Precision Agriculture Assignment On Smart Meter In Semios
Question
Task: Write a report on precision agriculture assignment exploring the project of precision agriculture for data-intensive farm management with a smart meter in Semios.
Answer
Introduction
The current report on precision agriculture assignmentdiscusses about Semios platform which is one of the powerful approaches in producing enhancements that help the growers in assessing as well as optimizing the response to the insect, health condition of plants on a real-time basis. The firm uses improved technologies such as big data as well as predictive analytics for the crops (SemiosBIO Technologies, 2020). The Company is planning to analyse precision farming techniques in the fields and theory to understand the project status that can be implemented under the techniques. In this regard, the report on precision agriculture assignment shall be focussing on analysing the two key objectives of the projects, and appropriate justification shall be provided. Based on this, the overall scope of the project shall be discussed in the sections of precision agriculture assignment in relation to the Company. The WBS structure shall be formed, which would discuss the estimates of the project, and justification shall be provided for selecting the estimates. Apart from this, risk in the project shall also be identified, and a contingency plan for the risks will also be framed.
Objectives and justification of the objectives selected.
The project that has been selected in the present context of precision agriculture assignment is precision agriculture for data-intensive Farm management with a smart meter in Semios. The project focuses on working with the participating farmers with the use of precision technology that can help in designing the agronomic trials. The use of precision farming, it would become easy to gather and analyse the data regarding the variability of soil as well as the condition of crops. Through this, efficiency can be maximized for the crop inputs within a small specialized area of farms. The two key goals of the project considered are discussed below within the precision agriculture assignment:
- To analyse the data on the soil variability and crop conduction through precision farming technique.
- To design a smart meter for tracking the pH level, soil moisture, and temperature of the soil.
The concept of precision agriculture explored in the precision agriculture assignment is becoming an attractive idea with respect to the management of natural resources as well realization of modern sustainable development. The technology shall be incorporating the satellite remote sensing and global positioning system as the country has access to the opportunities that are afforded by the satellite remote sensing through revolutionizing agriculture. With the successful completion of project goals, the firm can successfully help the farmers in harnessing them for large scale agricultural production. For meeting the efficiency goals, the variability within the field needs to be controllable (Carpio et al., 2020). Efficiency in the areas of crop input illustrates that few crops inputs such as chemical as well as fertilizers shall be used. Through this, both economic and environmental benefits can be achieved.
Scope of the project
The firm examined in the segments of precision agriculture assignment believes that the farmer gets started only when they have completely understood the three key elements on which the technology entirely depends. This includes information, technology, as well as management.
- The project shall focus on analyzing the key areas which act as a valuable resource. Timely as well as accurate information is necessary for the various phases of production from the planning through the post-harvest.
- Modern technology is another success to keep up with the changes that might benefit the operation. There is a need for proper management, precision crop production for efficient production (Marucci et al., 2017). It is necessary for the framers to know the ways in which information can be interpreted and ways through which sound decisions can be made.
- In this regard, the project manager needs to select the necessary technology and equipment that can produce high accuracy applications. The comprehensive precision agriculture system has been viewed in two key phases, namely site-specific management as well as post-harvest process control.
- For the post-harvesting processing, sensors shall be used for monitoring the process. This would result in delivering the best quality products that can be successfully provided to the consumers (Orsini et al., 2019).
- Analysis of the data presented in the precision agriculture assignment shall thus help in better matching the chemical as well as fertilizers with the requirement of crops. It would prevent the over-application that can be non-beneficial for the environment.
- The management practices that are typically generated by the precision farming technologies shall thereby promote good land stewardship.
WBS
Team objectives
|
Work |
Time (days) |
|
Creation of the project team |
6 |
|
Preparing project budget and overall plan |
8 |
|
Selection of site for data collection form soil |
5 |
|
Execution of market research |
7 |
|
Hiring skilled workers |
4 |
|
Coordinating and discussing the tasks |
12 |
|
Implementing the technologies on a practical scale |
25 |
Implementation plan
An effective implementation plan requires to be developed through with varied tasks within the project can be efficiently completed. For this, a step by step procedure shall be selected, and the tasks need to be monitored and thereby ensure that it can be completed within the time with quality. This would further ensure the achievement of quality and achieving the objective of the project.
Work breakdown structure
With the work breakdown structure basis the case scenario of precision agriculture assignment, varied tasks of the project can be efficiently planner with effective procedure designing.
|
WBS ID |
Level |
Element |
Description |
Resources |
|
1 |
1 |
Developing a project team |
· Evaluating employee skills |
· Human · resources
|
|
2 |
1 |
Developing a project budget |
· Evaluating the expenses associated with the project |
· Financial resources |
|
3 |
1 |
Initiating project |
· Declaring the project scopes and objectives |
· Financial · Human resources |
|
4 |
1 |
Site location survey |
· Planning and installation of the equipment required for data collection |
· Technological · Human resource · Financial resource |
|
5 |
1 |
Submitting requirements and biding of process |
· Tracking the process of land selection |
· Human resources |
|
6 |
1 |
Installation setup |
· Checking the requirements as per the project deliverables |
· Human resources · Technological resources |
|
7 |
1 |
Testing of equipment |
· Monitoring the accuracy of the equipment |
· Technological resources |
|
8 |
1 |
Quality assessment |
· Analyzing the quality of the crops that are produced through precision techniques |
· Technological resources |
|
9 |
1 |
Documentation |
· Recording the material in an appropriate manner |
· Human resources |
|
10 |
2 |
Setting up period for the project |
· Declaring the time scale and schedule for the project |
· Human resources |
|
11 |
2 |
Network designing implementation |
· Analyzing the ways of equipment implementation |
· Human resources · Technological resources |
|
12 |
2 |
Processing of equipment order |
· Checking the requirements of the equipment order as required |
· Technological resources |
|
13 |
2 |
Setting up a connection |
· Installation of the equipment that has arrived at the site location |
· Technological resources |
|
14 |
2 |
Testing of connectivity |
· Checking up the connection between the equipment |
· Technological resources |
|
15 |
2 |
Acceptance test performance |
· Analyzing the test performance of the equipment |
· Technological · Human resources |
|
16 |
3 |
Working permit |
· Achieving compliance with the work permits |
· Human resources |
|
17 |
3 |
Equipment delivery process |
· Ensuring the safe delivery of the other equipment |
· Human resources |
|
18 |
3 |
Setting up configuration |
· Checking the accuracy of the equipment working when integrated |
· Technological resources |
|
19 |
3 |
Site integration |
· Splitting the sites to check the soil quality at an individual location |
· Technological · Human resources |
|
20 |
3 |
Handing over process to the operation team |
· Providing the necessary details of management and work to the operation team of the Company |
· Technological · Human resources |
|
21 |
3 |
Executing market research |
· Conducting market research to analyze the needs |
· Human resources · Sales team |
|
22 |
3 |
Developing the equipment |
· Integrating the technology to make a smart meter that can assess the soil quality easily |
· Technological resources |
|
23 |
3 |
Sales monitoring |
· Checking up the sales of the crops produced through application software |
· Sales team |
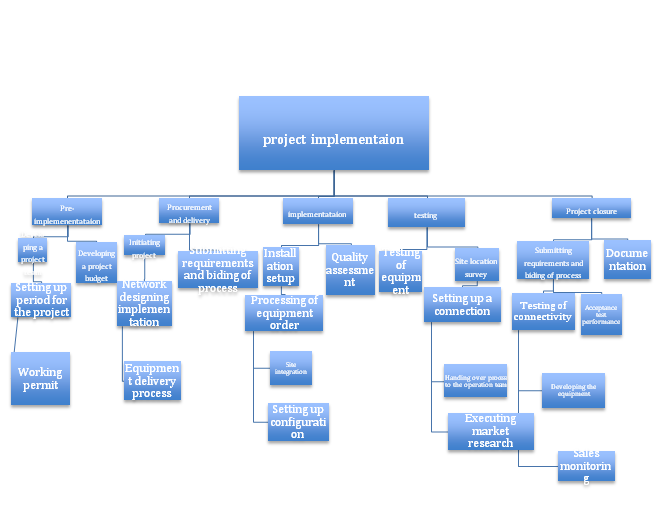
Schematic diagram of WBS
(Source: Self developed)
Justification for the estimates considered
The estimates that have been considered herein precision agriculture assignment will help in assuring quality planning, quality assurance, as well as quality control. There are three key elements of managing the quality of the project. It is necessary for the project manager to identify quality planning. This might include survey location, licensing process, procurement, installation as well as setting up of configuration, and acceptance tests. Based on this information provided in the precision agriculture assignment, the documentation shall be made, which further ensures the project quality. The quality can be assured through the reliability of the network response time and handling time. In terms of quality control, the project manager needs to locate the operational maintenance, reporting the performance monitoring as well as control the delivery service.
Risk that the project is exposed to
The key risk that the project is exposed includes the following points mentioned in the precision agriculture assignment:
- Technological and security risks: Precision agriculture aims at reducing the costs, labour, as well as possible risks in prodigy better crops with increasing production. However, there is a counter side to this with the increasing growth risk of cybersecurity. Precision agriculture generates large data, and there are various security issues associated with it. There are significant concerns over the ownership as well as data usage with the ways in which it is stored. Data can be collected with the implementation of IoT and cloud computation (Liu et al., 2017). The lack of encryption and adoption of the regulation, such as GDPR might result in further disrupting the situation of data management.
- Introduction of rogue data within the sensor network that damages the cop or herd: Incase of highest value crop, smart sensor implementation has a major application. These sensors are connected through the Wi-fi networks and make the decision at the sources (Say et al., 2018). Faulty sensors might disrupt the system ad could potentially result in adverse health impacts
Which steps are considered for mitigating the risks outlined in the precision agriculture assignment?
- It is necessary to consider a comprehensive system of supervision as well as a checklist that shall help in ensuing the sanctions of the requirements by the project manager
- Implementation of Email and web browser processions
- Limiting and controlling the network ports (Bhakta et al., 2019)
- Inventory and control asset software implementation in the project
- Separating the operational technologies as well as the business operations
- Ensuring good communication and compliances with the owner and within the involved team
- Making realistic schedules as well as thoroughly supervising the schedule
Create a contingency plan for the one identified risk
Contingency plan for security risks includes the following points provided in the precision agriculture assignment:
- Implement physical controls: The use of physical controls shall augment the cybersecurity controls. This would ensure restricting access to major technology areas.
- Incidence response as well as efficient management: Developing data ownership, data procession, as well as data recovery facilities, shall ensure rapid recovery from the security threats (Gandorfer& Meyer-Aurich, 2017)
Conclusion
It can be concluded from the above discussion on precision agriculture assignmentthat it is necessary for the firm to consider the smart meter system that has been developed for checking the quality of the soil in remote locations. There are varied risks that are associated with the precision farming project, as there is the implementation of technological aspects. This makes the project vulnerable to various risks that need to be mitigated, and a backup has also been provided in this context. The work breakdown structure developed within the precision agriculture assignment has also been discussed for the successful implementation of the project by the project manager. Based on this, the required efficient production and system capabilities can be improved.
References
Bhakta, I., Phadikar, S., &Majumder, K. (2019). State?of?the?art technologies in precision agriculture: a systematic review.
Precision agriculture assignmentJournal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(11), 4878-4888.
Carpio, R. F., Potena, C., Maiolini, J., Ulivi, G., Rosselló, N. B., Garone, E., &Gasparri, A. (2020).A Navigation Architecture for Ackermann Vehicles in Precision Farming. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 5(2), 1103-1110.
Gandorfer, M., & Meyer-Aurich, A. (2017).Economic potential of site-specific fertilizer application and harvest management. In Precision Agriculture: Technology and Economic Perspectives (pp. 79-92). Springer, Cham.
Liu, Y., Langemeier, M. R., Small, I. M., Joseph, L., & Fry, W. E. (2017).Risk management strategies using precision agriculture technology to manage potato late blight.Agronomy Journal, 109(2), 562-575.
Marucci, A., Colantoni, A., Zambon, I., &Egidi, G. (2017). Precision farming in hilly areas: The use of network RTK in GNSS technology. Agriculture, 7(7), 60.
Orsini, R., Basili, D., Belletti, M., Bentivoglio, D., Bozzi, C. A., Chiappini, S., ...&Malinverni, E. S. (2019, May). Setting of a precision farming robotic laboratory for cropping system sustainability and food safety and security: preliminary results. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 275, No. 1, p. 012021). IOP Publishing.
Say, S. M., Keskin, M., Sehri, M., &Sekerli, Y. E. (2018). Adoption of precision agriculture technologies in developed and developing countries.Online J. Sci. Technol, 8(1), 7-15.
SemiosBIO Technologies. (2020). precision agriculture assignmentRetrieved 24 July 2020, from https://semios.com/












