Management Assignment: Developing a WHS Management System for Australian Hardware
Question
Task:
For this management assignment you are required to plan and develop a WHS management system for a fictional organisation, Australian Hardware, to assist them to comply with WHS legislation. Identify and use sources of expert advice to plan your system, gather a portfolio of evidence of your research into WHS management system including samples of documentation and prepare a report outlining and explaining the system, duty holders, resources, and approval required.
Answer
Introduction
The company Australian hardware, undertaken in this management assignment, has been facing quite a lot of issues regarding the healthcare and safety protocols of their respective employees and staff. In the past few months, they have been suffering from certain employee health-related issues. The company has upgraded to include 138 workhouses nationally, which has led to an increase in the work of the employee force. The employees are being overworked and without a proper structure. This has resulted in a completely lost time to injury frequency rate has gone up to 13.9 for them. This is way past the standard limitation as per the legislature concerned. Thus, to rectify this blunder, a system of employee health management has to be put into action. This worker's healthcare system will properly enable the management to keep a record and establish a planned approach in terms of employee health and safety. The workplace public safety control scheme protects more than just health and safety policy. Which requires health and safety procedures, programs, guidelines and databases, and entails the incorporation of occupational welfare and fitness directly with the other enterprise applications. Getting an efficient monitoring strategy can enhance the capacity to consistently detect threats and monitor risks to the organization.
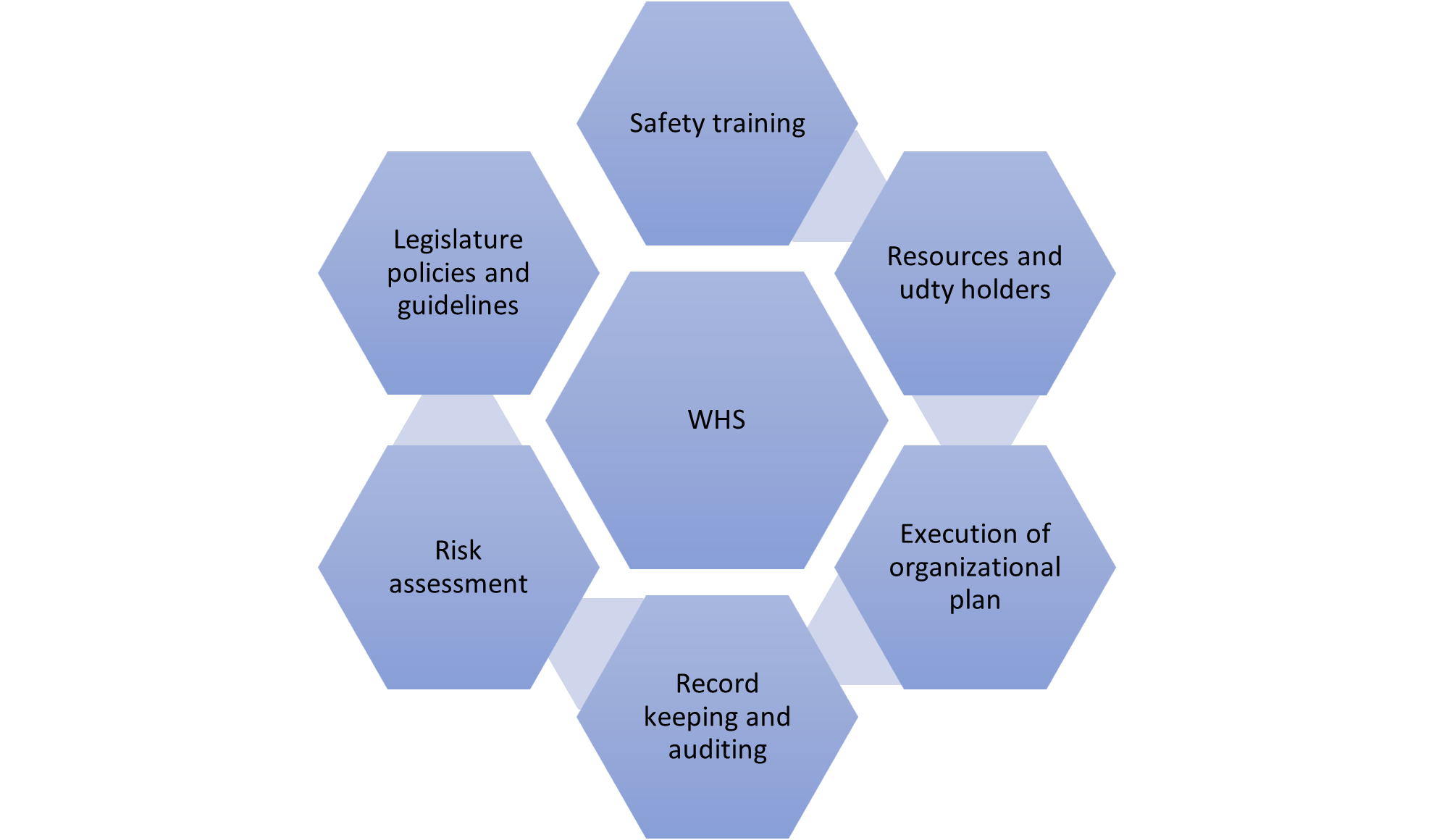
Fig: WHS management system
(Source: self-made)
Safety training management
The entire workforce of the firm, spanning from top leadership to field staff, has to consider their responsibility in terms of implementing and sustaining a fair and secure workplace. Executive leadership must recognize their position in policy-making and should continue to lead the employee workplace healthcare organizational structure and programs (Safe & Workplaces, 2019). Employers need to determine that employees are educated, skilled, and able to fulfill their duties. Managers must offer sufficient guidance and monitoring to the staff so that they can do their work effectively (Safe & Workplaces, 2019). And employees need to operate effectively, depending on how they have been prepared. Work environment safety training or preparation is also recognized as the most important activity in a firm or organization; it helps them to stay in the appropriate guidelines and by-laws and making an income while they work (Urdaniz, 2018). Learning is one form of work force practice (Safe & Workplaces, 2019). Workforce safety preparation should be performed in a number of productive sectors. The purpose of the employee induction program is to teach new hires how to perform their work comfortably and efficiently, but large firms recognize that it is important to go far deeper than the basics in terms of a healthcare management system. Workplace health preparation is as important as safety in the workplace itself (Urdaniz, 2018). It assists managers to maintain a stable and secure working atmosphere (Safe & Workplaces, 2019). It also allows workers to identify and fix potential dangers (Eldejany, 2019). It helps them to consider the best practices and standards of protection. Health preparation is all the more essential for organizations such as laboratories and building firms that employ dangerous products and machinery, just like Australian hardware (Eldejany, 2019). Security preparation is essential for employers or staff to recognize healthy procedures relevant to the task; therefore, personnel would be at greater risk of accident, sickness, or mortality at the office. Hence, one of the major parts of the WHS system is the proper training of the management and the ground level staff (Eldejany, 2019).
Audits and inspections
The company can closely monitor and develop its protection and health action plan and ensure that the general safety and security efficiency continues to progress. The company will benefit from related changes and apply concepts (Eldejany, 2019). A thorough analysis of results focused on reporting evidence and assessment system of the entire protection and care coordination framework should be carried out. All of this has to be carried out with respect to the Act of 2005. There should be a deep approach to quality management including the implementation of risk management procedures, processes, and techniques (Domashov, 2018). Output can be measured by the following:
- External assessment of main success metrics
- External correlation with the results of industry rivals and best practice in the job field of the company.
The Australian hardware company lacks a proper management system and recording facility. The establishment of one will greatly affect and influence the entire working atmosphere of the company (Domashov, 2018). The lost time to injury frequency has already gone well beyond the official permit and hence, it needs to be properly accounted for and settled down under the below 10 criteria (Marling, Horberry & Harris, 2019). The implementation of a thorough and efficient recording keeping and auditing service will ensure a manner of discipline and accord in the organization which will eventually benefit its business as well (Domashov, 2018). The annual reports that will be printed as per the audited record will establish a strong sense of communication between the employees and will reassure the stakeholders on the risks (Marling, Horberry & Harris, 2019).
Resources and duty holders
The company has sanctioned a balance of one million for the adaptation and implementation of the WHS program. The available resources at hand are as follows,
- Senior manager
- Store manager
- Team leader
- Workers
- WHS special consultant (Urdaniz, 2018).
All of these people have been approved for 2 hours of training each for the proper knowledge and education regarding workplace safety and employee health training (Urdaniz, 2018).
The necessary duty holders who will regulate and preside over the entire operation of the workplace safety and health are as follows,
- The shareholders of the Australian hardware company
- Local authorities or corporations associated with the regulation of the same
- The companies present in the council of trustees (Stjernström, Pashkevich & Avango, 2020).
- Committee members of the employee health and safety organization or union
Legislative policies
The company has to implement the proper measures to improve the overall state of the employee's health and safety in order to stay on the right side of the law. The prime legislative policy associated with this is the "WHS Act of 2011" and the "AS/NZS 4804:2001 Occupational health and safety management systems general guidelines on principles, systems and supporting techniques” (Faruq, 2018). These two acts ensure that the facilities and firms are upto date with their employee health and safety protocols with respect to the standards/ degrees of business being carried out (Victoria, 2018). In this case, the Australian hardware has to lower its lost time to injury frequency from 13.9 to somewhere below 10 (Stjernström, Pashkevich & Avango, 2020). Without compliance with the necessary legislative protocol, the government has the right to pertain to the business dormant until further notice (Stjernström, Pashkevich & Avango, 2020).
Organizational needs
The organization needs to implement the health and safety protocols into their casual business activities and protocols. Doing so will automatically change the entire atmosphere and nature of the business. All provisions that need to be followed are as follows:
- Supported by the constructive involvement and collaboration of workers by adequate communication, the usage of the protection council. This will bring about a token of faith of the entire council which will assist in the future business endeavors as well (Faruq, 2018);
- The managers and their subordinates need to maintain a good structure of transparency and harmony. The prosperity of the entire management plan lies in the collective effort of the employees and the management (Faruq, 2018).
A presence of a coordinated and structured strategy to the execution of safety and health policies by an integrated method of safety and health management is highly imperative. The goal is to mitigate the risks involved (Victoria, 2018). Risk management approaches can be used to define goals and establish expectations for the removal of threats and the avoidance of risks (Khairi, Ismail & Jaafar, 2020Most of the risk can be averted during the feasibility check phase of the buildings, as the structure will be defined as per the risks associated and how to avoid them. The risk will always be present, but there have to be strategies to account for those risks, if the primary solution has failed, then the secondary external solution will be implemented (Victoria, 2018). Quality metrics can be developed and used to assess accomplishment (Miyake et al., 2016). Clear measures that encourage a healthy atmosphere of protection and wellbeing should be established (Khairi, Ismail & Jaafar, 2020). There ought to be a mutual comprehension of the vision, ethics, and goals of the firm on the concern of employee safety and physical and mental wellbeing (Victoria, 2018). The noticeable and productive governance of senior executives creates a more positive cultural identity of safety and security. Being in accordance with the management system will ensure that:
- There is a minimized risk of injury or health hazards in the workplace or the business premises (Dougall, 2019).
- A significant reduction in public claims will be evident (Miyake et al., 2016).
- A lower cost of worker’s compensation will be available
- There will be an increase in employee productivity and motivation
- The damages due to the reason of security concerns will all be vanquished with a proper management system and coordination.
References
Domashov, I. (2018). Western Tien-Shan World Heritage Site (Kyrgyz Part): From Traditional to Modern Management Challenges. ???????= JOURNAL OF WORLD HERITAGE STUDIES, (2018), 83-88.
Dougall, S. (2019). Workplace health and safety (WHS) implications for farmers hosting unconventional gas (UG) exploration & production. Policy and Practice in Health and Safety, 17(2), 156-172.
Eldejany, R. (2019). The relationship between safety management systems, safety performance and customer satisfaction in the Australian construction industry: A quantitative research proposal. Journal of Research in Marketing, 10(1), 766-771.
Faruq, Q. O. (2018). Management of training to prevent occupational violence: a case study of the Work Health and Safety Management System (WHSMS) in a hospital in Victoria (Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University).
Khairi, N. D., Ismail, H. N., & Jaafar, S. M. R. S. (2020). Embracing tourist behaviour in managing Melaka WHS. E&ES, 447(1), 012035.
Marling, G., Horberry, T., & Harris, J. (2019). Development and Validation of Plain English Interpretations of the Seven Elements of the Risk Management Process. Management assignment Safety, 5(4), 75.
Miyake, R. T. M., de Paiva Badiz Furlaneto, F., Narita, N., Takata, W. H. S., & Creste, J. E. (2016). Economic evaluation of different types of nutritional management in yellow passion fruit vines (Passiflora edulis Sims.). Australian Journal of Crop Science, 11(11), 1572.
Safe, P., & Workplaces, H. (2019). Management System.
Stjernström, O., Pashkevich, A., & Avango, D. (2020). Contrasting views on co-management of indigenous natural and cultural heritage–Case of Laponia World Heritage site, Sweden. Polar Record, 1-11.
Urdaniz, A. V. Z. (2018). Regional Heritage Dimensions vs. Management Boundaries. International Review for Spatial Planning and Sustainable Development, 6(2), 64-81.
Victoria, Z. U. A. (2018). Regional Heritage Dimensions vs. Management Boundaries: A comparative framework of European and Asian countries. Sustainable Development, 6(2).












