Leveraging IT in the Banking Sector: Case Studies and Critical Analyses
Question
Task: How can project charters facilitate mutual understanding of project aims and objectives among stakeholders in large-scale IT projects, using the example of Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing initiative?
Answer
Question 1: Introducing the organisation, including the impact of IT on shaping the business operations of the organisation
Introduction to the chosen organisation
Barclays Plc is a well-known international financial company with a long history that extends over three centuries. Providing a vast array of financial goods and services to consumers, corporations, and institutions, this global banking giant is a major player in the global commercial landscape. This essay will look at the different kinds of information systems that Barclays uses, talk about how technology, society, and management have changed over the course of information technology's (IT) evolution, and critically assess how IT has shaped the organisation's business operations to meet its goals (Khan et al., 2020). Additionally, it will assess how IT may enhance international company operations and the competencies required to meet the difficulties of the global market, considering pertinent ideas such as Absorptive Capacity and Information Transformation.
Types of Information Systems at Barclays Plc
Barclays uses a variety of information systems to improve customer service and expedite business processes. These consist of:
• Client Relationship Management (CRM) Systems:: By monitoring client interactions, enhancing tailored services, and raising customer satisfaction, CRM systems assist Barclays in managing its large customer base more successfully.
• Transaction Processing Systems (TPS):These systems allow millions of transactions to be processed safely and effectively, and they are essential to day-to-day banking operations (Hsu et al., 2021).
• Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics Systems:These tools help with risk management, strategic planning, and decision-making by drawing insightful conclusions from data.
• Core Banking Systems: These systems handle accounts, deposits, withdrawals, and a range of financial products. They are the foundation of the bank's operations.
• Systems for Fraud Detection and Cybersecurity:Barclays depends on robust systems for fraud detection and cybersecurity to safeguard sensitive client data and uncover fraudulent activity, guaranteeing a safe and secure financial setting (Usman and Hammar, 2021).
Evolution of IT at Barclays
There have been substantial managerial, societal, and technological shifts during Barclays' IT history.
• Technological Evolution: Barclays has welcomed the changes brought about by technological breakthroughs, which have been instrumental in modernising the banking sector (Kirikkaleli and Adebayo, 2021). For example, the emergence of online and mobile banking platforms has been facilitated by the Internet and mobile technologies, allowing users to execute transactions, monitor account balances, and manage accounts from their devices. In addition to improving consumer convenience, this technological advancement has decreased the need for physical branches, which has resulted in cost savings (Baloch et al., 2021). Furthermore, by combining machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), Barclays is now better equipped to identify fraud, automate customer service, and forecast market trends. Virtual assistants and chatbots now offer round-the-clock assistance,
• enhancing the effectiveness of consumer interactions.
• Social Development:The emergence of a tech-savvy clientele has caused a societal change in the banking sector. Customers in the millennial and Gen Z generations, in particular, seek smooth online experiences and prefer digital connections (Litvinenko, 2020). In response, Barclays has made investments in digital onboarding procedures, smartphone applications, and user-friendly interfaces. This appeals to a broader range of customers and satisfies the expectations of the younger generation.
• Management Development: Barclays has reorganised its management procedures to adapt to changes brought about by IT. Project management, cross-functional teams, and agile approaches are now essential components of the bank's IT initiatives (Cheng et al., 2021). Barclays can provide software upgrades and enhancements more quickly because of the adoption of DevOps and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) techniques. The bank is now able to react to consumer needs thanks to this management development.
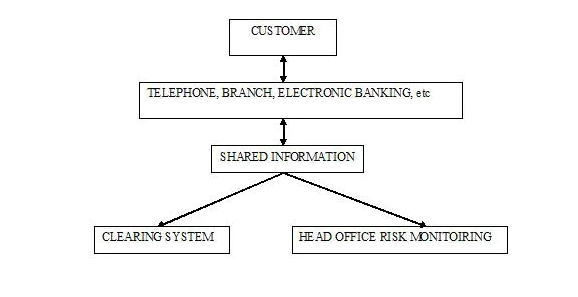
Figure 1: Information Technology's Evolution in the Banking Sector
(Source: Francis, 2010)
Information Technology's Effect on Business Operations
Barclays' business operations have undergone a radical change because of IT. The following are some significant areas where IT has influenced how the company operates:
Digital Transformation:Barclays' IT investments have made it possible for a thorough digital transformation to occur, giving clients access to online and mobile app banking services. As a result, there are now fewer physical branches and operating expenses.
Data-Driven Decision-Making: The bank can now gather, examine, and use enormous volumes of data to inform decisions thanks to IT systems (Alam and Murad, 2020). Product development, consumer segmentation, and risk management have all improved.
Improved client Experience:Barclays now has a more positive client experience thanks to IT, which has made it possible for them to provide individualised services, round-the-clock customer assistance, and effective self-service choices.
Worldwide reach:Barclays is now able to operate internationally and in several nations. Consistent service delivery across foreign markets is made possible by the integration of IT systems.
Operational Efficiency:A lot of banking procedures have been automated by IT systems, which has reduced human error, streamlined operations, and reduced expenses.
Enhancing International Business Operations:Barclays' international business operations stand to benefit even more from information technology.
Integration and Collaboration:By enabling cross-border cooperation and the integration of various financial procedures, IT systems provide a consistent strategy for conducting business internationally (Chang et al., 2020).
Risk management:Barclays may gain a better understanding of possible risks and global market trends by utilising IT-enabled predictive modelling and advanced analytics.
Regulatory Compliance: By helping to monitor and adhere to worldwide regulatory obligations, IT systems help to ensure a smooth global presence.
Competencies for Overcoming Global Market Challenges: Barclays and its staff require the following critical competencies to tackle global market challenges:
Digital Literacy: To properly access and utilise IT systems, employees need to be highly proficient in digital literacy.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Knowing the dynamics of the global market and using that knowledge to guide decisions need proficiency in data analysis.
Flexibility: To remain competitive in the global banking sector, one must possess flexibility due to the rapid rate of technology advancements (Umar et al., 2020).
Knowledge of cybersecurity: Expertise in cybersecurity is essential to safeguard client data and uphold confidence in the growing threat landscape.
Cross-Cultural Communication:Since it fosters solid bonds and guarantees seamless commercial transactions, effective cross-cultural communication is crucial for worldwide operations. As a multinational financial organisation, Barclays Plc has seen significant change. The bank now responds to difficulties in the global market, serves clients more effectively, and runs its operations more profitably thanks to information technology (Adebayo and Kirikkaleli, 2021). Barclays must continue to integrate IT systems and acquire appropriate skills in order to succeed in the dynamic global banking sector.
Barclays Plc's success as a worldwide financial organisation is primarily due to the way it uses different information technologies. The research duly draws attention to the many kinds of information systems in use, each of which serves a particular purpose in the banking industry. These systems—cybersecurity, CRM, TPS, BI, and core banking—are essential for improving customer happiness and operational efficiency. They demonstrate how flexible Barclays is in utilising technology to support many areas of its operations. The report also does an excellent job of documenting Barclays' IT history, touching on issues of technology, society, and management. The bank's use of mobile and internet technologies, its incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and its shift to user-friendly interfaces are all in line with the continuous changes taking place in the banking sector (Sinha et al., 2020). Barclays's response to client needs is demonstrated by its acknowledgement of the societal transition, particularly about the tastes of younger generations. The study's discussion of managerial development effectively illustrates how Barclays has modified its internal procedures to adapt to changes caused by IT. The implementation of DevOps principles and agile methodology demonstrates a dedication to improving responsiveness and efficiency in a changing industry.
There is also a thorough analysis of how IT affects Barclays' business operations. Key results of the bank's IT activities include digital transformation, data-driven decision-making, enhanced client experience, global reach, and operational efficiency. These outcomes are consistent with the larger patterns in the banking sector, where technology is changing the way that clients communicate with banks and how banks conduct business internationally. The study's main discussion is on how IT might help Barclays' international business operations, and it makes a good case for the necessary competencies (YuSheng and Ibrahim, 2019). In the rapidly changing global banking market, integration, risk management, regulatory compliance, and competencies, including data analysis, digital literacy, flexibility, cybersecurity knowledge, and cross-cultural communication, are essential. The report offers a thorough and organised investigation of how Barclays Plc uses information systems, how IT has changed inside the company, and how IT has revolutionised its business processes. It draws attention to the steps Barclays has taken and the significance of IT in the contemporary banking sector.
Question 2: Critically discuss the importance of rational supplier evaluation methods to determine the ICT procurement needs
Practical information and communication technology (ICT) procurement is essential to improving organisational operations and services in the fast-paced, fiercely competitive global banking sector. Finding and choosing the best suppliers to meet the organisation's ICT buying needs is a crucial duty for procurement managers at companies like Barclays Plc (Cheng et al., 2021). The use of logical supplier assessment techniques is crucial to the effective procurement of ICT solutions. The significance of these assessment techniques is examined critically in this article, with particular attention paid to the Cost-Based, Weighted Point Average, and Categorical systems.
Rational Supplier Evaluation Methods' Significance
• Types of Systems:: One of the most essential techniques for assessing ICT vendors is the Categorical System. This method entails classifying possible providers based on preset standards and determining if they are appropriate for specific procurement requirements. Barclays Plc benefits from this approach in a number of ways.
• Comprehensive Evaluation:The Categorical System makes it possible to evaluate suppliers thoroughly by considering a number of variables, including cost, supplier reputation, service delivery, and product quality (Acheampong et al., 2020). This all-encompassing strategy guarantees that all critical ICT procurement considerations are made.
• Supplier Risk Mitigation:Barclays Plc, like a lot of other financial organisations, has a lot of risks when it comes to purchasing IT. By assessing elements like supplier stability and adherence to industry norms, the Categorical System helps detect and reduce these risks.
• Customisation:Using this approach, companies may adapt the assessment criteria to suit their requirements and goals (Phan et al., 2020). Barclays Plc has the ability to modify the categories to highlight elements that are most pertinent to its requirements for ICT procurement.
• System of Weighted Point Averages:Different assessment criteria are given weights by the Weighted Point Average System according to their respective value to the organisation (Shahbaz et al., 2020). Because it enables the procurement team to give value to important aspects, this strategy is essential to Barclays Plc as it ensures that the supplier selection process is in line with the organisation's strategic goals and objectives.
• Aligning strategically:Barclays Plc may match supplier selection to its strategic goals by balancing the assessment factors. For instance, the assessment method might provide more weight to innovation and technical progress if they are essential to the organisation's ICT purchase.
• Openness and Uniformity:When evaluating suppliers, the Weighted Point Average System provides openness (Acheampong, 2019). It offers a methodical approach for assessing possible vendors. And guarantees the consistency and objectivity of the decision-making process.
• Data-Driven Decisions:By quantifying the assessment criteria, this approach promotes data-driven decision-making. It lowers the possibility of subjective biases by allowing Barclays Plc to make well-informed decisions based on quantitative evaluations.
• System Based on Costs:Barclays Plc places a strong priority on a cost-based system due to the highly cost-sensitive nature of the banking sector (Saud et al., 2020). With a primary focus on the financial elements of supplier assessment, this strategy highlights the return on investment, cost-effectiveness, and total cost of ownership.
• Cost-Effectiveness:Being economical is a top priority for financial organisation Barclays Plc. The procurement team may evaluate suppliers according to their capacity to offer ICT solutions that are both economical and in line with the organisation's financial limitations by using the Cost-Based System.
• ROI Evaluation:Barclays Plc can evaluate the supplier's long-term return on investment using this strategy. The firm may make well-informed decisions that optimise value over an extended period of time by assessing the total cost of ownership (Sun et al., 2019). A competitive edge In the banking sector, obtaining a competitive edge requires cost-based evaluation. By using this strategy, Barclays Plc may use suppliers to agree on advantageous terms, which will eventually help the company and its clients.

Figure 2: Digital Procurement and its Benefits
(Source: Chakraborty, 2023)
Practical information and communication technology (ICT) solution procurement is essential for organisational success in the dynamic and fiercely competitive global banking sector. Procurement managers, like those at Barclays Plc, are primarily responsible for finding and choosing the best ICT providers in this situation (Guru and Yadav, 2019).
By taking a comprehensive approach, it is ensured that all critical aspects of ICT procurement are fully considered, which lowers the possibility of making poor judgments. The banking sector is no new to the dangers that come with purchasing ICT. Serious repercussions may result from system malfunctions, security lapses, or noncompliance with industry standards. The Categorical System assesses variables like supplier stability and compliance to help businesses like Barclays Plc identify and reduce these risks. It guarantees that a complete awareness of potential dangers forms the basis for the selection of suppliers (Lerner and Nanda, 2020). Because of the categorical system's adaptability, companies may tailor the assessment criteria to meet their unique requirements and top objectives. Barclays Plc has the ability to customise the categories to highlight elements that are most pertinent to its ICT procurement specifications. This flexibility is essential for adjusting to the dynamically shifting nature of the global banking sector.
The Weighted Point Average System gives evaluation criteria weights according to their respective relevance. Barclays Plc needs this approach because it helps the procurement team to match supplier choices to the strategic aims and objectives of the company. Alignment with strategic objectives is critical in a business that is changing quickly. For example, the Weighted Point Average System enables variables such as innovation and technical development to be assigned a more considerable weightage throughout the evaluation process if they are deemed essential to Barclays Plc's ICT procurement (Gherghina et al., 2020). The organisation's long-term success is directly impacted by the supplier selection process thanks to this strategic alignment. When evaluating suppliers, consistency and transparency are essential. The Equilibrium Point The Average System offers a methodical framework for assessing possible suppliers, guaranteeing an open and impartial decision-making process. Establishing openness is crucial in fostering confidence among stakeholders and showcasing responsibility. Making judgments based on quantitative evaluations is a sensible approach in a society where data is abundant. The Weighted Point Average System gives assessment criteria numerical values in order to promote data-driven decision-making. By using this method, the possibility of subjective biases is decreased, and decisions are made based on facts rather than opinions.
For companies like Barclays Plc, the Cost-Based System is essential in the cost-sensitive banking sector. The primary focus of this technique is on the financial elements of supplier assessment, with a particular emphasis on competitive advantage, ROI, and cost efficiency. For financial organisations, cost-effectiveness is paramount (Tchamyou et al., 2019). Using a cost-based system, procurement teams may evaluate suppliers according to their capacity to offer ICT solutions that are both affordable and in line with the organisation's financial restrictions. For the purpose of maximising resource allocation and lowering financial risks, this emphasis on cost-effectiveness is essential. A long-term view is crucial for every business, and Barclays Plc can evaluate the long-term return on investment linked to a particular supplier according to the Cost-Based System. The firm may make well-informed decisions that optimise value over an extended period of time by assessing the total cost of ownership. This guarantees that the advantages of ICT procurement investments are long-lasting. Gaining a competitive edge in the highly competitive banking sector requires the implementation of the Cost-Based System (Wang et al., 2021). Barclays Plc may use this strategy to get good terms from suppliers, which will eventually help the company and its clients. Reducing expenses may also allow the company to make investments in other domains, augmenting its total competitiveness.
Effective supplier assessment techniques are essential for businesses operating in the international banking sector to succeed. The Categorical System offers a comprehensive risk-reduction strategy that may be tailored to meet particular requirements. The Weighted Point Average System guarantees transparency, data-driven decision-making, and strategy alignment. A competitive edge, ROI evaluation, and cost efficiency all depend on the implementation of the cost-based system. These supplier assessment techniques need to be carefully considered and modified by Barclays Plc in order to satisfy the changing needs of the banking sector. By using these logical assessment techniques, the company may make strategic and well-informed judgments that improve its ICT procurement procedures, thus boosting its performance internationally. These strategies give the skills needed to handle the complexity and challenges of ICT procurement in a field that is continuously changing.
Question 3: Critical review of the impact of good leadership and teamwork by discussing an ambitious information technology software project
The combination of information technology (IT) and information systems (IS) has been a significant factor in the recent dramatic change in the banking sector. The effective execution of big IT projects increasingly depends on leadership and cooperation as firms adjust to the changing environment. This article examines the value of effective leadership and cooperation in the context of Barclays Plc, a well-known international financial company, and its endeavour to carry out a large-scale IT software project with a focus on cloud computing. The analysis will use a model of cooperation and leadership to show how this project was successfully implemented.
Prior to exploring the Barclays Cloud Computing project case study, Talking about how IT has changed in the banking sector is crucial. Over time, the banking industry has undergone substantial change, moving from traditional brick-and-mortar operations to digital banking. Technology breakthroughs have fueled this shift by allowing banks to deliver services more globally, safely, and effectively (Gherghina et al., 2020). Like many other banks, Barclays realised that it needed to use IT to its advantage in order to remain competitive in the global market. Their drive to integrate cutting-edge IT solutions that would improve their business operations began with this discovery.
Information Technology's Influence on Business Operations: The banking industry has seen a significant transformation in corporate processes due to information technology. It has made it possible for banks to provide a variety of services, improve customer experiences, boost productivity, and guarantee legal compliance. Specifically, cloud computing has been a disruptive technology in this area. Because of its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, cloud computing is an essential instrument for banks to adjust to the always-shifting market conditions.
The Barclays Cloud Computing Project: Barclays saw how cloud computing might improve its worldwide business operations and revolutionise its IT infrastructure. An extensive amount of their IT systems had to be migrated as part of the ambitious initiative to cloud-based services. Data storage, customer-facing services, and essential banking software were included in this. The project made use of a range of cloud-hosted information systems, including data analytics, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and customer relationship management (CRM). The bank's executives thought that this change would not only lower infrastructure costs while simultaneously quickening the digital transformation process, making it possible for businesses to service a worldwide clientele more successfully.
Leadership's Effect on the Cloud Computing Project: Effective leadership is crucial for the design and execution of any IT project. In order to move the Barclays Cloud Computing project ahead, leadership was essential. The Chief Information Officer (CIO) overseeing the project had a well-defined implementation strategy and goal. A committed group of IT specialists who were all in agreement with the project's goals assisted the CIO. Hersey and Blanchard's Situational Leadership Model to examine the effects of leadership can be used. According to this paradigm, followers' degree of preparation affects how effective a leader is. Within the framework of the Barclays Cloud Computing initiative, the CIO acknowledged the team members' varied backgrounds and expertise. While some people knew a lot about cloud technology, others needed additional help. As a result, the CIO modified their leadership philosophies and offered guidance and assistance when required. The CIO also gave good communication a lot of attention. To keep the crew in sync with the objectives and advancement, open lines of communication were maintained throughout the project. As a result, team members felt more committed and owned since everyone was clear about their duties and responsibilities.
Figure 4: Significance of Project Charter in innovating banking sector by Information Technology
(Source: Iqbal, 2021)
Collaboration's Effect on the Cloud Computing Project: A large-scale IT project's successful execution depends on practical cooperation. A multidisciplinary team led by Barclays carried out the Cloud Computing project. Participants from a range of areas, including operations, compliance, and IT. These teams' actions were mainly coordinated by the project management office (PMO). Tuckman's Stages of Group Development model to assess the effects of collaboration can be used. The group went through storming, norming, performing, and shaping phases. There were some difficulties at first as team members had to become used to their new responsibilities and procedures. However, thanks to strong leadership, the group moved rapidly into the performance and norming phases, where they cooperated to meet project objectives. In addition, PC 4.3 listed planning, executing, monitoring, and closure as project management stages. During the stages of implementation and monitoring, the team's cohesiveness and cooperation were essential. Frequent feedback sessions and status meetings, and kept an eye on to make sure the project did not get behind schedule.
The ambitious Cloud Computing project at Barclays Plc is evidence of the need for collaboration and leadership in carrying out major IT projects. Strong leadership and cooperative collaboration were the key factors in the project's success by using leadership models like Hersey and Blanchard's Situational Leadership and teamwork models like Tuckman's Stages of Group Development. Team members felt empowered, and there was open communication when there was strong leadership. The group had several phases of growth before performing at a high level. The project's success was also enhanced by the existence of a clearly defined project charter and network diagram, which made sure that everyone understood the goals and that tasks were completed in an organised fashion. The bank's worldwide business operations were bolstered by the Barclays Cloud Computing initiative, which also strengthened the bank's IT infrastructure. It is evidence of the revolutionary potential of IT in the banking sector, propelled by solid cooperation and leadership.
The study offers a thorough examination of the function of cooperation and leadership within the framework of Barclays' large-scale Cloud Computing initiative. It does an excellent job of highlighting how crucial these elements are to the accomplishment of challenging IT projects in the banking industry. Setting the stage is the conversation of how IT has changed in the banking sector, which emphasises how competitively the sector must adapt and use technology. Additionally well-explained is the debut of cloud computing as a revolutionary technology (Wang et al., 2021). The study's examination of teamwork using Tuckman's Stages of Group Development and leadership using the Situational Leadership Model shows a thorough comprehension of how these concepts were used in the Barclays project. Remarkable features include the leader's capacity to adjust to the preparedness levels of team members and the efficient communication plan, both of which are essential in large-scale IT projects. To effectively illustrate the project management techniques that led to the project's success, a project charter and network diagram are required. These instruments guarantee lucidity of intent, goals, and effective distribution of resources. The essay offers a coherent and perceptive examination of the crucial roles that cooperation and leadership played in the Barclays Cloud Computing initiative. It clearly illustrates how these components, when paired with proper project management instruments, were crucial to achieving the project's objectives and, consequently, influencing the banking sector.
Question 4: Critical discussion on how the project charter can help in bringing together all those involved with a mutual understanding of project aims and objectives
The banking business is a dynamic and fiercely competitive space where satisfying market needs and being competitive require the effective execution of large-scale IT projects. The importance of a project charter in uniting all stakeholders behind a shared understanding of the goals and objectives of the project is critically examined in this article. With an emphasis on the Cloud Computing project at Barclays Plc, it also emphasises the significance of a project charter in expanding and consolidating project management expertise for the execution of an IT software project.
Project Overview: A Shared VisionA project charter is a fundamental document in project management that facilitates communication and coordination between all project participants. The project charter in relation to the Barclays Cloud Computing project played a crucial part in making sure that everyone involved—from team members to the leadership—had a common grasp of the goals of the project.
Project Goals and Scope: The Cloud Computing project's goals and scope were outlined in the project charter. It delineated the precise objectives, including the migration of essential banking applications and the improvement of global business operations via the integration of cloud technology. Everyone involved knew exactly what was expected of them and why the project was being undertaken, thanks to this precise scope description.
Suppositions: Any project has assumptions, and it is essential to record those assumptions. Fundamental presumptions, including the accessibility of cloud service providers, regulatory compliance, and resource availability, were outlined in the project charter for Barclays Plc (Lerner and Nanda, 2020). Taking these presumptions into consideration, the project crew was ready to handle any obstacles that could come up
Positions and Accountabilities: For a project to succeed, roles and duties must be clearly defined. Team members were given explicit roles and duties in the project charter, which made it obvious who was in charge of what. The work distribution was made effective, and misunderstanding was reduced because of this clarity.
Graphs utilising Gantt charts: Project planning and progress monitoring require the use of project timeframes. Gantt charts that showed the project's timetable, including dependencies, deadlines, and milestones, were included in the project charter. All participants were guaranteed to be aware of the project's time frame thanks to this visual depiction, which also made project management more effortless.
Top-Level Dangers: In project management, risk assessment and management are essential. The Cloud Computing project's high-level hazards were mentioned in the project charter. The team was able to create risk mitigation measures and backup plans by acknowledging these concerns.
Project Finance: Project execution is inextricably linked to financial issues. Information about project finance, including the project budget, was supplied in the project charter. This financial openness guaranteed that there would be no unanticipated financial obstacles and that the project would be sufficiently funded.
Combining and Expanding Our Understanding of Project Management: The project charter expands and unifies project management knowledge in addition to fostering understanding between stakeholders. For Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing project, the charter functioned as a guide that contained important project management details.
Integration of Information: Project charters, which gather crucial project information into a single document, help to organise knowledge about project management. Stakeholders and team members can obtain details on the project's goals, roles, duties, and schedule, see the charter. Consolidation guarantees that knowledge is easily accessible and centralised.
Extension of Understanding: The project charter broadens our understanding of project management by containing essential details regarding the project's assumptions, hazards, and finances. It acts as a knowledge base that helps project managers decide wisely, adjust to changing conditions, and successfully manage risks. It also helps determine the amount of money needed to carry out the job.

Figure 4: Significance of Project Charter in innovating banking sector by Information Technology
(Source: Iqbal, 2021))
Stages of Project Management for IT Software Project Execution: Following well-defined project management stages is crucial to provide sufficient project management controls for the execution of an IT software project. Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing initiative followed these steps to guarantee a well-organised and effective execution.
Organising Phase: During the planning phase, the requirements, goals, and scope of the project are defined. Making a project charter, which lists essential project specifics, is part of it. Since it offered a clear road map for the Cloud Computing project, the charter was extremely helpful to Barclays Plc throughout the planning phase.
Stage of Execution: The project's actual implementation takes place at the executing stage. This phase of the cloud computing project included tasks including building up data storage systems, providing customer-facing services, and moving critical banking operations to the cloud. The project charter's roles and duties served as a guide for the execution phase.
Stages of Monitoring and Control: Tracking project progress and making sure it is completed successfully need the monitoring and management stage. Conforms to the specified goals and parameters. As seen in the instance of Barclays Plc, regular status meetings and feedback sessions were crucial at this point. Gantt charts in the project charter were used to track deadlines and dependencies.
Final Phase: Finalising the project, gaining the required permissions, and making sure all project goals have been reached are all part of the closure stage. The Cloud Computing project's project charter was reviewed to see whether all goals had been met and whether significant risks had been sufficiently managed.
Creating a Network Diagram: An effective tool for project management is a network diagram, which shows the relationships between different tasks, the kinds of networks being employed, and the participation of different tasks in a framework. The network diagram for Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing project showed how the many project activities were interdependent.
Project Initiation: During this stage, the project charter's aims and objectives were defined.Requirement analysis is the process of determining and verifying the specifications needed to migrate essential banking systems to the cloud.
Resource Allocation: Using the project charter as a guide, assign the required resources, such as financial and human resources.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Provider: Selecting the right cloud service provider according to the needs and goals of the project.
Data migration: Ensuring data security and integrity while moving data from on-premises systems to the cloud.
Testing and Quality Assurance: Strict testing was carried out to guarantee that the cloud-based solutions complied with regulations and quality requirements.
Implementing Client-Facing Services: Launching client-facing cloud services to improve client interactions.
Risk Mitigation: Putting into practice the plans outlined in the project charter to reduce high-level risks, such as data security and regulatory compliance.
Critical Route Determination: A project's critical path is the order of tasks that, in the event of a delay, would cause the project to be delayed overall. In Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing project, the operations with the most extended duration and the least scheduling flexibility were on the critical path.
Gantt chart
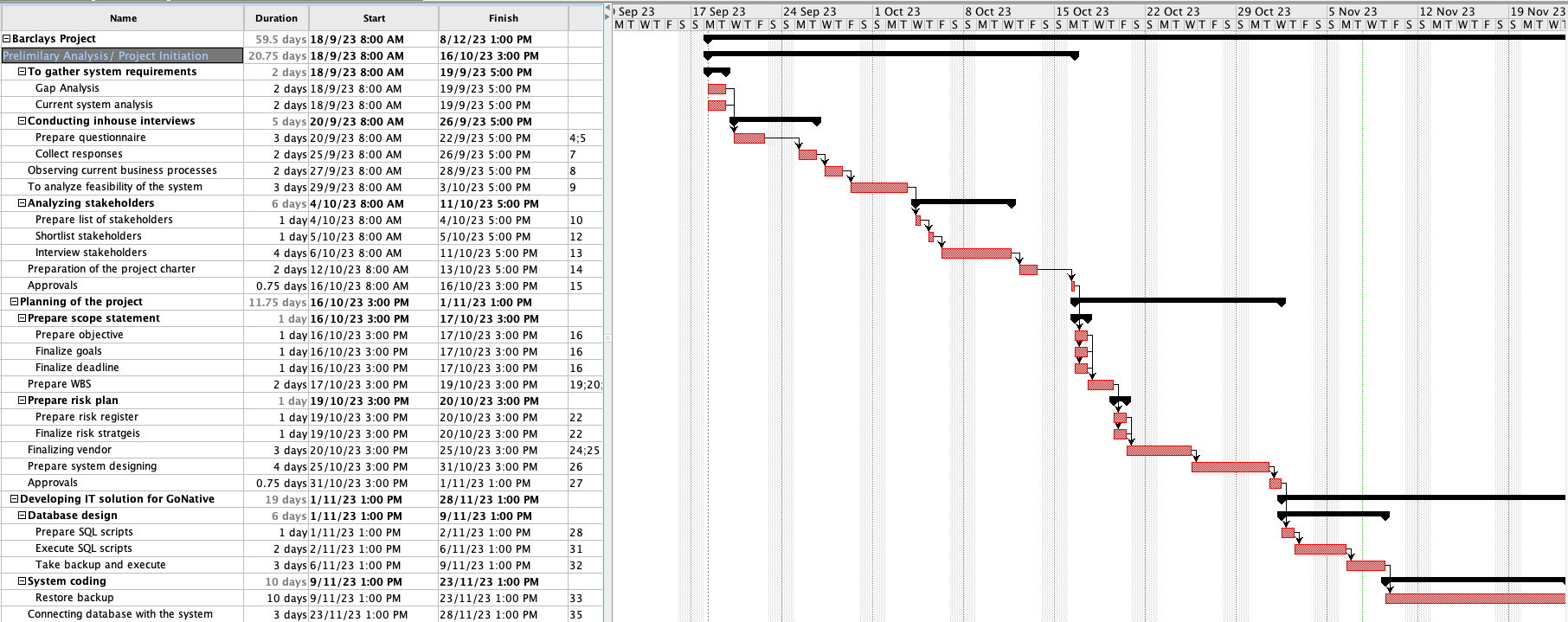
Network diagram

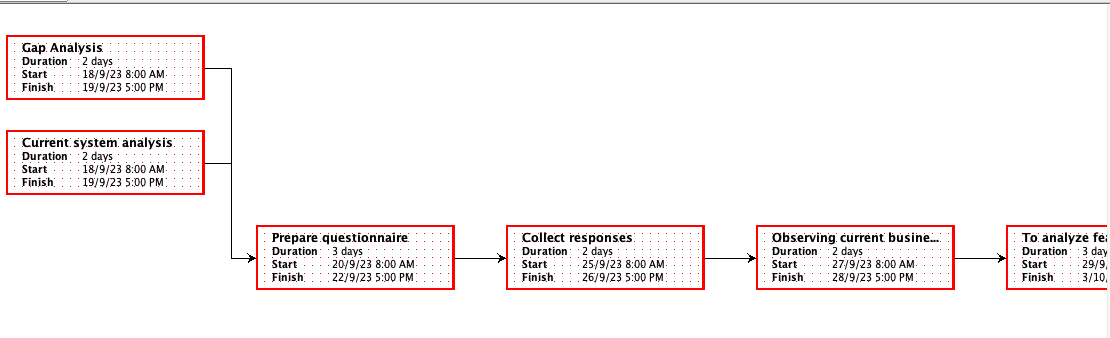

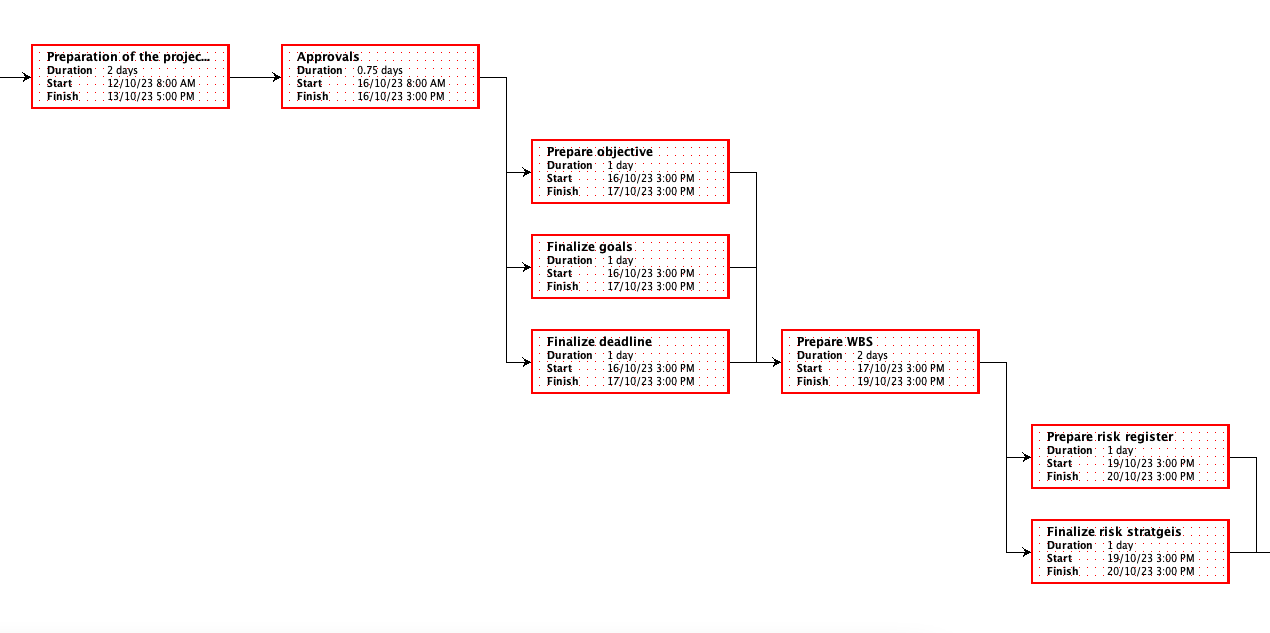

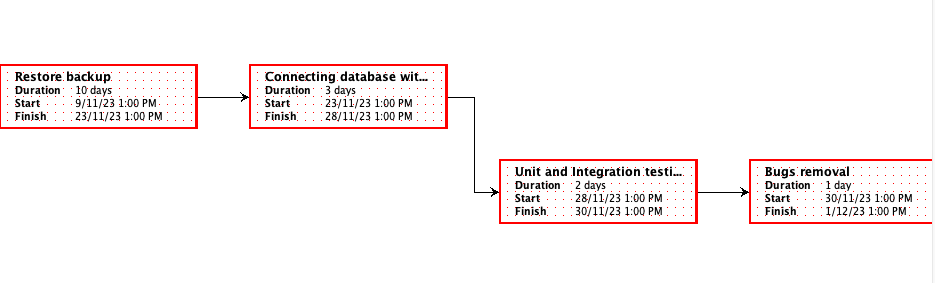

The tasks in the crucial route were:
Analysing requirements: One of the most critical and time-consuming tasks was determining the precise requirements for moving essential banking applications to the cloud.
Data Migration: Transferring data from on-premises systems to cloud-based platforms was a crucial and intricate task that needed meticulous preparation and carrying out.
Testing and Quality Assurance: An essential part of the project was doing thorough testing to guarantee quality and regulatory compliance, which took a lot of time.
Implementing Client-Facing Services: Implementing cloud-based customer-facing services was a crucial route activity since it was closely related to the main goals of the project.
It is impossible to overestimate the importance of a project charter in the fast-paced, fiercely competitive banking sector, especially when it comes to large-scale IT initiatives like Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing project. The foundation of any successful project management effort is the project charter, which unifies and expands project management knowledge while fostering understanding among stakeholders. The project charter guarantees that all parties involved in the project are aware of its goals, assumptions, risks, funds, schedule, roles, and duties by providing unambiguous definitions (Sakharov, 2021).
This alignment reduces misunderstandings, improves communication, and creates a collaborative atmosphere—all of which are critical for meeting the market's always-changing expectations. In addition, the project charter centralises crucial project information and aids in well-informed decision-making, making it an invaluable reference tool. It supports all phases of project management, from planning and execution to closure, monitoring, and controlling, guaranteeing an organised and effective execution of IT software projects. The significance of thorough planning and risk mitigation is further exemplified by the network diagram and identification of crucial route activities in Barclays Plc's Cloud Computing project. As a result, the project charter serves as more than simply a document; instead, it is a strategic instrument that enables businesses to flourish in the highly competitive banking sector by enabling them to innovate, adapt, and project accomplishment and client contentment.
References
Acheampong, A.O., 2019. Modelling for insight: does financial development improve environmental quality?. Energy Economics, 83, pp.156-179.
Acheampong, A.O., Amponsah, M. and Boateng, E., 2020. Does financial development mitigate carbon emissions? Evidence from heterogeneous financial economies. Energy Economics, 88, p.104768.
Adebayo, T.S. and Kirikkaleli, D., 2021. Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalisation, and technological innovation on environmental degradation in Japan: application of wavelet tools. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 23(11), pp.16057-16082.
Alam, M.M. and Murad, M.W., 2020. The impacts of economic growth, trade openness and technological progress on renewable energy use in organisation for economic co-operation and development countries. Renewable Energy, 145, pp.382-390.
Baloch, M.A., Ozturk, I., Bekun, F.V. and Khan, D., 2021. Modeling the dynamic linkage between financial development, energy innovation, and environmental quality: does globalisation matter?. Business Strategy and the Environment, 30(1), pp.176-184.
Chakraborty, A., 2023. What Is Digital Procurement? 2023 Comprehensive Guide. [online] Available at:
Chang, V., Baudier, P., Zhang, H., Xu, Q., Zhang, J. and Arami, M., 2020. How Blockchain can impact financial services–The overview, challenges and recommendations from expert interviewees. Technological forecasting and social change, 158, p.120166.
Cheng, C., Ren, X., Dong, K., Dong, X. and Wang, Z., 2021. How does technological innovation mitigate CO2 emissions in OECD countries? Heterogeneous analysis using panel quantile regression. Journal of Environmental Management, 280, p.111818.
Cheng, Y., Awan, U., Ahmad, S. and Tan, Z., 2021. How do technological innovation and fiscal decentralisation affect the environment? A story of the fourth industrial revolution and sustainable growth. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 162, p.120398.
Du, K., Li, P. and Yan, Z., 2019. Do green technology innovations contribute to carbon dioxide emission reduction? Empirical evidence from patent data. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146, pp.297-303.
Francis, A., 2010. Role of Information Technology (IT) in the Banking Sector - MBA Knowledge Base. [online] MBA Knowledge Base. Available at:
Gherghina, ?.C., Botezatu, M.A., Hosszu, A. and Simionescu, L.N., 2020. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): The engine of economic growth through investments and innovation. Sustainability, 12(1), p.347.
Guru, B.K. and Yadav, I.S., 2019. Financial development and economic growth: panel evidence from BRICS. Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Science, 24(47), pp.113-126.
Hsu, C.C., Quang-Thanh, N., Chien, F., Li, L. and Mohsin, M., 2021. Evaluating green innovation and performance of financial development: mediating concerns of environmental regulation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(40), pp.57386-57397.
Iqbal, M., 2021. What Is Project Charter and Its Importance? - PMP/CAPM by Mudassir Iqbal. [online] Mudassir Iqbal. Available at:
Khan, Z., Hussain, M., Shahbaz, M., Yang, S. and Jiao, Z., 2020. Natural resource abundance, technological innovation, and human capital nexus with financial development: a case study of China. Resources Policy, 65, p.101585.
Kirikkaleli, D. and Adebayo, T.S., 2021. Do renewable energy consumption and financial development matter for environmental sustainability? New global evidence. Sustainable Development, 29(4), pp.583-594.
Lerner, J. and Nanda, R., 2020. Venture capital’s role in financing innovation: What we know and how much we still need to learn. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 34(3), pp.237-261.
Litvinenko, V.S., 2020. Digital economy as a factor in the technological development of the mineral sector. Natural Resources Research, 29(3), pp.1521-1541.
Phan, D.H.B., Narayan, P.K., Rahman, R.E. and Hutabarat, A.R., 2020. Do financial technology firms influence bank performance?. Pacific-Basin finance journal, 62, p.101210.
Sakharov, D.M., 2021. Central bank digital currencies: Key aspects and impact on the financial system. Finance: Theory and Practice, 25(5), pp.133-149.
Saud, S., Chen, S. and Haseeb, A., 2020. The role of financial development and globalisation in the environment: accounting ecological footprint indicators for selected one-belt-one-road initiative countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 250, p.119518.
Shahbaz, M., Raghutla, C., Song, M., Zameer, H. and Jiao, Z., 2020. Public-private partnerships investment in energy as new determinant of CO2 emissions: the role of technological innovations in China. Energy Economics, 86, p.104664.
Sinha, A., Sengupta, T. and Alvarado, R., 2020. Interplay between technological innovation and environmental quality: formulating the SDG policies for next 11 economies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 242, p.118549.
Sun, X., Li, Z., Wang, X. and Li, C., 2019. Technology development of electric vehicles: A review. Energies, 13(1), p.90.
Tchamyou, V.S., Erreygers, G. and Cassimon, D., 2019. Inequality, ICT and financial access in Africa. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 139, pp.169-184.
Thamhain, H. J., 2000. Criteria for effective leadership in technology-oriented project teams. Paper presented at PMI® Research Conference 2000: Project Management Research at the Turn of the Millennium, Paris, France. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute.
Umar, M., Ji, X., Kirikkaleli, D. and Xu, Q., 2020. COP21 Roadmap: Do innovation, financial development, and transportation infrastructure matter for environmental sustainability in China?. Journal of environmental management, 271, p.111026.
Usman, M. and Hammar, N., 2021. Dynamic relationship between technological innovations, financial development, renewable energy, and ecological footprint: fresh insights based on the STIRPAT model for Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(12), pp.15519-15536.
Wang, Y., Yang, Y., Fu, C., Fan, Z. and Zhou, X., 2021. Environmental regulation, environmental responsibility, and green technology innovation: Empirical research from China. PLoS One, 16(9), p.e0257670.
YuSheng, K. and Ibrahim, M., 2019. Service innovation, service delivery and customer satisfaction and loyalty in the banking sector of Ghana. International journal of bank marketing, 37(5), pp.1215-1233.












