Network Design Assignment: Understanding Concepts Of Computer Networking & Administration
Question
Task:
The network design assignment consists of the following tasks:
Task 1:
Understand network design
1.1: What is the importance of having a computer network and what are the benefits for users?
1.2: Describe the functionalities of this each layer in Hierarchical internetworking model
-Access Layer
-Distribution Layer
-Core Layer
1.3: What is link aggregation and its benefits?
Task 2:
2.1: How to set up a VLAN in IEEE 802.1Q standard? Describe the role of the Router and Switch in VLAN
2.2: Differentiate Basic NAT vs One-to-many NAT. Describe following methods of translation
- one-to-one NAT
- (Address)-restricted-cone NAT
- Port-restricted cone NAT Symmetric NAT
2.3: Select an Operating System and give step by step guide to enable and to configure Remote Desktop for Administration
2.4: You are required to set up a LAN to your workplace. Describe how you would cope with scalability?
Task 3
Administer a network
3.1 As a network administrator what are your main duties? Describe tools that you can use to automate or effectively carry out these tasks. What are the common troubleshooting tasks and explain how you would resolve them
3.2 Explain Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) with examples
3.3 What is “link aggregation” and how do you configure it to benefit your network
Answer
Network Design Assignment Task 1
Understand Network Design
1.1 Importance Of Computer Network
The computer network is an integration of computers configured to share information and files wit is linked with the communication channels. The data is received, transmitted, and exchanged by the nodes. It is transmitted in voice traffic or video traffic. Various types of computer networks are Personal Area Network (PAN), Local Area Network (LAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), Wide Area Network (WAN) and Home Area Network (HAN) are chosen based on the requirements of data transmission.
There are many reasons why the network is important to the organization or individual. To run a business, the computer network is important. It varies from network applications, backup or recovery tools, and the way of storing the information. The computer network is essential for File sharing, printers, sharing media, media center servers, and video games (Steele 2019).
Benefits for user
It helps for the growth of the business operation. It does not allow to share the information alone rather it increases the productivity, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, storage capacity, flexibility, and security of data. The benefits of computer networking are cost, boost storage capacity, flexibility, and streamlined communication.
1.2 Functionality Of Hierarchical Internetworking Model
In the hierarchical network model, there are three types of layers such as the access layer, distribution layer, and core layer. This framework helps to ensure that the network is easy to implement and troubleshoot the problems. In access layer, user are provided with permission to access the network. Distribution layer provides the connectivity based on the policy and the core layer provides the high-speed connectivity and transport required by the devices in the distribution layer (Network Direction 2018).
Every layer has its own functions to choose the correct system and features within the model. It provides the accurate planning and minimize the cost.
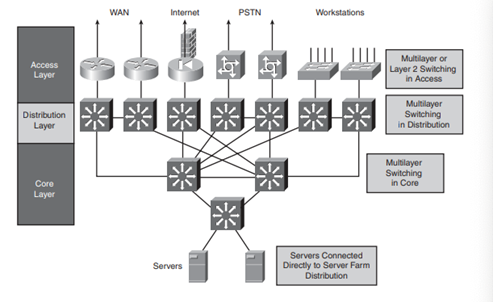
Internetworking model
Access layer
In this layer there is the point where the client can access the network. It is used for providing the switching environment and multilayer switching environment. For local workstations and servers, access can be provided via shared media LANs or switched media LANs. It provides fast ethernet, EtherChannel, and gigabit ethernet uplinks from the access layer to the distribution layer to establish the connection and to reduce the broadcast domain size.
Distribution layer
This layer lies in the middle of the core layer and access layer. It provides the connection point between the access sites and the core layer. It provides access for a group and provides the connection based on the policy.
Core layer
The functionality of the core layer provides the data transport efficiently, in this layer, multilayer routing or layer 2 switching is done. The devices in the core layer are responsible for the failures that occurs due to the traffic and to respond to the topology changes. it can perform the routing process in the multilayer switch with no cost. it can implement the network topologies and scalable protocols instantly to provide the alternate path and load balancing.
1.3 Link Aggregation
Link aggregation enables the combination of the multiple Ethernet links as a single link via two network devices. It is also called ethernet bonding, link bonding, port aggregation, and port trunking (Auvik 2021).
Benefits
The benefits of link aggregation are as follows:
- Increase in reliability
- When one physical link goes down then the traffic will be dynamically assigned to the other physical link so there will be reliability in the link aggregation.
- Better physical resources usage
- Traffic can be balanced between the physical links
- It is expensive to upgrade the physical network but without any additional requirements the bandwidth can be increased.
Working Of Link Aggregation Control Protocol
It is an IEEE standard that lets the network devices send the Link Aggregation Control Protocol Data Unit (LACPDUs) for establishing the link. LAG (Link Aggregation Group) should be configured in every device but Link Aggregation Control Protocol helps to prevent the problems that occur during the link aggregation set up. When one member stopped sending the LACPDUs then it is removed from the Link aggregation group which prevents the packet loss. When the network devices are sent and linked to connect with the other devices by identifying LAG it is connected then the transmission and reception process is occurred in an order.
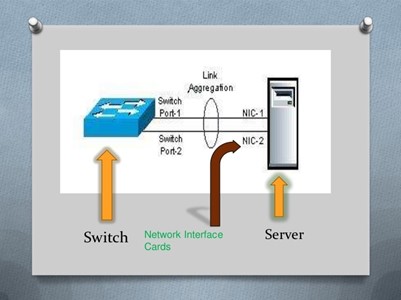
Working of LACP
Task 2
Vlan Setup In Ieee 802.1q
The IEEE 802.1Q is defined as Dot1q which by default support VLAN on the Ethernet network. Suppose if we need to connect to VLAN from two-point which have different switches, we need to use the method called trunk to connect between two switches in VLAN. The trunk can be configured between switch and router. A trunk port has a VLAN tag to an Ethernet frame to indicate which frame belongs to which VLAN with Access port we can send untagged traffic.
Role Of Router And Switch In Vlan
Using the router and switch it is possible to transfer only specific VLAN trunking. The router and the switch configuration are responsible for configuring Dot1q. VLAN creation and management are the responsibility of switches. The switch will insert the VLAN Tag into the Ethernet frame. The router is used to communicate between two VLANs. this is also called Routing on a stick.
2.2 Difference Between Basic Nat Vs One To Many Nat
Basic NAT
It enables one-to-one NAT mapping for the users with the IP address and the destination applications (Myxroads 2015).
One to many NAT
In one-to-many NATs, the port is forwarded using the NAT rule where only a particular port is forwarded to the internet LAN address (Myxroads 2015).
One-to-one NAT
One-to-one NAT enables to map of all the IP address from WAN to LAN network. The ports and the protocols are forwarded since the internal address is connected directly with the internet (Myxroads 2015).
Address- restricted cone NAT
In this type, the mapping occurs between the same internet and external IP address and port number. An external IP address can send the packet to the internal host if it has been already sent (Myxroads 2015).
Port restricted cone NAT
In this type, the mapping occurs between the same internet and external IP address and port number. If the port number is mapped previously with the external host can alone send the packet to the internal ports (DH2i 2020) (Myxroads 2015).
Symmetric NAT
In this type, all the requests should be the same from the internal and destination IP address and the port should be mapped with the same external IP address and the port (Myxroads 2015).
2.3 Remote Desktop Administrator
To set up a remote desktop on windows following steps should be followed (Whitney 2021):
Step 1: Go to start -> settings -> remote Desktop. Enable the Remote desktop.
Step 2: The prompt appears. Click confirm.
Step 3: to configure the remote PC from windows, go to windows accessories and select the remote desktop.
Step 4: give the IP address of the remote PC that should be connected. Click on show options and give the user name to log in. Click on connect.
Step 5: Enter the password credentials for PC. Check to remember me box if the passwords should not be entered every time. Click ok.
Step 6: A message will be received that remote computer identity could not be verified. select yes if it should not ask again.
Step 7: Now the connection is established to perform the task.
2.4 Lan Scalability
If I was asked to step up the LAN for the workplace first, we need to check the overall capacity of the network by scalability test. For example server response time, throughput, network usage, all the legacy systems should be managed. Proper networking tools should be installed in the network to monitor all the devices which are connected to the network. If we need to increase the network productivity, we can scale out instead of scaling up. For example, if we need to scale up we can use a switch that supports multiple vendors instead of buying from the same vendor which supports only one switch for upscaling.
Task 3
Administer A Network
3.1 Network Administrator
Network Administrators Have The Following Duties
- Configuration of hardware such as routers, switches, and server
- To upgrade, repair and maintain the computer networks
- To troubleshoot the issues in the network
- To assist the network architecture with required network models
- To deploy and update the software
- To manage the server and the operating systems
- To implement the security principles
- To manage the physical network storage and cloud network storage
Tools such as traceroute, Nmap and Wireshark are used to carry out their duties effectively. Traceroute is the tool that is used to find the path of the network. Nmap is the open-source tool that is used for defending the network attack. it discovers and map the network via more requests of particular host. Wireshark is the open-source software that is used for capturing the live network traffic in the website. using this the malicious attack can be identified and protected. A common troubleshooting task is “unable to connect to the internet”. To resolve this, the modem and the router should be rebooted. Using traceroute the communication breaks can be identified and this shows which router causes the problem then connects with the ISP to find further information (CBT Nuggets 2019). Another network problem is "HTTP error". Using the wireshark, it reports the errors with the HTTP protocol and therefore it could be resolved.
3.2 Spanning Tree Protocol
It is a link management protocol that is used for supporting the redundant link which stops the switch loop in the spanning tree protocol network. This protocol is implemented in the bridges and switches that are enabled with the switch interfaces (INAP 2008).
The spanning-tree uses an algorithm for searching the redundant links in the Local Area Network and choosing the best path. It is generally used for putting all the links in the forwarding or blocking form. After this process, the links other than the redundant links will be in the forwarded state and the redundant links will be in the blocked state. It does not use multiple links to a single destination.
Examples of Spanning Tree protocol
For every switching network, there will be one root bridge per network, one root and designated port with non-root bridge and segment, and unused, non-designated ports. The data traffic is forwarded by Root ports and designated ports and discarded by the non-designated ports. Below is an example network diagram for spanning tree protocol:
Selecting the root bridge
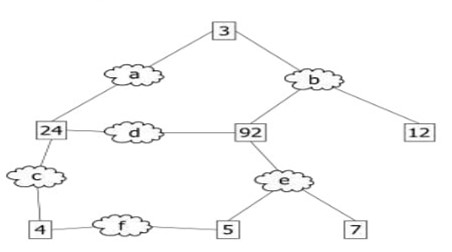
In the above example network, the boxes which are numbered represents the bridges and letters represents the network segments.
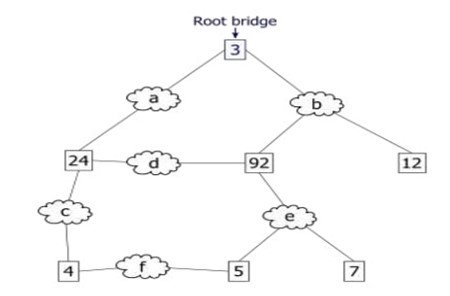
Here, the bridge ID with small value is 3 so it is the root bridge.
The bridge with the least ID is considered the root bridge.
Bridge Protocol Data Units are sent out using the Bridge ID. It contains priority bridge and Switches based MAC addresses. All switches check whether the Bridge ID is sent or not.
The property of the spanning tree is that message that comes from any connected devices to the root bridge traverses a least-cost path. This port is considered as a destination port of the network segment. And the port which is not a root port is a blocked port. The cost for traversing the network segment is 1. The least path starts at bridge 4 to the root bridge with network segment C. It has the least path so the root port is 1.
There are four states in spanning trees such as block state, listen state, learn state, and forward state.
The block state is the non-designated port that does not involve in the forwarding state. The listening state is the initial state where it is started after the blocked state. It decides that the interface should involve in forwarding the frame. Learn state helps to involve in forwarding the frame. Forwarding state, the frames are forwarded. When the port fails or is shut down by the administrator it is disabled.
3.3 Link Aggregation
This method combines single links to improve the performance of the network. Commonly used devices for combining the network devices are switch to switch, server, network storage device, and multiple port access point. Some of the network devices use Link Aggregation Control Protocol for preventing the error in the link aggregation process (Auvik 2021).
Configuration LACP in the stand-alone devices can be done by changing the settings as active or passive. If the actor and the partner are in passive mode then no exchange of LACPDUs results that Ethernet links are not coming. If the actor or partner is active then they exchange the links. By configuring this to the network has various benefits such as increasing the reliability of the network connection, better usage of physical resources, and cost-effective.
References
Steele, C. (2019). Why is Computer Networking Important? | Digital Divide Council. [online] Digital Divide Council. Available at: http://www.digitaldividecouncil.com/why-is-computer-networking-important/.
Network Direction. (2018). Hierarchical Network Model - Network Direction. [online] Available at: https://networkdirection.net/articles/network-theory/hierarchicalnetworkmodel/.
Auvik. (2021). Network Basics: What Is Link Aggregation & How Does It Work? [online] Network design assignment Available at: https://www.auvik.com/franklyit/blog/network-basics-link-aggregation/.
Myxroads.com. (2015). What is the difference between One-to-One and One-to-Many NAT? [online] Available at: http://www.myxroads.com/kb/a32/what-is-the-difference-between-one-to-one-and-one-to-many-nat.aspx [Accessed 25 Oct. 2021].
CBT Nuggets. (2019). Online IT Training Videos, IT Certification Training | CBT Nuggets. [online] Available at: https://www.cbtnuggets.com/blog/technology/networking/7-common-network-issues-and-how-to-resolve-them-fast.
?DH2i. (2020). Understanding Different NAT Types and Hole-Punching. [online] Available at: https://dh2i.com/kbs/kbs-2961448-understanding-different-nat-types-and-hole-punching/ [Accessed 25 Oct. 2021].
Whitney, L. (2021). How to Use Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Connection. [online] PCMag India. Available at: https://in.pcmag.com/software/114298/how-to-use-microsofts-remote-desktop-connection [Accessed 25 Oct. 2021].
?INAP. (2008). Spanning Tree Protocol Explained! - INAP. [online] Available at: https://www.inap.com/blog/spanning-tree-protocol-explained/.












