Risk Management Assignment: ERM Framework for Risk Managed Renewable Energy
Question
Task: Your submission for risk management assignment will comprise an Enterprise Risk Management Framework (ERM) for the organisation.
The Risk Management Framework will cover the following elements:
1. The outline and design of the ERM framework
2. The organisational internal and external context
3. Organisational roles, authorities, responsibilities and accountabilities, including allocated roles to support the framework
4. How the framework will be reviewed and improved (frequency, method, documentation and responsibilities)
5. Detail description of the risk management process (written as a guidance to users)
6. Guidance on what is an acceptable level of risk
7. Risk criteria tables (consequence, likelihood, and combined risk level)
8. Risk register for use across the organisation
9. A glossary of terms
10. Agreement on the framework from the organisation’s governing body
Meta:In this risk management assignment, an enterprise risk management framework of the company Risk Managed Renewable Energy (Australia) (RMRE) is presented.
Answer
Introduction
Renewable energy has become one of the essential parts of society as they are naturally beneficial for the environment. In this risk management assignment, we have taken companies like Risk Managed Renewable Energy (Australia) (RMRE) who focus on the development of renewable energy. Later the risk management of this project is analysed and the successful outcomes of the project. We analyse how it might be effective in using such a framework and focusing on the main goal of the project. In the ultimate, there are findings on the time plan with dedicated milestones to be achieved by the company.
ERM Framework
ERM is a risk management framework which mainly focuses on the combination of many kinds of leaders who are managing the responsibilities and the duties that are involved with the organisation. ISO 31000:2018 Framework is the structure that is provided to guide on the path on the operations that are involved with the risk management in the company. This is the kind of framework that is mainly applied by the organisations in order to improve their tack list and success (Pierce, & Goldstein, 2018). The more depth of this framework provides the particular identification of the risks that might be there in the organisation. Through this pathway the organisation can figure out their structure where to avoid the risks and the cost management. This is a team work of the organisation and it revolves in the integration, solutions, inclusives, dynamics, best information and the free flow of the continuous improvements. With the help of the identification the organisation can more focus on the goals that will be set for each of their times. The stakeholders for the company and the precise decision makers might be a fruitful way of presenting the goals.
Organizational internal and external context
Every organisation has its own internal and external context in order to recognise the weak part of the company. Internal context of the organisation varies from the risk that might be a root cause from within the company. While the external context is the outside environment of the organisations like the client and the main objectives. The internal risk factors can be easily maintained by the people who are within the company by bringing out the solutions that will be provided but the external context does not have the verified hand on the risk management. It might come directly and unaltered (Annamalah et al., 2018). Like the main external factors are the market forces in which the organisation goals, management with the client’s, shareholders, practices, lawsuits and many more external factors might be involved. In order to analyse the outside external factors, it is very much necessary to be involved within for a long period of time. The internal context can be more composite and the main focus can be right on point like objectives, structures and systems. Objectives of every organisation do vary from time to time but it is very important to figure out the main point of focus. The objectives help in leading with further futuristic goals for the organisation. After the identification of the objective, the structural view comes in the follow up. It helps in figuring it out the value point and the discussing of the risk managements that will be done in the internal context (Mahmod et al. 2018). Execution of such discussion and process are mainly into the systems which might be an important resource of the required database in order to supervise on those ideas and give a valuable decision of the situation and the consequence. In the understanding of both the internal and the external, it can be determined that the organisation benefits do lie on the decisions and the aims that are revolving from time to time. The analysis of every situation matters in order to avoid risk of consequence.
Acceptable Level of Risk (organizational roles, responsibilities, authorities, allocated roles)
Risk Managed Renewable Energy PVT Ltd is an Australian company that is more inclined towards the power generation of electricity and their supported company was Siemens. Their projects might be a help in the generation as they have planned to implement a renewable energy framework which is more suited to power generation (Al-Obaidli, Govindan, & Al-Ansari, 2021). The role of this organisation might have powerful influence in the long run since the renewable energy is one of the main components that the world might need in the upcoming future. This project will help in the development of the generation of power in the areas of Australia. They take the help of the solar panels in order to have the energy renewed. This project is about to have a success role in the near future for about 7 years. This organisation will have the responsibility to serve the nation and also help in the production of the electricity in the minimal way. The energy consumption is generally high in various places in the world and one day there might be a time where the electricity might be running out of power. Renewable source of energy will be helping to balance out the excess damage and companies like RMRE are one of them who are putting their shoes forward for such development (Kul, Zhang, &Solangi, 2020). The organisation will be helping nature and also the community and setting an example for many people. But now the implementation of such a process and the project might be slightly risky as the investment amount will be greater. In order to have success through this framework a thorough research on the project of risk management is very much required in order to achieve success. If the project gets successfully implemented, there will be a hike in the economic sector as well as there will be more involvement of the stakeholders. The project execution also does depend on the employees who will be appointed in this project. The employees should be given training on such working areas in order to avoid any kind of accidents that might be occurring (Copping, Freeman, &Overhus, 2020). There should be a framework which works on the continuous development in the project and making it more advanced. Planning before the execution of any kind of project is very much needed.
Improvements in the framework
Improvement in the risk management process of the framework includes risk management improvement initiatives and also the risk based decision making process.
So this is one of the most important aspects which is called monitor and review the risk as the ongoing process must be implemented in the form of monitoring and review on a regular and analysing mode to assess the exact result. It creates the sense that there is a direct link between key decisions and organisations risk management strategy. There are some factors which can be applied to improve the risk management framework which are as follows – be clear about your remit, identify risks early on, be positive, estimate and prioritise the risks, describe the risk appropriately, take ownership and responsibility, use appropriate strategies to manage the risk, learn from the past mistakes, documents the risk in the proper risk register, keep review and monitoring (Taghizadeh-Hesary, & Yoshino, 2020). It is known tha each risk is not the same in nature so the management must first identify the nature and the level of risk so that for that particular risk, the special personnel can be assigned to resolve the issue. For the treatment of the risk involved developing the range of options for mitigating the risk, assessing those actions and plans, and then implementing those plans. After identifying the possible risk, the management needs to analyse and evaluate the risk for each one. The most common process of analysing the risk is to use a scale that rates each risk on the likelihood of it occurring (Geddes, Schmidt, & Steffen, 2018). So this is one of the most important aspects which is called monitor and review the risk as the ongoing process must be implemented in the form of monitoring and review on a regular and analysing mode to assess the exact result.
Risk management processes
There are some steps involved in the risk management process which are Identify the risks, analyse and evaluate risk, treat and manage risk, communicate and consult, monitor and review, establish the context, implement a risk management framework based on risk policy and to record.
- Identify the risks – We know that each risk is not the same in nature so the management must first identify the nature and the level of risk so that for that particular risk, the special personnel can be assigned to resolve the issue (Cheung, Davies, &Trück, 2019).
- Analyse and evaluate risk – After identifying the possible risk, the management needs to analyse and evaluate the risk for each one. The most common process of analysing the risk is to use a scale that rates each risk on the likelihood of it occurring.
- Treat and manage risk – For the treatment of the risk involved developing the range of options for mitigating the risk, assessing those actions and plans, and then implementing those plans.
- Communicate and consult – After all the three processes are done, the external and internal stakeholders should take place and come in for the risk management process.
- Monitor and review – So this is one of the most important aspect which is called monitor and review the risk as the ongoing process must be implemented in the form of monitoring and review on a regular and analysing mode to assess the exact result (Guerin, 2017).
- Establish the context – The scope for the risk defined management steps and sets all the set criteria for which the risk will be assessed and the scope and the target will be determined within the context of the organisation’s goals.
- Implement a risk management framework – This is the putting of the strategic plan for managing and identifying the risk threats and finding an opportunity into an action plan.
Overview on the acceptable level of risk
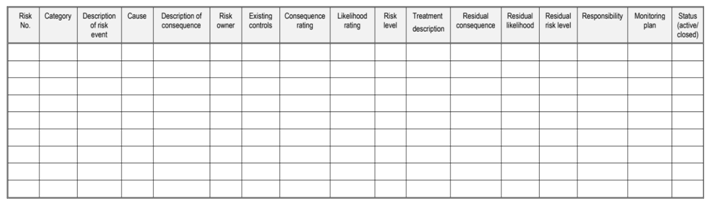
Guidance on what are acceptable levels of risk to the organisation – A risk is acceptable when it is tolerable and when it falls below the certain prescribed level. A risk is only said to be tolerable when it can be managed by the assigned team and there is a low level of cost and low level of effort involved. And for that purpose 5*5 risk matrices are introduced in an organisation for the risk tolerance.
- Categories of risk – Generally, there are three categories or level of risk and that is Low level of risk, medium level of risk and high level of risk. So generally, low level of risk and max to max medium level of risk are considered to be good (Li et al., 2017).
- How conflicting interests will be managed – If the management wants to reduce the level of risk in their organisation or in their company so they first need to reduce or minimize their different thoughts of the employees which are creating the conflicting mode of operation for getting the set goals.
- Risk attitude and/ or risk appetite can be incorporated – The level of risk for which any organisation or company is ready to take and willing to accept that level of risk at the time of pursuing its goals or objectives is called the risk appetite or risk attitude (Alizadeh et al., 2020).
Risk criteria table
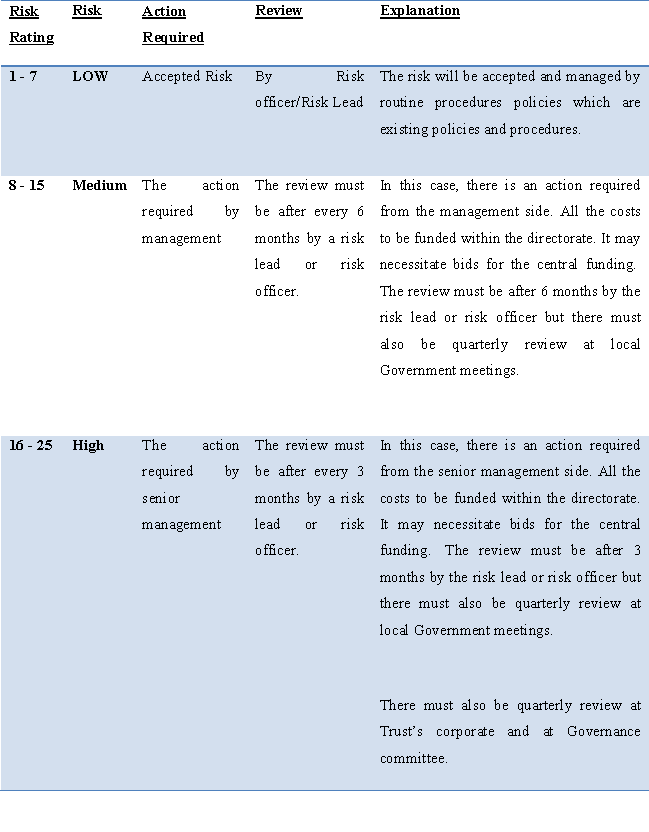
Risk Register
A risk register is a book type or document type which records all the identified risks of any organisation or of any company. And this is not only which is registered in the risk register book but there are other factors as well which is kept in the risk register book like the consequences and likelihood of a risk occurring, the actions which are taken by entrepreneur to reduce those risks and it is also mentioned in the risk register book that which person or who is responsible to manage all those risk as per the risk level (Alves et al., 2019).
This register is used to identify the possible or forecast-able risk in a project or an organisation which might derail the intended outcomes and it is also important to fulfil the regulatory compliance. Whereas the risk register is often used during the execution of the project so it is a tool of risk management. There are so many factors that have been included in the risk register such as nature of the risk, identified risk, level of risk, who is responsible for that risk as per the nature and level of risk because for each level of risk there are different persons assigned to resolve the issue.
Glossary of Terms
(1) Strategic Risk = All those internal and external events which may make difficult or even impossible to achieve the objectives and strategic goals of an organisation are called strategic risk (Jabbarzadeh, Fahimnia, &Sabouhi, 2018).
Strategic Risk example – It is the probability where an event might interfere with a company business model.
(2) Risk Management = The management which is carried on for the evaluation, prioritization and identification of risks which will be followed by economical application of resources and coordination to minimize, monitor and minimize the probability or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities.This approach is incorporated by a business organization in order to minimize any further risk or damage to the property.
(3) Renewable Energy = This is a useful energy which is collected from renewable resources and replenished by natural sources like sunlight, wind, rain, waves, tides and geothermal heat (Steffen, 2018). This type of energy source stands in the opposite of fossil fuels which have been used more quickly and fast than they are replenished.This energy sources are often referred to clean energy source as the waste generation during the process is minimal.
(4) Risk assessment = This is the combined effort of – (a) analyzing and identifying which may negatively impact assets, individuals or the environment, (b) possible judgments on the basis of the tolerance of the risk and on the basis of the risk analysis and other factors as well.Based on the process of risk assessment the risk management and the implementation of the risk control plan takes place.
Agreement
Gain commitment to fulfil the risk management process – This is something of a legal foundation and bound for those members who are involved and committed to resolve the issue of risk management. So if those persons will unable to resolve the issue within the stipulated period of time, the management can take the legal action against them or can impose a penalty. This is the combined effort of – analyzing and identifying which may negatively impact assets, individuals or the environment. And, possible judgements on the basis of the tolerance of the risk and on the basis of the risk analysis and other factors as well (Eriksson, &Gray, 2017). So the persons involved in these issue resolutions will guide the management regarding the challenges and risks involved.
Authority to manage the framework – If there will be a proper and legally agreement between the parties for the proper management of the risk planning and execution so the management will have to also give the authority to the team so that they will have a power to execute the things to be done in accordance with the risk mitigation (Steffen, 2018).
Signature boxes – All the parties must sign the agreement for which they are entering into the risk management process agreement.
Conclusion
So before directly concluding the risk management, first the management needs to take the questions with themselves concerning identification of the risks associated with the organisation, how risk can be avoided, how risk can be controlled, what is risk management process. So there are following steps to introduce in risk management such as identify risks, prioritize the risks, risk response plan, control and monitor risk. This is the combined effort of – analyzing and identifying which may negatively impact assets, individuals or the environment. Besides this, the possible judgements must be made based on the tolerance of the risk and on the basis of the risk analysis and other factors as well. Now to control the risk, the most common and best method to minimize the risk is that not introducing the hazard in the workplace and the communication should be adopted in a proper way so that less unproductivity will occur. This register is used to identify the possible or forecast-able risk in a project or an organisation which might derail the intended outcomes and it is also important to fulfil the regulatory compliance. Whereas the risk register is often used during the execution of the project so it is a tool of risk management.
Every organisation has its own internal and external context in order to recognise the weak part of the company. Internal context of the organisation varies from the risk that might be a root cause from within the company. While the external context is the outside environment of the organisations like the client and the main objectives. The internal risk factors can be easily maintained by the people who are within the company by bringing out the solutions that will be provided but the external context does not have the verified hand on the risk management. It might come directly and unaltered. Like the main external factors are the market forces in which the organisation goals, management with the client’s, shareholders, practices, lawsuits and many more external factors might be involved. In order to analyse the outside external factors, it is very much necessary to be involved within for a long period of time.
Theinternal context can be more composite and the main focus can be right on pointlike objectives, structures and systems. Also try to find out the safety mode from the unnecessary risk like the management can introduce management and establish a management committee on all risk factors. ?
References
Alizadeh, R., Soltanisehat, L., Lund, P. D., &Zamanisabzi, H. (2020).Improving renewable energy policy planning and decision-making through a hybrid MCDM method. Energy Policy, 137, <111174.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421519307608
Al-Obaidli, H., Govindan, R., & Al-Ansari, T. (2021).Statistical Decision-Theoretic Risk Management for Planning Renewable Energy Pathways. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering (Vol. 50, pp. 1795-1801). Elsevier.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323885065502783
Alves, A., Gersonius, B., Kapelan, Z., Vojinovic, Z., & Sanchez, A. (2019).Assessing the Co-Benefits of green-blue-grey infrastructure for sustainable urban flood risk management. Journal of environmental management, 239, 244-254.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030147971930338X
Annamalah, S., Raman, M., Marthandan, G., &Logeswaran, A. K. (2018).Implementation of enterprise risk management (ERM) framework in enhancing business performances in oil and gas sector. Economies, 6(1), 4.https://www.mdpi.com/253898
Cheung, G., Davies, P. J., &Trück, S. (2019). Transforming urban energy systems: The role of local governments’ regional energy master plan. Journal of Cleaner Production, 220, 655-667. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652619301982
Copping, A. E., Freeman, M. C., &Overhus, D. (2020). Risk Retirement for Environmental Effects of Marine Renewable Energy. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA. https://tethys.pnnl.gov/sites/default/files/publications/Risk_Retirement_for_Environmental_Effects_ of_Marine_Renewable_Energy.pdf
Eriksson, E. L. V., &Gray, E. M. (2017). Optimization and integration of hybrid renewable energy hydrogen fuel cell energy systems–A critical review. Applied energy, 202, 348-364.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261917306256
Geddes, A., Schmidt, T. S., & Steffen, B. (2018). The multiple roles of state investment banks in low-carbon energy finance: An analysis of Australia, the UK and Germany. Energy Policy, 115, 158-170. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421518300090
Guerin, T. F. (2017). Evaluating expected and comparing with observed risks on a large-scale solar photovoltaic construction project: A case for reducing the regulatory burden. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 74, 333-348. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364032117302459
Jabbarzadeh, A., Fahimnia, B., &Sabouhi, F. (2018). Resilient and sustainable supply chain design: sustainability analysis under disruption risks. International Journal of Production Research, 56(17), 5945-5968. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00207543.2018.1461950
Kul, C., Zhang, L., &Solangi, Y. A. (2020).Assessing the renewable energy investment risk factors for sustainable development in Turkey. Journal of Cleaner Production, 276, 124164.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652620342098
Li, C., Xu, Y., Yu, X., Ryan, C., & Huang, T. (2017). Risk-averse energy trading in multienergymicrogrids: A two-stage stochastic game approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 13(5), 2620-2630.https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8010361/
Mahmod, M. S., Aziz, K., Yazid, A. S., Rasid, N., Salleh, F., Ghazali, P. L., &Mahmood, S. (2018). A Conceptual Framework of ERM Practices among SMEs IN Malaysia. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(11), 1209-1221. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fauzilah-Salleh/publication/334500572_A_Conceptual_Framework_of_ERM_Practices_among_SMEs_IN_ Malaysia/links/5d485865299bf1995b693676/A-Conceptual-Framework-of-ERM-Practices-among-SMEs-IN-Malaysia.pdf
Pierce, E. M., & Goldstein, J. (2018). ERM and strategic planning: A change in paradigm. International Journal of Disclosure and Governance, 15(1), 51-59. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1057/s41310-018-0033-3
Steffen, B. (2018). The importance of project finance for renewable energy projects. Energy Economics, 69, 280-294. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140988317303870
Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., & Yoshino, N. (2020).Sustainable solutions for green financing and investment in renewable energy projects. Energies, 13(4), 788.https://www.mdpi.com/638352 ?
Appendices