corporate Culture: Organizational culture defines how employees interact with each other. human resources planning needs to take into account the amount of flexibility in terms of hours, dress code, and formality tolerated by the company. Additionally, it ensures staff coverage during all working hours defined by company operational policies.
The Business' Structure: Organizational structure impacts human resources planning. Functional, divisional, or matrix structures require different staffing. In a functional structure, employees perform specialized tasks. In a divisional structure, each department has representation from each required function, such as sales, marketing, development, and support. In a matrix structure, an employee reports to two different bosses, one represents its function and the other managing the division (Zehir, et. al., 2016).
Available Funding: HR planning must occur within the budget allowed to maximize profitability. Seasonal demands for additional staff may impact hiring plans, so a small business needs to anticipate this. The need for specialized skills may also impact planning. To meet short-term needs, companies may outsource non-core activities. Meeting long-term needs typically involves offering training and development opportunities to the workforce. Additionally, to maximize productivity, morale, and loyalty, employers can plan events. If a small business lacks the financial resources to offer comprehensive HR programs, it can provide lists of free resources related to professional development, workforce wellness, and team-building. Adjusting to funding levels may make the human resources plan a challenge to small businesses.
2) Key elements of a human resource management strategy.
The Harvard system, as previously discussed, is an HR model that takes a holistic approach to human resources, with various levels of outcome. An assessment of the multinational retailer Tesco's HRM strategy shows that he is using the basic basis of the Harvard model in the implementation of his HR strategy. According to the model, Tesco's HRM begins with stakeholder interest. These actors include shareholders, management, staff associations, the government and more. The HRM policies are characterised by these interests. Situational considerations simultaneously affect these interests (Kosheleva and Bordunos, 2018). Situational considerations include employee features, unions, etc.
Situation factors and involvement of stakeholders impact HRM policies. They include key HR tasks such as recruiting, training and recruitment processes. The execution of HRM strategies leads to positive HRM outcomes if things are handled properly. Staff retention, cost-effectiveness, dedication, and expertise are among them. These positive HRM outcomes have long-term human, institutional, and social implications.
Task 5
Recruiting the workforce, retaining employees, and managing organization and employees target is a basic function of the HRM. Apart from these an effective HR system work in many other areas of the organization like developing a strong work culture, positive environment, the safety of employees, and providing better health for them.
HRM Practices: Human resource Practices are part conceptual, part implementation of an HR strategy, comprised of systems that follow the normal or customary way of doing business. The term "best practices" refers to the HR systems that have the greatest impact on the workforce and the organization (Mousa and Othman, 2020).
Organizational Behaviour
Organizational Behaviour is the observation of people working together in an organization to achieve the given target. It is the study of people or group behaviour to know their mental approach towards company's growth.
Planning for Change
Change is part of life, it may occur in business planning. Planning means be ready for future changes in strategies, structures of business, employment, company's financial fluctuations, etc. It is all about creating a picture of organization goals and structure in employees of an organization in such a way that they understand the goals and can work for them (Delery and Roumpi, 2017).
Training and Development
Training is an essential task, need to provide everyone, even well-educated or skilled person need training to understand the structure of an organization and type of work in the organization. Every organization has their own goal achieving strategies, processes, and way of work. To make understand a fresher about the organization scenario training required. For existing workers training and development strategies are used to create some ingenious ideas, fresh skills, so that they can achieve the organization goal efficiently.
In order to maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace, EasiClean must invest in the training and development of its employees. Human Resources Development (HRD) focuses on both training employees for their current jobs and developing skills for their future roles and responsibilities.
Training involves change in attitude, skills or knowledge of a person with the resultant improvement in the behaviour. For training to be effective it has to be a planned activity conducted after a thorough need analysis and target at certain competencies, in a learning atmosphere. Development implies opportunities created to help employees grow. It is more of long term or futuristic in nature as opposed to training, which focuses on the current job. It also is not limited to the job avenues in the current organization but may focus on other development aspects also (Chams and García-Blandón, 2018).
Health and Safety
The Health and safety of the employee is the responsibility of HRM. The HR discusses with the top-level management of the organization and creates rules and regulations, safety guidelines for hazardous and dangerous work.
Selection and Retention
Recruiting people in the organization and maintaining the demand and supply of the workforce is an essential task of HRM. They hire the best talent; give them better training, give rewards and promotions to engage them in the company. Education, benefits, appraisals compensation, promotions, etc. used to engage a worker in the company's productivity. HRM monitors the work and performance of each and every employee to increase and maintain productivity (Hitka, et. al., 2020).
Performance Appraisal and Reward Management
Performance appraisal known as employee appraisal is a method by which the performance of an employee is evaluated in terms of quality, quantity, cost, and time. Performance appraisal is a part of the development and is linked to other human resources functions. A performance appraisal is a systematic, general, and periodic process that assesses an individual employee's job performance and productivity in relation to certain pre-established criteria and organizational objectives.
Today organizations are showing a high degree of commitment towards the reinforcement of reward practices which are aligned with other HR practices and the goals of the organization for attracting, retaining, and motivating employees so as to IKEA. Efficient reward practices help in attracting result-driven professionals who can thrive and succeed in performance-based environments. An effective reward system should be linked with the performance development system, which focuses on performance-based pay and offers ample learning opportunities along with a healthy work environment.
Flexible Work Practices
Flexible working is on the rise, giving employees flexibility on where, when, and the hours they work. It is traditionally been associated with the needs of parents and carers, but increasingly organizations are recognising the business benefits of a more flexible way of working. The HR department has two jobs when it comes to supporting managers with flexible working. Firstly, to ensure the process of dealing with flexible working requests is fair and legally compliant (Katou, 2017).
Strategic Management
HR always efforts to increase the services with its experience of how human resource affects organizational success. The HR research about the company's strategy, its targets, and its planning then according to requirement, HR takes a decision about the workforce needed.
Wages and Salaries
The HRM always work hard to cut the wages and expenses of the organization. The wage and salary surveys are done by the HRM to maintain compensation costs with the company's current financial status and desired revenue (Úbeda-García, et. al., 2017).
Analysing Benefits
It is important to analyse what an organization did to set new targets and to improve efficiency and productivity. Analysis of performance ensures the growth of the organization. In this function, the HRM monitors and ensure the benefits of employees as well as of employers.
Safety and Risk Management
An employee wants to work in such an environment, where he or she feels happy and safe to work. Before entering into any organization an employee look for all the safety features of the organization and try to search for a possibility of personal development. So, it is the responsibility of HRM to provide such a workplace where all can work for the organization with happiness (Úbeda-García, et. al., 2017).
Liability Issues
The HRM takes responsibility not to misuse employees and their knowledge by unfair work practices by maintaining workforce and organization relations strong. Training and development are provided to educate about the company goals and achieving strategies to ensure the best result.
Employee Satisfaction
Creating a friendly environment to work with a positive competition and ensuring individual’s growth with the company's growth, is the responsibility of HRM. In such an environment, each and everyone associated with an organization gets benefit and satisfaction (Rajapakse, 2017).
The HR articulates the Vision, Mission, and Values by knowing about organization structure, working process, product, and services. It defines the goal of the organization and the need for the business by drawing up HRM Plan using the detailed study of the business. Creating the structure, departments, and a number of designations in the organization according to the need, manpower planning is a process of recruiting an appropriate person for the designation within desired ranges of salary who works hard to achieve the organization goal. Performance Management System is to check the employee's performance in the organization whether the employee is working or not.
Benefits of HRM for an employer
The HRM has a function of managing human resource and establishes a relationship between human resource, organization structure, and organization goals. This is done to increase productivity and performance by managing the product and services of an organization. It has various important benefits for the organization.
- It creates and maintains positive behaviour in an organization.
- It provides training to ensure employees development (Cooke, 2018).
- It always tries to build a Workplace where employee enjoys the work.
- It always motivates workers towards their goals and individual development.
Benefits of HRM for an employee
The HRM has dual responsibilities to maintain and protect the benefits of human resource and the organizations. For employers, they manage employee relations and identify. They maintain the relations between the company and working people in such a way that benefits both employees and employers. They maintain safety features for employees, protect their benefits, and take care of their freedom (Funminiyi, 2018).
- Dispute resolution: The HRM is always available and responsible authority to resolve the dispute between organizations and their employees.
- Training and development: Training is an essential key to educate people about the structure of the company, available designations, process of work, product and service delivery and maintaining services. It is important to train a fresher about the company and his/her role for the company (Ekpo, et. al., 2017).
- Employee Relations: The HRM ensures a strong work culture where all the employees work together with different roles to achieve an organizational goal. They create positive competition between worker which benefits both company and the workforce.
- Information Resource: The HRM provides a detailed structure of the company their product and services to employees. They give information about wages, salary, leaves, training, responsibilities, promotions, and progress.
1) Strategic human resource management strategy for McDonald’s
The human resource planning process involves four general, broad phases. Each move must be taken sequentially in order to achieve the ultimate goal of developing a strategy enabling the company to effectively identify and retain sufficient skilled staff to meet the needs of the company. The strategic policies are aligned with the recruitment policies as it ensures achieving overall objectives of the firm.
Steps to Strategic Human Resource Planning
The human resource planning process involves four general, broad phases. Each move must be taken sequentially in order to achieve the ultimate goal of developing a strategy enabling the company to effectively identify and retain sufficient skilled staff to meet the needs of the company.
Assessing Labor Supply
The first step in human resource planning is to determine the current human resources supply of the company. The HR department investigates the organization's strength depending on the number of workers, their capabilities, competencies, roles, advantages, and skill level in this step.
Forecasting Labor Demand
The second phase requires that the company outlines its employees' future. The HR Department may address such problems, such as promotions, retirements, dismissals and transfers, which are essential to a company's future needs (Knezovi?, Bušatli? and Ri?i?, 2020). The Department of Human Resources will also analyse external factors influencing labour demand, such as emerging technologies that may increase or minimise workers demand.
Balancing Labor Demand and Supply
Forecasting job demand is the third step in the HRP process. HR produces a gap analysis that identifies precise requirements for narrowing the company's labour supply versus potential demand. This analysis will often generate a series of questions, such as:
- If the staff members need to learn new skills
- Whether more managers are required by the organization
- If all employees play to their strengths in the roles that they are playing currently
Developing and Implementing a Plan
The answers to the questions on the gap analysis help HR decide how the HRP project should be conducted in the final phase. Now it's up to HR to put its strategy into action and integrate it with the rest of the company (Storey, Ulrich and Wright, 2019). The department will need a budget, resources to implement the strategy, and a collaborative effort from all departments to implement the strategy.
In order to fulfil its objectives of:
- becoming a world leader in the building industry
- achieving highest level of quality and timely completion of value added projects to become the customers' first option
- delivering the highest quality of service in the construction sector while delivering outstanding craftsmanship on each project
Velocity UK Ltd. can employ the above-mentioned steps of strategic HRM planning. These steps will ensure that the organizational objectives are met with the least amount of friction.
Alignment Planning Model: This approach is used since it helps the management to align resources available with the management and overall objectives. Under this, the steps followed are;
- The top-management outlines firm’s objectives, activities, resources, and other requirements (Vanstraelen and Schelleman, 2017).
- Identifying the effectiveness of these strategies and techniques and methods that can be used for improving existing policies.
- Determining the types of improvements required across all functions that enable rectifying the mistakes (Harrison and Bazzy, 2017).
- Including the latest changes in the strategic planning process.
Scenario Planning: This method of planning ensures that management applies strategic planning techniques for identifying operations issues. This is done by;
- Evaluating external forces and predicting changes in the business landscape that affects performance.
- Identify appropriate solutions for mitigating issues and responding to changes.
2) The proposed human resources management strategy will support the achievement of the business objectives for this organization.
The proposed human resources management strategy will help McDonald’s to increase the productivity of the organization by;
Employee Relations: Every individual shares a certain relationship with his colleagues at the workplace. The relationship is warm, so-so or bad. The relationship can be between anyone in the organization between co-workers, between an employee and his superior, between two members in the management, and so on. It is important that the employees share a healthy relationship with each other to deliver their best performances (Kaufman, 2020).
Employee-Employee relation: The employees must be comfortable with each other for a healthy environment at work. It is the prime duty of the superiors and team leaders to discourage conflicts in the team and encourage a healthy relationship among employees. A healthy relationship among the employees goes a long way in motivating the employees and increasing their confidence and morale. An employee must try his level best to adjust with each other and compromise to his best extent possible. An individual however hardworking he is, cannot do wonders alone. It is essential that all the employees share a cordial relation with each other, understand each other’s needs and expectations and work together to accomplish the goals and targets of the organization (Bozhinovska, 2019). Conflicts and misunderstandings only add to tensions and in turn decrease the productivity of the individual.
Employee-Employer Relation: Employers and Employees often work in close quarters, they necessarily develop relationships. Managing these relationships is vital to business success, as strong relationships can lead to greater employee happiness and even increased productivity. This relationship should be mutually respectful. The degree of closeness in these relationships will depend on both the employer and the employee. Some employers opt to keep their employees at a distance and another elect to become friendlier with their employees. The employer-employee relationship should be one of mutual reliance. The employer is relying upon the employee to perform her job and, in doing so, keep the business running smoothly. Conversely, the employee is relying upon the employer to pay and enable employees to support financially.
Human resource management helps Organization by strategic planning for the organization in which future goals and the required workforce are obtained. HR helps to maintain the wages and salaries of employees according to the company's financial status and projected revenue. They help to reduce the company's costs by analyzing each factor in recruitment. HRM create an environment which is safe and risk-free so that employee can enjoy their work. It ensures the relationship between the employees and between the company and employees. HRM works hard for recruiting people, giving them training, promoting them according to their performance, and satisfy them in the company (Kasekende, et. al., 2020).
A positive environment always gives positive results. HRM always works hard to develop a positive workplace where people can work together to achieve common goals. Good employee relation makes decision making easy as they have a mutual understanding of the work and strategies. People respect each other and have a positive competition that leads the organization to a new level of growth. As the organization is growing, it is beneficial for employees associated with it. HRM manages such an environment to ensure all-rounder progress for the organization and associated workforce.
Potential Barriers to the Implementation of a Human Resource Management Strategy
The suggested plan, however, is not foolproof. There are certain barriers which can hinder the implementation of the plan. The barriers are as follows:
- Inadequate assessment of environmental and cultural factors influencing plan acceptance.
- Inability to grasp the business's strategic needs, resulting in HR strategic plans being seen as negligible, if not harmful.
- Failure to consider the significance of building enablers for initiatives.
- Inability to persuade top management to accept the project entirely.
- Inability to gain employees' acceptance and understanding (Barrena-Martinez, López-Fernández and Romero-Fernandez, 2018).
- Failure to track and control the strategy's implementation, as well as take decisive corrective measures when things go wrong.
- Failure to ensure that the resources required carrying out the programme is available; in this case, HR support is essential.
- Failure to realise that the plan will put new demands on line managers' commitment and skills, as they will be forced to play a key role in its implementation.
References
Al-Sarayrah, S. et al., 2016. The Effect of Culture on Strategic Human Resource Management Practices: A Theoretical Perspective. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research, 7(4)(704-716).
Boon, C., Eckardt, R., Lepak, D. P. and Boselie, P., 2018. Integrating strategic human capital and strategic human resource management.. The International Journal of Human Resource Management., Volume 29(1), pp. 34-67.
Boudlaie, H. et al., 2020. Designing a human resource scorecard: An empirical stakeholder-based study with a company culture perspective.. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation., 16(4), pp. 113-147.
Bozhinovska, T., 2019. Boards' involvement in strategic human resource decisions: towards an integrative model. Journal of Human Resource Management, 22(1), pp. 70-78.
Chams, N. and Garcia-Blandon, J., 2018. On the Importance of Sustainable Human Resource Management for the adoption of Sustainable Development Goals. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 141(C), pp. 109-122.
Cooke, F. L., 2018. Concepts, contexts, and mindsets: Putting human resource management research in perspectives. Human Resource Management Journal, 28(1), pp. 1-13.
Delery, J. E. and Roumpi, D., 2017. Strategic human resource management, human capital and competitive advantage: is the field going in circles. Human Resource Management Journal, 27(1), pp. 1-21.
Ekpo, N. B., Etukafia, N. and Udofot, P. O., 2017. Finance manager and the finance function in business sustainability. nternational Journal of Business, Marketing and Management, 2(1), pp. 31-38.
Funminiya, A. K., 2018. Impact of Organizational Structure on Employee Engagement: Evidence from North Central Nigeria. International Journal of Advanced Engineering, Management and Science, 4(8).
Grimshaw, D., Johnson, M., Keizer, A. and Rubery, J., 2017. The governance of employment protection in the UK: how the state and employers are undermining decent standards.. In: A. Piasna and M. Myant, eds. Myths of employment deregulation: how it neither creates jobs nor reduces labour market segmentation. Brussels: ETUI, p. 225.
Harrison, T. and Bazzy, J. D., 2017. Aligning organizational culture and strategic human resource management. Journal of Management Development, 36(10).
Hitka, M. et al., 2020. Differentiated approach to employee motivation in terms of finance.. Journal of Business Economics and Management, pp. 1-17.
Inyang, U., 2020. Whistleblowing as a Corporate Governance Mechanism: A Comparative Analysis of Employee-Whistleblower Protection in the United Kingdom and Nigeria. [Online]
Available at: https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-dandq=Inyang%2C+U.+%282020%29.+Whistleblowing+as+a+Corporate+Governance+Mechanism%3A +A+Comparative+Analysis+of+Employee-Whistleblower+Protection+in+the+United+Kingdom+and+ Nigeria.+Available+at+SSRN+3547899.
[Accessed 01 12 2020].
Kasekende, F., Nasiima, S. and Otengei, S. O., 2020. Strategic human resource practices, emotional exhaustion and OCB: the mediator role of person-organization fit. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, 3(7), pp. 275-295.
Katou, A. A., 2017. How does human resource management influence organizational performance? An integrative approach-based analysis. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 66(6), pp. 797-821.
Kaufman, B. E., 2020. The real problem: The deadly combination of psychologisation, scientism, and normative promotionalism takes strategic human resource management down a 30?year dead end. Human Resource Management Journal, 30(1), pp. 49-72.
Merritt, C. C., Kennedy, S. S. and Kienapple, M. R., 2019. The cost of saving money: Public service motivation, private security contracting, and the salience of employment status. Public Performance and Management Review, 42(4), pp. 920-946.
Mousa, S. K. and Othman, M., 2020. The impact of green human resource management practices on sustainable performance in healthcare organizations: A conceptual framework. Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 118595, p. 243.
Muindi, J. M., 2017. Effectiveness of strategic human resource management practices in enhancing performance: A case of the office of the Attorney-General and Department Of Justice in Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, United States International University-Africa. [Online]
Available at: http://erepo.usiu.ac.ke/bitstream/handle/11732/3224/JACQUELINE%20M.%20MUINDI%20GEMBA%202017.pdf?sequence=1andisAllowed=y
[Accessed 01 12 2020].
Nieves, J. and Quintana, A., 2018. Human resource practices and innovation in the hotel industry: The mediating role of human capital. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 18(1), pp. 72-83.
Papa, A. et al., 2018. Improving innovation performance through knowledge acquisition: the moderating role of employee retention and human resource management practices. Journal of Knowledge Management, 24(3), pp. 589-605.
Rajapakse, R. P. C. R., 2017. Importance of Soft Skills on Employability of Finance Graduates. Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies, 5(1), pp. 136-141.
Tomicic-Pupek, K., Pihir, I. and Kolaric, J., 2017. Process based approach in Development of an innovative Strategic Human Resource management. In: Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings. s.l.:s.n., pp. 678-684.
Úbeda-García, M., Claver-Cortés, E., Zaragoza-Sáez, P. and Marco-Lajara, B., 2017. Human resource flexibility and performance in the hotel industry: The role of organizational ambidexterity. Personnel Review, 46(4), pp. 824-846.
Vanstraelen, A. and Schelleman, C., 2017. Auditing private companies: what do we know?. Accounting and Business Research, 47(5), pp. 565-584.
Wynn, M. T., 2016. Chameleons at large: entrepreneurs, employees and firms-the changing context of employment relationships. Journal of Management and Organization, 22(6), pp. 826-842.
Zehir, C., Gurol, Y., Karaboga, T. and Kole, M., 2016. Strategic human resource management and firm performance: the mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, Volume 235, pp. 372-381.












