Planning a web-based reporting system for Rimu Art
Question
Task: You need to produce the project plan. In producing the plan, you can make the assumptions you consider necessary; these assumptions must be explicit in the document you are going to produce. Provide a print out of the Gantt chart showing all the activities involved in the project as it was planned. Identify the activities in the critical path; enumerate them.Has any resource been overallocated? If yes, explain which ones have been overallocated and what corrective action you would take. How would you redistribute the workload? Justify your answer. Is it possible to complete the project by Monday 14 August working on normal time? If not, what corrective actions should you take? What are the implications?Produce a time-phased budget. Taking into consideration your answer to the previous question, is it possible to complete the project within the estimated budget? If yes, explain how. If not, what would you do?
Answer
Task 1: Critical activity
GANTT CHART
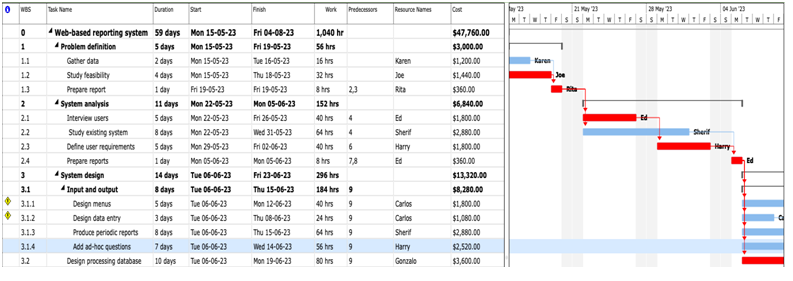
In the given case study, there are several activities that need to be performed in order to implement a new software system. However, there is one critical activity that stands out as being essential to the success of the project - defining user requirements.
Defining user requirements is critical because it lays the foundation for the entire project. If user requirements are not properly defined, the software system that is ultimately implemented may not meet the needs of its users. This can result in a system that is difficult to use, inefficient, and ultimately fails to achieve the desired outcomes.
The first step in defining user requirements is to interview users. This allows the project team to gain an understanding of the users' needs, preferences, and expectations. It is important to conduct these interviews in a systematic and structured manner to ensure that all relevant information is collected.
Once the interviews are completed, the project team can use the information gathered to prepare a report that summarizes the user requirements. This report should clearly outline the needs of the users, as well as any constraints or limitations that may impact the design of the software system.
With the user requirements clearly defined, the project team can then move on to the next steps in the project, such as designing the processing database, customizing the software, and testing the system. Throughout these activities, it is important to refer back to the user requirements to ensure that the system is meeting the needs of its users.
It is also important to evaluate the system at various stages of the project to ensure that it is meeting the desired outcomes. This evaluation should be done in a systematic and objective manner, using both qualitative and quantitative measures. The results of the evaluation should be documented in a report, which can be used to make any necessary adjustments to the system.
In addition to designing and implementing the software system, it is also important to train users on how to use the system effectively. This training should be tailored to the needs of each user group and should be delivered in a way that is easy to understand and follow. The results of the training should also be documented in a report, which can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the training and make any necessary adjustments.
Task 2:
Overloaded resources can occur when a team member is assigned too many tasks, or when multiple team members are assigned to the same task, resulting in a lack of coordination and inefficiencies. This can lead to delays in project completion, as well as decreased productivity and morale.
To address overloaded resources in the Rimu Art project, the project manager Karen Thorsen should first identify the tasks that are at risk of being delayed due to resource overloading. She can then reassign tasks or redistribute workload among team members to balance the workload.
Also, it can resolved by replacing the overloaded resources with other resources having same cost.
All the red highlighted resources are overloaded as generated from MS Project.
One way to redistribute workload is to prioritize tasks based on their importance and urgency. Karen can then assign the most critical tasks to team members with the most availability and experience, while delegating less important tasks to other team members.
Another solution to address overloaded resources is to bring in additional resources. This can be done by hiring new team members or outsourcing certain tasks to third-party vendors. However, this solution should only be considered if the budget allows and if the new resources can be effectively integrated into the existing team.
Lastly, Karen can also consider implementing tools and processes to improve collaboration and coordination among team members. This can include regular team meetings to discuss project progress and identify areas where additional support is needed, as well as project management software to track task assignments and deadlines.
Task 3:
In order to determine what corrective actions should be taken, it is important to first understand the current situation and the factors contributing to the delay in completing the project on time.
Assuming that each activity has been completed as planned up to this point, and that the remaining activities can be completed in the estimated duration, the expected completion date for the project would be 04th August.
August working on normal time. This means that the project needs to be accelerated by one week. In order to achieve this, the following corrective actions can be taken:
• Increase the level of resources: One of the main reasons for delay in completing the project is lack of resources. To accelerate the project, additional resources such as staff, equipment, or software tools can be utilized to speed up the remaining activities. However, this could have implications on the project budget and may require approval from the project sponsor or stakeholders.
• Reduce the duration of critical activities: Another approach to accelerating the project is to reduce the duration of critical activities. For instance, activities such as preparing reports or training users can be done in shorter timeframes by eliminating non-essential components. However, this could also have implications on the quality of the outputs and the satisfaction of the project stakeholders.
• Fast-tracking: This involves overlapping or performing activities in parallel rather than sequentially. For instance, the activities of designing processing database and evaluating can be done in parallel. This could accelerate the project, but there are implications in terms of increased risks of rework, errors, and conflicts among team members.
• Overtime and weekend work: Another approach is to have team member’s work overtime or during weekends to accelerate the project. This could increase the workload and stress levels of team members, which could result in reduced productivity, lower quality work, or burnout.
In conclusion, there are several corrective actions that can be taken to accelerate the project and complete it by Monday 14 August. However, each of these actions has implications on project resources, schedule, quality, risks, and stakeholder satisfaction. It is important to evaluate each option carefully and choose the one that provides the best balance between the project objectives, constraints, and stakeholder needs.
Therefore, it is possible to complete the project by Monday 14 August working on normal time. To address this, the project manager should take corrective actions such as:
• Crash the schedule: This involves reducing the duration of critical path activities by adding resources to complete the work faster. For example, the project manager could hire additional staff or ask team members to work overtime to speed up the completion of critical activities.
• Fast-tracking: This involves overlapping activities that were initially planned to be done sequentially. For example, the project manager could start training users while software testing is still ongoing. However, fast-tracking increases the risk of rework and may require additional resources to manage.
• Re-evaluating the project scope: The project manager could also re-evaluate the project scope and see if some of the non-critical activities can be deferred or removed to reduce the project duration.
The implications of not taking corrective actions to address the schedule overrun include:
• Delayed project completion: The project will not be completed by the desired deadline, which can impact other projects or business operations.
• Increased project costs: Overtime or additional resources required to complete the project faster will result in increased project costs.
• Lower quality: Rushing critical activities to meet the deadline may compromise the quality of the project deliverables.
• Decreased morale: Team members may become demotivated if they have to work long hours or overtime to meet the deadline, which can lead to decreased productivity and morale.
Task 4:
To produce a time-phased budget, we need to estimate the costs associated with each activity and allocate them over the project's duration.
Assuming that the project starts on Monday, may 15th, and finishes on, Friday, August 04th, the total project duration is 59 working days. Using the information from the case study, we can estimate the costs associated with each activity as follows:
|
Task Name |
May |
June |
July |
August |
|
Gather data |
$600 |
$600 |
- |
- |
|
Study feasibility |
$720 |
$720 |
- |
- |
|
Prepare report |
- |
$360 |
- |
- |
|
Interview users |
$600 |
$600 |
$600 |
$1,000 |
|
Study existing system |
$720 |
$1,080 |
$1,440 |
$640 |
|
Define user requirements |
$600 |
$600 |
$600 |
$1,000 |
|
Prepare reports |
- |
$360 |
- |
- |
|
Input output |
$1,440 |
$2,160 |
$2,880 |
$1,800 |
|
Design process database |
$1,200 |
$1,200 |
$1,200 |
$1,000 |
|
Evaluate |
- |
- |
$360 |
$360 |
|
Prepare report |
- |
- |
$360 |
$360 |
|
Develop software |
$1,500 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Assemble hardware |
$1,200 |
$1,200 |
$1,200 |
$1,000 |
|
Build network |
$720 |
$720 |
$720 |
- |
|
Prepare report |
- |
- |
$360 |
$360 |
|
Test software |
$720 |
$720 |
$360 |
$360 |
|
Test hardware |
- |
$720 |
$360 |
$360 |
|
Test network |
- |
$720 |
$360 |
$360 |
|
Prepare report |
- |
- |
- |
$360 |
|
Train users |
$720 |
$360 |
$360 |
- |
|
Deploy system |
- |
- |
- |
$1,200 |
|
Prepare report |
- |
- |
- |
$360 |
|
Total Cost |
$11,460 |
$11,640 |
$11,760 |
$10,940 |
|
Cumulative cost |
$11460 |
$23100 |
$34860 |
$45800 |
Based on the time-phased budget, the total cost of the project is $45800 over 59 working days.
If we assume that the project must be completed by Monday, August 14th, then we have enough time to complete the project within the estimated budget, as the critical path takes 59 working days to complete.
To keep the project on track, we could consider the following corrective actions:
• Increase the number of resources working on the critical path activities, such as hiring more software developers or database designers, to reduce the duration of those activities.
• Reduce the scope of the project by removing some of the non-essential features to simplify the design and implementation process.
• Reallocate resources from the non-critical path activities to the critical path activities to ensure that they are completed on time.
If these actions are taken, then the project will likely be on budget, and additional time and resources will not be required to complete the activities, leading to potential cost save and on time delivery.












