Project Plan Assignment Focusing On Task Management
Question
Task: The Chair of the Committee, Dr Shane Doyle, has tasked you with providing the project board with further information regarding the project. The Chair will act as the Project Executive for the project board. You are to develop a tailored project plan that reflects the project described in this document and which aligns with PMBoK and Prince2 requirements.
Answer
Introduction
The study of project plan assignment explores the concept of project plan as a formal document that aims at providing guidance to control and execute the entire project. Project plan is viewed essential for a successful completion of a project. Basically, project plan varies from business to business but there are some common elements in every project plan that are commonly used such as scope, goals, milestones, project deliverables, work breakdown structure, project budget, human capital, risk management plan, communications plan, stakeholder management plan and change management plan. The project manager of an organization is responsible for crafting project plan by aligning the objectives and goals that is considering the inputs from the team and core stakeholders. However, the purpose of the project management plan is to define the approach that is to be applied by the project team in delivering the scope of the project management. In this particular assignment the core intention is to prepare a project plan on behalf of The School of Engineering and Technology (SET) which is interested in developing, designing and building educational hubs in five campuses of CQU that is located at Rockhampton, Brisbane, Perth, Sydney and Melbourne. The purpose of this particular project plan is to highlight the scope, schedule, risks, tolerances, cost baseline, stakeholder’s management, requirements management and the lessons learnt.
2. Discussion
2.1 Project description
2.1.1 Project description, background and major deliverables of Project plan assignment: Project description basically details about the background as well as the deliverables. Precisely, project description highlights the objectives as well as the project goals (McGuinness et al., 2017).
|
Project description |
Background |
Deliverables |
|
The committee of the School of Engineering and Technology (SET) will evolve a project that will establishing, develop and design the educational hubs at five major campuses of CQU that are located at Rockhampton, Brisbane, Perth, Sydney and Melbourne. Basically the project will be accomplished in three major stages: · Sourcing the acceptable facility space that will be utilized by the committee for construction of the educational hubs. This includes negotiation leasing arrangements. · Establishment of the educational hubs at the CQU campuses in five major locations. · Conducting the initial ceremonies considering the traditional custodians of the land on which the new educational hubs will be constructed. |
The Indigenisation Committee of the School of Engineering and Technology (SET) is basically interested in developing the projects that aims at providing visibility to the traditional culture of the world by considering the lands of traditional custodians on which the campuses are built. However, in this context the committee of SET decided to initiate educational hubs that will effectively support and encourage education as well as comprehend the need of creating awareness of the local indigenous people. |
The major project deliverable are under lain in the points: · Encourage as well as supporting education · Understanding the need of creating awareness about the local indigenous people. |
Table 1: Details of project description
Source: Learner
2.1.2 Justification
|
Output |
Outcome |
Benefits |
|
Development of the educational hubs in five major campuses of CQU which is situated at Rockhampton, Brisbane, Perth, Sydney and Melbourne. |
Delineating the oldest culture of the world by considering the traditional custodians because on their lands the campuses will be building (Kowal, 2015). |
|
Table 2: Justification of the project
Source: Learner
Figure 1: Justification of a project
Source: Learner
2.2 Stakeholders
2.2.1 Key stakeholders list
In this particular section of project plan assignment the key stakeholders of the project will be discussed in details along with their description of interest and influence.
|
Serial number |
Stakeholder |
Category |
Description of interest |
Description of influence |
|
1 |
Committee |
Initiators |
The Indigenisation Committee of the School of Engineering and Technology (SET) are basically the initiators of this particular project and hence their level of interest is high. One of the major internal stakeholder of this project are the committee members and their priority is the successful completion of the establishment of the project in the major five campuses of CQU. |
As the committee of the SET falls under the category of major internal stakeholder of the project or as the initiators they can influence the project because of having the authority to change the scope or even the project objectives. |
|
2 |
Investors or banking authority |
Sponsors |
The investors as well as the banking authorities of the project are considered as the sponsors who financially will be assisting the entire project activities developed by the SET committee and hence their level of interest in this case is high due to the effective return on their investment. In other words it can be said that the investors are basically interested in extracting higher return on their investment in such project. |
The investors or banking authorities are the financial sponsor of the project and hence the success of the project largely depends on the financial assistance and hence this stakeholder group has high influence on the project. |
|
3 |
Traditional custodians |
Suppliers (Land) |
The interest level is high but comparatively lowered than the Committee and the investors. Precisely, they are the land owners and their interest level is only limited to the leasing arrangements. |
This particular stakeholder group can effectively influence the project because they are the major facility space providers that is their lands will be utilized for the establishment of the educational hubs and any disagreement can delay the entire project. |
|
4 |
Facility providers |
Supplier (Raw materials) |
The facility providers falls under the category of suppliers that is the raw materials for the construction of the educational hubs are provided by this stakeholder group. The interest of this particular stakeholder group is not explicitly associated with the project because the suppliers only provides raw materials for the construction in an exchange of money and thereafter they are not involved on any activities of the project. |
The facility providers can highly influence the project because without raw materials the construction of the education hubs in the major locations of CQU campuses are not possible. |
|
5 |
Government |
National community |
The government are considered as the external stakeholder of this project that falls under the category of national community. This stakeholder group has lower interest on this particular project because the education or literacy rate in Australia is high. |
The project can get influenced by the government policies or reforms that is introduction of any regulation regarding establishment of educational hubs in Australia can impact the project initiated by the committee of the SET. |
|
6 |
Students |
User |
Basically, the users of this particular project of the SET are the students and hence their level of interest in this context of project plan assignment is high because of the enhanced education opportunity offered to them. |
The users directly cannot influence the project activities because they do not play any crucial role in the completion of the project. However, the success rate of such project can be influenced by this stakeholder group because they are the ultimate users of such educational hubs. |
Table 3: List of stakeholders
Source: Learner
2.2.2 Stakeholders engagement assessment matrix for project plan assignment
Stakeholders engagement is regarded a procedure through which an organization engages the core people of the business who might have an influential impact on the decision making process (Lappi et al., 2015). However, stakeholder engagement assessment matrix is considered as a process through which the level and direction of the stakeholder engagement are analyzed (Sanghera, 2019). Thus the matrix is viewed as an analytical technique listed in the PMI process plan.
|
Response Table |
||||||
|
# |
Stakeholders |
Unaware |
Resistant |
Neutral |
Supportive |
Leading |
|
|
Committee |
|
|
|
C, D |
C, D |
|
2. |
Investors or banking authority |
|
|
|
C, D |
C |
|
3. |
Project management team |
|
|
|
|
C, D |
|
4. |
Facility providers |
D |
|
D |
C |
|
|
5. |
Government |
C |
|
D |
|
|
|
6. |
Students |
|
|
|
|
C, D |
Table 5: Stakeholder assessment matrix
Source: Learner
2.2.3 Stakeholder communication
|
Communication method |
Interactive, push or pull |
Justification |
|
Stakeholder communication is perceived as one of the most critical components that can define the scope as well as success of the project (Butt et al., 2016). |
In this particular context, it is suggested to adopt interactive communication method in order to communicate with the key indigenous stakeholders. |
Interactive communication method in this context will allow the free exchange of thoughts and expressions and will allow two way flow of communication. This communication method will benefit the SET in understanding the scope of the educational hubs. |
Table 6: Stakeholder communication method
Source: Learner
2.2.4 Obtaining Expert Judgment
The specialist judgment in this context of project plan assignment can be obtained through Delphi techniques and interviews. Delphi techniques are the mostly used expert judgment tool and hence under this particular technique the estimates of the project management group are reviewed by the individual experts in order to receive the forecasts from those individual experts (Galanis, 2018). The degree of consensus is enhanced with each round. Interviews are viewed as the best expert judgment tool wherein the insights of the knowledgeable as well experienced people can be gathered at an economical range (Fontana and Prokos, 2016).
|
Experts |
Methods or techniques |
|
Project management expert (individual) |
Delphi techniques |
|
Investor group |
Interview |
Table 7: Expert judgment
Source: Learner
2.3 Requirements management
2.3.1 Traditional custodian/s of the land on which CQ university campuses are located
Aboriginal as well as Torres Strait Islander people of Australia were confronted to significant exclusion from the society and hence they should be considered as the core stakeholders of the project (Kowal, 2015). Considering multiple key stakeholder is considered as an appropriate approach because as multiple educational hubs are established in different locations and hence will be inappropriate to consider single stakeholder as a representative of the traditional stakeholders.
2.3.2 Opening statement style
The opening ceremony of the contemporary educational hubs should be named Acknowledgement of Country because this would reflect an acknowledgement, opportunity and respect to the conventional owners as well as current custodians of the land on which the CQU educational hubs are constructed- the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people (Cohrs and Vollhardt, 2019). However, such title of the opening ceremony of the educational hubs will highlight the distinctive position of Torres Strait Islander people as well as the Aboriginal in the culture and history of Australia.
2.3.3 Requirements gathering for CQU educational hubs for indigenous studies project
Requirements gathering is regarded as a procedure of identifying, documenting as well as managing the requirements and needs of the project that are aligned with the objectives (Heldman, 2018). However, in this context of project plan assignment, it is suggested to utilize the documentation from the project of Vietnamese community which was engaged with the development of the educational hub in Sydney. Basically, the design of the educational hubs are identical in nature and hence utilization of such desk to research design will be beneficial for the project in terms of successful completion within the estimated time frame.
2.3.4 Requirements traceability
To trace or track the improvements of this particular project which is involved in designing multiple campuses would require Requirements Traceability Matrix. This document will ensure that the scope and requirements of the project is met.
2.3.5 Requirements prioritization process
The process of prioritizing the requirements can be defined as a procedure that can effectively manage the relative significance along with the urgency of several project essentials in order to cope up with the finite resources of the projects. However, adequacy in such process ensures that the competitive requirements of the project stakeholders are addressed properly.
|
Priority |
Explanation |
|
High and critical |
Establishment of the educational hubs in the major locations of CQU campuses as well as the financial assistance provided by the investors and banking authorities. |
|
Medium and important |
Acknowledging the conventional land custodians |
|
Low and desirable |
Developing opening ceremony in the educational hubs of CQU. |
Table 8: Requirements prioritization process
Source: Learner
2.3.6 MoSCoW technique
|
Response Table |
||
|
# |
Components |
Explanation |
|
1. |
Must have |
Financial support as well as support from the suppliers to accomplish the development of the educational hubs |
|
2. |
Should have |
Acknowledgement of the conventional land custodians |
|
3. |
Could have |
Separate requirement gathering process for the completion of the project |
|
4. |
Won’t have |
User approval for establishment of educational hubs because this will provide opportunity to the students to enhance their qualifications. |
Table 9: MoSCoW technique
Source: Learner
2.4 Scope
2.4.1 Introduction to scope
Work package (WP) is considered as a category of similar activities within a project that is the smallest unit of work which further has been reduced from the work breakdown structure (WBS). Precisely, the project activities are broken into smaller parts for the successful completion. In this particular task of project plan assignment, the work breakdown structures are segmented into six major work packages namely:
- Sourcing and securing the facility space
- Negotiating leasing arrangement
- Designing the educational hubs
- Building the educational hubs
- Organizing the introductory ceremony
- Conducting the opening ceremony
In the present study of project plan assignment, the WBS dictionary aims at describing in details the components of WBS with the scope, deliverables, milestones and even the resources, quality and costs. In this particular case, the WBS dictionary will highlight the WBS ID, nature of work, budget estimation and the time frames that effectively connects the statement of work.
2.4.2 Work Breakdown structure
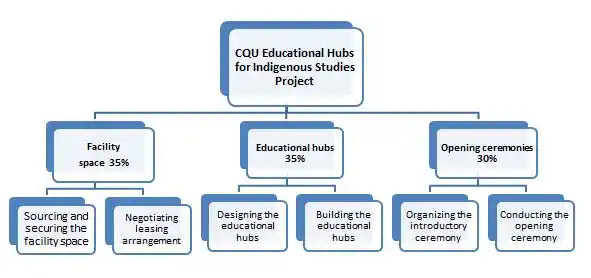
Figure 2: WBS of the project
Source: Learner
2.4.3 WBS dictionary
|
Sourcing and securing the facility space |
|
|
WBS ID |
1.1 |
|
Description of work |
This the first work package of the WBS of the project and hence the initial step for developing the educational hubs are sourcing and securing the facility space. This includes identification of the facility sources effectively for further establishments of educational hubs in five major locations. The lands of traditional custodians are considered as the facility space and hence the land owners will be acknowledged. |
|
Cost estimate |
$50, 000 |
|
Start and finish dates |
1st November 2019 to 30th November 2019 |
|
Negotiating leasing arrangement |
|
|
WBS ID |
1.2 |
|
Description of work |
In this particular activity, the negotiating leasing arrangements will be discussed with the traditional custodians whose lands will be utilized by the SET for establishment of the educational hubs. However, the leasing amount as well as dates will be negotiated in this particular work package. |
|
Cost estimate |
$200, 000 |
|
Start and finish dates |
1st December 2019 to 2nd January 2020 |
|
Designing the educational hubs |
|
|
WBS ID |
2.1 |
|
Description of work |
After the confirmation of the facility space, the educational hubs will be designed and hence the architect in this work package aims at designing the educational hubs effectively considering the position of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people in the culture as well as history of Australia. |
|
Cost estimate |
$ 50, 000 |
|
Start and finish dates |
3rd January 2020 to 31st January 2020 |
|
Building the educational hubs |
|
|
WBS ID |
2.2 |
|
Description of work |
This is considered as the core activity in this project because it is involved with developing the educational hubs in the CQU campuses. The particular work package includes construction of the building for establishment of educational hubs. Five educational hubs will be constructed in different locations. |
|
Cost estimate |
$500, 000 |
|
Start and finish dates |
1st February 2020 to 31st March 2021 |
|
Organizing the introductory ceremony |
|
|
WBS ID |
3.1 |
|
Description of work |
After the completion of the construction of the educational hubs the project team of the SET will organize an introductory ceremony which will effectively plan the activities related to the inauguration of the educational hubs. This inauguration ceremony will named Acknowledging of the Country. |
|
Cost estimate |
$50, 000 |
|
Start and finish dates |
1st April 2021 to 30th April 2021 |
|
Conducting the opening ceremony |
|
|
WBS ID |
3.2 |
|
Description of work |
Conducting the opening ceremony will involve the inauguration activity along with that the objectives and purpose of such educational hubs will be discussed in details and thereafter the conventional owners as well as the current custodians will be acknowledged. |
|
Cost estimate |
$150, 000 |
|
Start and finish dates |
1st May 2021 |
2.5 Schedule
Sourcing and securing the facility space
|
ACTIVITY |
DESCRIPTION OF WORK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
DURATION (DAYS) |
|
1. |
Searching for the facility space |
1st November 2019 |
12th November 2019 |
12 days |
|
2. |
Sourcing the facility space |
13th November 2019 |
20th November 2019 |
8 days |
|
3. |
Securing the facility space |
21st November 2019 |
30th November 2019 |
10 days |
Negotiating leasing arrangement
|
ACTIVITY |
DESCRIPTION OF WORK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
DURATION (DAYS) |
|
1. |
Interacting with the traditional owners as well as current custodians about the utilization of their lands for establishment of educational hubs |
1st December 2019 |
8th December 2019 |
8 days |
|
2. |
Negotiation of the leasing amounts and dates with the concerned parties |
9th December 2019 |
24th December 2019 |
16 days |
|
3. |
Entering into an agreement |
27th December 2019 |
2nd January 2020 |
8 days |
Designing the educational hubs
|
ACTIVITY |
DESCRIPTION OF WORK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
DURATION (DAYS) |
|
1. |
Gathering documentation from Vietnamese project which was involved with establishment of educational hub in Sydney |
3rd January 2020 |
6th January 2020 |
3 days |
|
2. |
Designing the infrastructure of the building |
7th January 2020 |
25th January 2020 |
19 days |
|
3. |
Getting finalized design from the committee, investors and project board |
26th January 2020 |
31st January 2020 |
6 days |
Building the educational hubs
|
ACTIVITY |
DESCRIPTION OF WORK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
DURATION (DAYS) |
|
1. |
Site cleaning and foundation digging |
1st February 2020 |
28th April 2020 |
88 days |
|
2. |
Construction of the buildings |
29th April 2020 |
31st December 2020 |
247 days |
|
3. |
Applying the coat of paint, electric services, sewage lines and parking tiles |
1st January 2021 |
31st March 2021 |
90 days |
Organizing the introductory ceremony
|
ACTIVITY |
DESCRIPTION OF WORK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
DURATION (DAYS) |
|
1. |
Making the educational hubs ready for the inauguration ceremony |
1st April 2021 |
10th April 2021 |
10 days |
|
2. |
Developing plans for introductory ceremony including the activities to be conducted and the title |
11th April 2021 |
24th April 2021 |
13 days |
|
3. |
Getting the approval from the committee and other concerned parties |
25th April 2021 |
30th April 2021 |
6 days |
Conducting the opening ceremony
|
ACTIVITY |
DESCRIPTION OF WORK |
START DATE |
END DATE |
DURATION (DAYS) |
|
1. |
Inauguration of the educational hubs in the CQU campuses |
1st May 2021 |
1st May 2021 |
1 day |
|
2. |
Discussion of the objectives and purposes of such establishment |
1st May 2021 |
1st May 2021 |
1 day |
|
3. |
Acknowledging the conventional owners as well as the current custodians of the lands on which the hubs are built |
1st May 2021 |
1st May 2021 |
1 day |
2.6 Cost baseline
The cost baseline table is presented below:
|
Response Table |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Timeline (months) |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
WBS id |
WP / Activity name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
|||
|
1.1 |
Sourcing and securing the facility space |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.2 |
Negotiating leasing arrangement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.1 |
Designing the educational hubs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
Building the educational hubs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.1 |
Organizing the introductory ceremony |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
Conducting the opening ceremony |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total monthly costs |
$50K |
$150K |
$100K |
$25K |
$25K |
$25K |
$25K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$40K |
$50K |
$150K |
|
|
|
Cumulative costs |
$50K |
$200K |
$300K |
$325K |
$350K |
$375K |
$400K |
$440K |
$480K |
$520K |
$560 |
$600K |
$640K |
$680K |
$720K |
$760K |
$800K |
$850K |
$1000K |
|
Table 10: Cost baseline table
Source: Learner
2.7 Risks
Project risks are basically viewed as the uncertainties that are exposed to the potentiality of the projects in achieving the objectives and goals. Determining, assessing and addressing the potential risks of the projects are considered as an essential part of the project management plan and hence this section of the project plan assignment aims at discussing the threats as well as opportunities that are exposed to this particular project of the set.
|
Response Table |
|||||
|
Project Name |
|
||||
|
Name
|
Description |
Likelihood |
Impact |
Response Type |
Mitigation Strategy |
|
Threat 1: Budget
|
Often large projects are confronted with budget control issues when the cost overruns. Basically the budgetary estimates are the forecasts which involves certain degree of uncertainty. In this context the project of establishment of educational hubs are confronted with some budgetary issues because of construction of five buildings at same time. |
The likelihood of occurring this particular risk is 50 percent that is a probability of 0.5 because of the construction of five educational hubs at same time. |
Budgetary constraints in the project of the SET will delay the delivery state that is the inauguration of the educational hubs will be delayed if the project encounters some budget risk. |
Reduce the risk |
Effective communication is considered as a mitigation strategy in this case wherein the further financial requirements will be communicated to the investors as well as banking authorities. |
|
Threat 2: Resistance to change
|
Resistance to change is considered as a situation wherein the project members defend the status quo. In this particular case the project members actively resists any changes because as this is an extensive activity any small changes would change the entire work breakdown structure. |
The chance of occurrence of this particular threat is relatively low because each project activities are approved from the committee and other stakeholders. |
However, resistance to the change in the project activities will reduce the feasibility of the project and hence this will negatively impact the project deliverables. |
Avoid the risk |
In order to resolve such issues the project management team must embrace transformational leadership style as a mitigation strategy. |
|
Threat 3: Architecture
|
Architecture risk is associated more with the construction based projects due to the failure of the designed architecture to support the requirements of the project. In this case such issue can arise because the architects has gathered the requirement needs from the documentation of the Vietnamese project. |
The likelihood of the occurring such risk is high in this particular project because of utilizing same documentation for the project. |
The impact of this risk is high and hence can result into the potential failure of the design for developing the educational hubs in the CQU campuses. |
Accept the risk |
Mitigation strategy for this particular threat is redesigning the architecture considering the culture and history of Australia. |
|
Threat 4: Resource
|
Resources are considered crucial in successful completion of the project. In this context, the project might confront with such issue due to the size of the project. |
The probability of the occurrence of this particular risk in the project of the SET is high. |
The scarcity or availability of the resources for establishment of the educational hubs can impact the delivery date of the project that is it can be delayed. |
Contingency that is developing plans to deal with such issues. |
Considering multiple supplier of raw materials are considered as the mitigation strategy that can deal with the issue. |
|
Opportunity 1: Completion within stipulated time
|
The completion of the project within stipulated time frame in this case is considered as the opportunity. This is possible due to the shared documentation and Approval from the committee. |
The likelihood of this opportunity is considered high |
This can impact the users that are the students because they can avail the educational opportunities. |
Share the opportunity |
Maintenance of the transparency is considered as the mitigation strategy in this context. |
Table 11: Risk register response table
Source: Learner
2.8 Tolerances
|
Response Table
|
|
|
Tolerance
|
Specific Tolerance Allowance |
|
Tolerance specified for time
|
Plus-minus 15 days that is the project completion can extend up to 15 days from the estimated completion date. |
|
Tolerance specified for cost
|
Plus-minus 10% of the estimated budget which reflects that the project budget will be 10 % more or less than the estimated one. |
Table 12: Tolerance table
Source: Learner
2.9 Lessons learnt after analyzing the various aspects within the present project plan assignment
|
Response Table |
||
|
Previous Lessons Learnt |
Proposed Action to Address (In the Current Project) |
In the Work Package which activity will be added |
|
Lesson 1 A higher (than expected) number of people, attending opening ceremonies at some of the campuses. The higher number of people resulted in overcrowding in small areas and some confusion in campus responsibilities for workplace health and safety compliance.
|
In order to address this issue online checking and ticketing system should be embraced which will ensure that only concerned individuals are attending the opening ceremony and for others the video of the ceremony will be shared in several mediums. |
Online checking and ticketing system will be added in 3.2 WP. |
|
Lesson 2: A supplier of goods and services who failed to address the various nuances existing between different indigenous Australians located in various geographical areas.
|
Back-up of suppliers of the goods and services that can address the needs of the different indigenous Australians situated in different locations. |
Arranging Back-up of the suppliers will be added in 3.1 WP. |
Table 13: Lessons Learnt Table
Source: Learner
Conclusion
The present project plan assignment is basically exploring a project management plan that has been prepared on behalf of The School of Engineering and Technology (SET) and hence the planning activities include several components that have been discussed in details in this assignment. The assignment has basically considered the project description, stakeholder’s management, requirement management, scope, schedule, cost baseline, risks, tolerances as well as lessons learnt.
Project plan assignments are being prepared by our project management assignment help experts from top universities which let us to provide you a reliable best assignment help service.
Reference List
Butt, A., Naaranoja, M. and Savolainen, J., 2016. Project plan assignment. Project change stakeholder communication. International Journal of Project Management, 34(8), pp.1579-1595.
Cohrs, J.C. and Vollhardt, J.R., 2019. Editorial Report and Acknowledgement of Reviewers, 2018. Journal of Social and Political Psychology, 7(1), pp.1-7.
Fontana, A. and Prokos, A.H., 2016. The interview: From formal to postmodern. Routledge.
Galanis, P., 2018. The Delphi method. Arch Hellen Med, 35(4), pp.564-70.
Heldman, K., 2018. PMP: project management professional exam study guide. John Wiley & Sons.
Kowal, E., 2015. Welcome to country. Cultural Studies Review, 21(2).
Kowal, E., 2015. Welcome to country: Acknowledgement, belonging and white anti-racism. Cultural Studies Review, 21(2), p.173.
Lappi, T., Haapasalo, H. and Aaltonen, K., 2015. Business Ecosystem Definition in Built Environment Using a Stakeholder Assessment Process. Management (18544223), 10(2).
McGuinness, M., Hall, B.C. and McGuinness, D.M., 2017. Project Description.
Sanghera, P., 2019. Planning for Communication and Stakeholder Management. In PMP® in Depth (pp. 313-341). Apress, Berkeley, CA.












